Abstract
Novel potential type electrochemical chiral biosensing system with unique capability of distinguishing and quantitating of tyrosine (Tyr) enantiomers by L-cysteic acid and left-handed chiral carbonaceous nanotubes (L-CCNT) modified glassy carbon electrode (L-Cys/L-CCNT/GCE) was first developed. The effect of sweep cycles of L-Cys and the kinds of L-CCNT on electrochemical chiral biosensing performance of L-Cys/L-CCNT/GCE were investigated. The electrochemical identification and quantitative determination of L- and D-tyrosine in their mixed solution were successfully achieved based on the different oxidation potential signals. The chiral structure of L-CCNT, the aromatic ring of Tyr, and also the intermolecular hydrogen bond between cysteic acid (CyA) and Tyr could possibly produce the difference in the free energy, which reflects as potential difference of L- and D-tyrosine. A good linear relationship between the potential, current, and different concentration ratios of L- and D-Tyr was obtained. Our present work realizes the simultaneous detection of Tyr enantiomers in their mixed solution based on the different potential signals, and it is of far-reaching significance in real electrochemical chiral biosensor study.

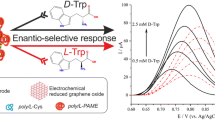
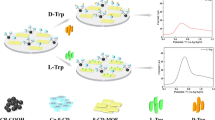
Construction of chiral recognition interface and the chiral biosensing mechanism for L-Tyr and D-Tyr








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthier D, Buffeteau T, Léger J, Oda R, Huc I (2002) From chiral counterions to twisted membranes. J Am Chem Soc 122:13486–13494
Schröder T, Schmitz K, Niemeier N, Balaban TS, Krug HF, Schepers U, Bräse S (2007) Solid-phase synthesis, bioconjugation, and toxicology of novel cationic oligopeptoids for cellular drug delivery. Bioconjug Chem 18:342–354
Uray G, Maier NM, Niederreiter KS, Spitaler MM (1998) Diphenylethanediamine derivatives as chiral selectors: VIII. Influence of the second amido function on the high-performance liquid chromatographic enantioseparation characteristics of (N-3,5-dinitrobenzoyl)-diphenylethanediamine based chiral stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 799:67–81
Li M, Liu X, Jiang F, Guo LP, Yang L (2011) Enantioselective open-tubular capillary electrochromatography using cyclodextrin-modified gold nanoparticles as stationary phase. J Chromatogr A 1218:3725–3729
Guo HS, Kim JM, Chang SM, Kim WS (2009) Chiral recognition of mandelic acid by l-phenylalanine-modified sensor using quartz crystal microbalance. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2931–2934
Su WC, Zhang WG, Zhang S, Fan J, Yin X, Luo ML, Ng SC (2009) A novel strategy for rapid real-time chiral discrimination of enantiomers using serum albumin functionalized QCM biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 25:488–492
Liang H, Ling T, Rick JF, Chou T (2005) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor able to enantroselectivly recognize d and l-tyrosine. Anal Chim Acta 542:83–89
Bustos E, García JE, Bandala Y, Godínez LA, Juaristi E (2009) Enantioselective recognition of alanine in solution with modified gold electrodes using chiral PAMAM dendrimers G4.0. Talanta 78:1352–1358
Pandey I, Kant R (2016) Electrochemical impedance based chiral analysis of anti-ascorbutic drug: l-ascorbic acid and d-ascorbic acid using C-dots decorated conductive polymer nano-composite electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 77:715–724
Guo DM, Huang YH, Chen C, Chen Y, Fu YZ (2014) A sensing interface for recognition of tryptophan enantiomers based on porous cluster-like nanocomposite films. New J Chem 38:5880–5885
Guo LJ, Zhang Q, Huang YH, Han Q, Wang YH, Fu YZ (2013) The application of thionine–graphene nanocomposite in chiral sensing for tryptophan enantiomers. Bioelectrochemistry 94:87–93
Yu LY, Liu Q, Wu XW, Jiang XY, Yu JG, Chen XQ (2015) Chiral electrochemical recognition of tryptophan enantiomers at a multi-walled carbon nanotube–chitosan composite modified glassy carbon electrode. RSC Adv 5:98020–98025
