Abstract
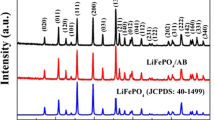
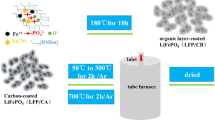
Olivine LiFePO4 (LFP) is a promising cathode material for high-rated lithium-ion batteries. However, olivine faced a severe disadvantage of low conductivity and sluggish transportation of Li+ ions, which slows down the chemical reactions and thus the retention capacity of battery. Therefore, in this work, nanocomposite LiFePO4/carbon was synthesized by a hydrothermal route. A mixing of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) on the composite electrode was investigated to enhance the electrochemical performance of nanocomposite LiFePO4/C. The XRD pattern and XPS spectrum showed a high crystallite of olivine phase and a successful coating of carbon onto the surface of olivine. Electrochemical properties were evaluated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and cyclability test. Lithium diffusion coefficients (DLi) were determined by the evolution of reduction peak on CV curves. An increase of DLi was observed with the increase of CNT amount in electrode composite. Practically, the composite electrode LFP/C/10%CNTs exhibited an excellent performance in cycling test and rate capability; a retention capacity of 98% was observed after 200 cycles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 144(4):1188–1194
Tarascon J-M, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414(6861):359–367
Tarascon J-M (2010) Key challenges in future Li-battery research. Philos Trans R Soc Math Phys Eng Sci 368(1923):3227–3241
Di Lecce D, Verrelli R, Hassoun J (2017) Lithium-ion batteries for sustainable energy storage: recent advances towards new cell configurations. Green Chem 19(15):3442–3467
Alves A, Bergman CP, Berutti FA (2013) Novel synthesis and characterization of nanostructured materials, engineering materials. Springer - Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41275-2-1
Li Z, Zhang D, Yang F (2009) Developments of lithium-ion batteries and challenges of LiFePO4 as one promising cathode material. J Mater Sci 44(10):2435–2443
Xie H-M, Wang R-S, Ying J-R, Zhang LY, Jalbout AF, Yu HY, Yang GL, Pan XM, Su ZM (2006) Optimized LiFePO4–polyacene cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 18(19):2609–2613
Chen J, Vacchio MJ, Wang S, Chernova N, Zavalij PY, Whittingham MS (2008) The hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of olivines and related compounds for electrochemical applications. Solid State Ionics 178(31-32):1676–1693
Chang H-H, Chang C-C, Wu H-C, Guo ZZ, Yang MH, Chiang YP, Sheu HS, Wu NL (2006) Kinetic study on low-temperature synthesis of LiFePO4 via solid-state reaction. J Power Sources 158(1):550–556
Amin R, Maier J, Balaya P, Chen DP, Lin CT (2008) Ionic and electronic transport in single crystalline LiFePO4 grown by optical floating zone technique. Solid State Ionics 179(27-32):1683–1687
Le VT, Nguyen HT, Luu AT et al (2015) LiMn2O4/CNTs and LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/CNTs nanocomposites as high-performance cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Acta Metall Sin Engl Lett 28:122–128
Nagaraju DH, Kuezma M, Suresh GS (2015) LiFePO4 wrapped reduced graphene oxide for high performance Li-ion battery electrode. J Mater Sci 50(12):4244–4249
Zhang K, Lee J-T, Li P, Kang B, Kim JH, Yi GR, Park JH (2015) Conformal coating strategy comprising N-doped carbon and conventional graphene for achieving ultrahigh power and cyclability of LiFePO4. Nano Lett 15(10):6756–6763
Lung-Hao Hu B, Wu F-Y, Lin C-T, Khlobystov AN, Li LJ (2013) Graphene-modified LiFePO4 cathode for lithium ion battery beyond theoretical capacity. Nat Commun 4:1687
Zhou X, Wang F, Zhu Y, Liu Z (2011) Graphene modified LiFePO4 cathode materials for high power lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem 21(10):3353–3358
Yang J, Wang J, Tang Y, Wang D, Li X, Hu Y, Li R, Liang G, Sham TK, Sun X (2013) LiFePO4–graphene as a superior cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries: impact of stacked graphene and unfolded graphene. Energy Environ Sci 6(5):1521–1528
Rui X, Zhao X, Lu Z, Tan H, Sim D, Hng HH, Yazami R, Lim TM, Yan Q (2013) Olivine-type nanosheets for lithium ion battery cathodes. ACS Nano 7(6):5637–5646
Rietveld HM (1969) A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J Appl Crystallogr 2(2):65–71
Young RA (1995) The Rietveld method. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Coelho P (2005) Topas technical reference manual. Bruker AXS, Billerica
Kozawa T, Kataoka N, Kondo A, Nakamura E, Abe H, Naito M (2014) One-step mechanical synthesis of LiFePO4/C composite granule under ambient atmosphere. Ceram Int 40(10):16127–16131
Eftekhari A (2017) LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 343:395–411
