Abstract
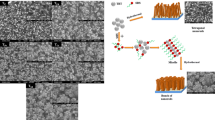
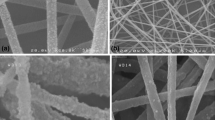
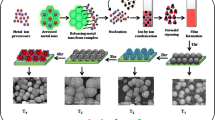
Cadmium selenide (CdSe) thin films were grown by electrochemical technique on fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO)-coated conducting glass substrates in the presence of organic surfactants. The influence of organic surfactants like polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) on different physico-chemical properties and its subsequent impact on photoelectrochemical (PEC) performance of CdSe thin films have been investigated. It has observed that the organic surfactants play an important role in modifying the surface morphology of CdSe thin films. The compact grain like morphology of pure CdSe is tuned to interconnected nanofibrous network on addition of PEG and to sprouting nanorods like morphology on addition of PVP. Among these nanostructures, CdSe sprouting nanorods exhibits improved power conversion efficiency of 0.55% as compared to nanofibrous (0.24%) and granular CdSe (0.16%) nanostructures. It reveals the fourfold enhancement in the PEC performance on PVP-mediated growth which can be attributed to conversion of compact dense nanostructure to porous and relatively high surface area nanostructure. This work exemplifies the ability of organic surfactant to modulate the surface morphology of the electrodeposits and pinpoints the organic surfactant that gives rise to the suitable morphology for PEC solar cell application.

TOC: The morphology of CdSe nanostructure has successfully tuned with use of surfactants to enhance the photoelectrochemical solar cell performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erata S, Ari M, Metina H (2008) Mater Chem Phy 111:114–120
Khandelwal A, Jena D, Grebinski J, Hull K, Kuno M (2006) J Electron Mater 35:170–172
Chang S, Hsiao Y, Li T (2014) J Electron Mater 43:3077–3081
Zarghami V, Mohammad M, Fray D (2012) J Electron Mater 41:3050–3055
Kurtz E, Schmidt M, Don B, Wachter S, Litvinov D, Gerthsen D (2001) J Cryst Growth 227:630–633
Meteleva YU, Radychev N, Novikov G (2007) Inorg Mater 43:455–465
Liu C, Wu P, Sun T, Dai L (2009) J Phys Chem C 113:14478–14481
Shinde S, Dubal D, Ghodake G, Fulari V (2014) J Electroanal Chem 727:179–183
Shinde S, Dubal D, Ghodake G, Lee D, Lohar G, Rath M, Fulari V (2014) Mater Lett 132:243–246
Xue J, Shen Q, Yang F, Liang W, Liu X (2014) J Alloys Compd 607:163–168
Inamdar A, Mujawar S, Ganesan V, Patil P (2008) Nanotechnology 19:325706–325713
Shen C, Zhang X, Li H (2001) Mater Sci Eng B 84:265–270
Fu J, Gao D, Xu Y, Xue D (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:54645468
Shen CM, Zhang XG, Li HL (2005) Appl Surf Sci 240:34–41
Devaraj S, Munichandraiah N (2007) J Electrochem Soc 154:A901–A909
Vanalakar SA, Suryawanshi MP, Mali SS, Moholkar AV, Kim JY, Patil PS, Kim JH (2014) Curr App Phy 14:1669–1676
Ghaemi M, Khosravi-Fard L, Neshati J (2005) J Power Sources 141:340–350
Vanalakar SA, Mali SS, Jo EA, Kim JY, Kim JY, Patil PS, Kim JH (2014) Solid State Sci 36:41–46
Vanalakar SA, Kamble AS, Shin SW, Mali SS, Agawane GL, Patil VL, Kim JY, Patil PS, Kim JH (2015) Sol Energy 122:1146–1153
Lokhande CD, Lee EH, Jung KD, Joo OS (2005) Mater Chem Phys 93:399–403
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A (1966) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi 15:627
Pawar SM, Moholkar AV, Rajpure KY, Bhosale CH (2006) J Phys Chem Solids 67:2386–2391
Lokhande C, Lee EH, Jung KD, Joo OS (2005) Mater Chem Phys 91:200–204
Dobryszycki J, Biallozar S (2001) Corros Sci 43:1309–1319
Vanalakar SA, Gang MG, Patil PS, Kim JY, Kim JH (2016) Indian J Eng Mater Sci 23:139–142
Vanalakar SA, Kim JH, Patil PS (2016) In: Thomas S (ed) Advanced polymeric materials: from macro- to nano-length scales, 1st edn. CRC Press, New Jerrcy
Lui X, Yang J, Wang L, Yang X, Lude L, Wang X (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 289:241–245
Zhang Z, Zhao B, Hu L (1996) J Solid State Chem 121:105–110
Tao D, Qian W, Huang Y, Wei F (2004) J Cryst Growth 271:353–357
Goel A, Rani N (2012) Open J Inorg Chem 2:67–73
Tan Y, Dai X, Li Y, Zhu D (2003) J Mater Chem 13:1069–1075
Toshima N, Nakata K, Kitoh H (1997) Inorg Chim Acta 265:149–153
Teranishi T, Miyake M (1998) Chem Mater 10:594–600
Gudage YG, Deshpande NG, Sagade AA, Sharma RP, Pawar SM, Bhosale CH (2007) Bull Mater Sci 30:321–327
Raut VS, Lokhande CD, Killedar VV (2017) J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:140–3150
Acknowledgements
One of the authors B. B. Sinha is grateful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India for award of Inspire fellowship. One of the authors S. A. Vanalakar is thankful to the University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India for providing fellowships under Raman Fellowship for Post-Doc Research in USA scheme (File No. 5/155/2016 (IC)). This work was partly supported by the converging research center program funded by the Ministry of science, ICT and Future planning (2013K000407) and Human Resource Development of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korea government Ministry of Knowledge Economy (no. 20124010203180).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 213 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamble, A.S., Patil, V.L., Sinha, B.B. et al. Influence of surfactants on electrochemical growth of CdSe nanostructures and their photoelectrochemical performance. J Solid State Electrochem 21, 2649–2653 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3651-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3651-y