Ou J, Zhu YH, Kong Y, Ma JF (2015) Graphene quantum dots/β-cyclodextrin nanocomposites: a novel electrochemical chiral interface for tryptophan isomer recognition. Electrochem Commun 60:60–63
Gu XG, Tao YX, Pan Y, Deng LH, Bao LP, Kong Y (2015) DNA-inspired electrochemical recognition of tryptophan isomers by electrodeposited chitosan and sulfonated chitosan. Anal Chem 87:9481–9486
Kimmel DW, LeBlanc G, Meschievitz ME, Cliffel DE (2012) Electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal Chem 84:685–707
Wang Y, Yin X, Shi M, Li W, Zhang L, Kong J (2006) Probing chiral amino acids at sub-picomolar level based on bovine serum albumin enantioselective films coupled with silver-enhanced gold nanoparticles. Talanta 69:1240–1245
Li XL, Tu XM, Zaric S, Welsher K, Seo WS, Zhao W, Dai HJ (2007) Selective synthesis combined with chemical separation of single-walled carbon nanotubes for chirality selection. J Am Chem Soc 129:15770–15771
Chen Y, Wei L, Wang B, Lim S, Ciuparu D, Zheng M, Chen J, Zoican C, Yang YH, Haller GL, Pfefferle LD (2007) Low-Defect, purified, narrowly (n,m)-dispersed single-walled carbon nanotubes grown from cobalt-incorporated MCM-41. ACS Nano 1:327–336
Yu YT, Qiu HB, Wu XW, Li HC, Li YS, Sakamoto Y, Inoue Y, Sakamoto K, Terasaki O, Che SA (2008) Synthesis and characterization of silica nanotubes with radially oriented mesopores. Adv Funct Mater 18:541–550
Liu SH, Duan YY, Feng XJ, Yang J, Che SA (2013) Synthesis of enantiopure carbonaceous nanotubes with optical activit. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:6858–6862
Yang SB, Feng XL, Wang XC, Müllen K (2011) Graphene-based carbon nitride nanosheets as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5339–5343
Wang CY, Wang ZX, Guan J, Hu XY (2006) Voltammetric determination of meloxicam in pharmaceutical formulation and human serum at glassy carbon electrode modified by Cysteic acid formed by electrochemical oxidation of L-cysteine. Sensors 6:1139–1152
Brunetti B, Desimoni E (2009) Determination of theophylline at a cysteic acid modified glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 21:772–778
Fei S, Chen J, Yao S, Deng G, He D, Kuang Y (2005) Electrochemical behavior of l-cysteine and its detection at carbon nanotube electrode modified with platinum. Anal Biochem 339:29–35
Spãtaru N, Sarada BV, Popa E, Tryk DA, Fujishima A (2001) Voltammetric determination of L-cysteine at conductive diamond electrodes. Anal Chem 73:514–519
Scholz F, Gulaboski R (2005) Gibbs energies of transfer of chiral anions across the interface water|chiral organic solvent determined with the help of three-phase electrodes. Faraday Discuss 129:169–177
Chen Q, Zhou J, Han Q, Wang YH, Fu YZ (2012) Electrochemical enantioselective recognition of tryptophane enantiomers based on chiral ligand exchange. Colloids Surf, B 92:130–135
Sulaiman Y, Kataky R (2012) Chiral acid selectivity displayed by PEDOT electropolymerised in the presence of chiral molecules. Analyst 137:2386–2393
Shamsi SA, Valle BC, Billiot F, Warner IM (2003) Polysodium n-undecanoyl-L-leucylvalinate: a versatile chiral selector for micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Anal Chem 75:379–387
Agnew-Heard KA, Sánchez Peña M, Shamsi SA, Warner IM (1997) Studies of polymerized sodium n-undecylenyl-L-valinate in chiral micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography of neutral, acidic, and basic compounds. Anal Chem 69:958–964
Dalgliesh CE (1952) The optical resolution of aromatic amino-acids on paper chromatograms. J Chem Soc 3940-3942
Davankov VA (1997) The nature of chiral recognition: is it a three-point interaction. Chirality 9:99–102
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21505031), colleges and universities science technology research project of Hebei Province (No. Z2015096) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No. B2016201018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Yao, R., Wang, Z. et al. Novel potential type electrochemical chiral recognition biosensor for amino acid. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 41–49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3719-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3719-8