Franger S, Le Cras F, Bourbon C, Rouault H (2003) Comparison between different LiFePO4 synthesis routes and their influence on its physico-chemical properties. J Power Sources 119–121:252–257
Mathew V, Gim J, Kim E, Alfaruqi MH, Song J, Ahn D, Im WB, Paik Y, Kim J (2014) A rapid polyol combustion strategy towards scalable synthesis of nanostructured LiFePO4/C cathodes for Li-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 18(6):1557–1567
Zhang N, Lin L, Xu Z (2014) Effect of synthesis temperature, time, and carbon content on the properties and lithium-ion diffusion of LiFePO4/C composites. J Solid State Electrochem 18(9):2401–2410
Liu H, Yang H, Li J (2010) A novel method for preparing LiFePO4 nanorods as a cathode material for lithium-ion power batteries. Electrochim Acta 55(5):1626–1629
Castro L, Dedryvère R, El Khalifi M et al (2010) The spin-polarized electronic structure of LiFePO4 and FePO4 evidenced by in-lab XPS. J Phys Chem C 114(41):17995–18000
Zhao R-R, Lan B-Y, Chen H-Y, Ma G-Z (2012) Hydrothermal synthesis and properties of manganese-doped LiFePO4. Ionics 18(9):873–879
Hong K-S, Yu S-M, Ha M-G et al (2009) Preparation of LiFePO4 using chitosan and its cathodic properties for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Bull Kor Chem Soc 30:1719–1723
Orliukas AF, Fung K-Z, Venckutė V, Kazlauskienė V, Miškinis J, Dindune A, Kanepe Z, Ronis J, Maneikis A, Šalkus T, Kežionis A (2014) SEM/EDX, XPS, and impedance spectroscopy of LiFePO4 and LiFePO4/C ceramics. Lith J Phys 54(2):106–113
Rho Y-H, Nazar LF, Perry L, Ryan D (2007) Surface chemistry of LiFePO4 studied by Mössbauer and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and its effect on electrochemical properties. J Electrochem Soc 154(4):A283
Nocuń M (2004) Structural studies of phosphate glasses with high ionic conductivity. J Non-Cryst Solids 333(1):90–94
Ramana CV, Ait-Salah A, Utsunomiya S, Morhange JF, Mauger A, Gendron F, Julien CM (2007) Spectroscopic and chemical imaging analysis of lithium iron triphosphate. J Phys Chem C 111(2):1049–1054
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2000) Electrochemical methods and applications. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Tran MV, Huynh NLT, Nguyen TT, Ha DTC, le PML (2016) Facile solution route to synthesize nanostructure Li4Ti5O12 for high rate Li-ion battery. J Nanomater 2016:1–7
Tang K, Yu X, Sun J, Li H, Huang X (2011) Kinetic analysis on LiFePO4 thin films by CV, GITT, and EIS. Electrochim Acta 56(13):4869–4875
Zhu Y, Wang C (2010) Galvanostatic intermittent titration technique for phase-transformation electrodes. J Phys Chem C 114(6):2830–2841
Van der Ven A, Bhattacharya J, Belak AA (2013) Understanding Li diffusion in Li-intercalation compounds. Acc Chem Res 46(5):1216–1225
Chen Y, Wang L, Anwar T, Zhao Y, Piao N, He X, Zhu Q (2017) Application of galvanostatic intermittent titration technique to investigate phase transformation of LiFePO4 nanoparticles. Electrochim Acta 241:132–140
Malik R, Burch D, Bazant M, Ceder G (2010) Particle size dependence of the ionic diffusivity. Nano Lett 10(10):4123–4127
Dhindsa KS, Kumar A, Nazri GA, Naik VM, Garg VK, Oliveira AC, Vaishnava PP, Zhou ZX, Naik R (2016) Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C nanocomposites due to in situ formation of Fe2P impurities. J Solid State Electrochem 20(8):2275–2282
Huang K-P, Fey GT-K, Lin Y-C, Wu PJ, Chang JK, Kao HM (2017) Magnetic impurity effects on self-discharge capacity, cycle performance, and rate capability of LiFePO4/C composites. J Solid State Electrochem 21(6):1767–1775
Delmas C, Maccario M, Croguennec L, le Cras F, Weill F (2008) Lithium deintercalation in LiFePO4 nanoparticles via a domino-cascade model. Nat Mater 7(8):665–671
Wang L, He X, Sun W, Wang J, Li Y, Fan S (2012) Crystal orientation tuning of LiFePO4 nanoplates for high rate lithium battery cathode materials. Nano Lett 12(11):5632–5636
Varzi A, Bresser D, von Zamory J, Müller F, Passerini S (2014) ZnFe2O4 -C/LiFePO4 -CNT: a novel high-power lithium-ion battery with excellent cycling performance. Adv Energy Mater 4:1400054(10):1–9
Chen J-M, Hsu C-H, Lin Y-R, Hsiao MH, Fey GTK (2008) High-power LiFePO4 cathode materials with a continuous nano carbon network for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 184(2):498–502
Zhao L, Ni J, Wang H, Gao L (2013) Na0.44MnO2–CNT electrodes for non-aqueous sodium batteries. RSC Adv 3(18):6650
Funding
This research was funded by Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) under the grant TX2017-18-01 and NV2018-18-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huynh, L.T.N., Tran, T.T.D., Nguyen, H.H.A. et al. Carbon-coated LiFePO4–carbon nanotube electrodes for high-rate Li-ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 2247–2254 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-3934-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-3934-y