Abstract
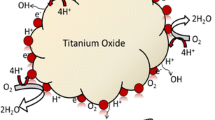
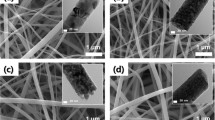
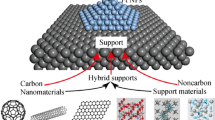
Durability is a major issue and has been the growing focus of research for the successful commercialization of polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs). Corrosion of carbon support is one of the major forms of Pt/C degradation and affects cell performance during prolonged operation. In the present study, TiO2 nanoparticles are incorporated in functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) to form TiO2-f-MWCNT nanocomposite-supported Pt which improves the durability of PEFC. Pt/TiO2-f-MWCNT electrocatalyst with different compositions has been prepared by a colloidal method, and their morphological and microstructural properties were investigated. Optimum ratio of TiO2-f-MWCNT-supported Pt shows improved overall cell performance than that of f-MWCNT-supported Pt. Accelerated stress test (AST) shows Pt/TiO2-f-MWCNT electrocatalyst possesses superior electrochemical activity and long-term stability for oxygen reduction in relation to Pt/f-MWCNT. High activity and durability is observed for TiO2-f-MWCNTs as catalyst support through its interaction with Pt and retains more than 75% of the initial electrochemical activity in PEFCs even after 200 h of AST.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kangasniemi KH, Condit DA, Jarvi TD (2004) Characterization of Vulcan electrochemically oxidized under simulated PEM fuel cell conditions. J Electrochem Soc 151:E125–E132
Ferreira PJ, Horn YS, Morgan D, Makharia R, Kocha S, Gasteiger HA (2005) Instability of Pt/C electrocatalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells a mechanistic investigation. J Electrochem Soc 152:A2256–A2271
Wang X, Li W, Chen Z, Waje M, Yan Y (2006) Durability investigation of carbon nanotube as catalyst support for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J Power Sources 158:154–159
Stevens DA, Dahn JR (2005) Thermal degradation of the support in carbon-supported platinum electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cells. Carbon 43:179–188
Reiser CR, Bregoli L, Pattersin TW, Yi JS, Yang JD, Perry ML, Jarvi TD (2005) A reverse current decay mechanism for fuel cells. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 8:A273–A276
Wilson MS, Garzon HG, Sickafus KE, Gottesfeld S (1993) Surface area loss of supported platinum in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 140:2872–2877
Shao Y, Yin G, Gao Y (2007) Understanding and approaches for the durability issues of Pt-based catalysts for PEM fuel cell. J Power Sources 171:558–566
Tang H, Qi Z, Ramani M, Elter JF (2006) PEM fuel cell cathode carbon corrosion due to the formation of air/fuel boundary at the anode. J Power Sources 158:1306–1312
Stevens DA, Hicks MT, Haugen GM, Dahn JR (2005) Ex situ and in situ stability studies of PEMFC catalysts—effect of carbon type and humidification on degradation of the carbon. J Electrochem Soc 152:A2309–A2315
Vinod Selvaganesh S, Selvarani G, Sridhar P, Pitchumani S, Shukla AK (2011) Durable electrocatalytic-activity of Pt–Au/C cathode in PEMFCs. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:12623–12634
Huang SY, Ganesan P, Park S, Popov BN (2009) Development of a titanium dioxide-supported platinum catalyst with ultrahigh stability for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications. J Am Chem Soc 131:13898–13899
Tintula KK, Sahu AK, Shahid A, Pitchumani S, Sridhar P, Shukla AK (2010) Mesoporous carbon and poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) composite as catalyst support for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 157:B1679–B1685
Bessel CA, Laubernds K, Rodriguez NM, Baker RTK (2001) Graphite nanofibers as an electrode for fuel cell applications. J Phys Chem B 105:1115–1118
Serp P, Corrias M, Kalck P (2003) Carbon nanotubes and nanofibers in catalysis. Appl Catal 253:337–358
Shanahan PV, Xu L, Liang C, Waje M, Dai S, Yan YS (2008) Graphitic mesoporous carbon as a durable fuel cell catalyst support. J Power Sources 185:423–427
Vinod Selvaganesh S, Sridhar P, Pitchumani S, Shukla AK (2014) Pristine and graphitized-MWCNTs as durable cathode-catalyst supports for PEFCs. J Solid State Electrochem 18:1291–1305
Shao YY, Yin GP, Gao YZ, Shi PF (2006) Durability study of Pt /C and Pt /CNTs catalysts under simulated PEM fuel cell conditions. J Electrochem Soc 153:A1093–A1097
Shao YY, Yin GP, Zhang J, Gao YZ (2006) Comparative investigation of the resistance to electrochemical oxidation of carbon black and carbon nanotubes in aqueous sulfuric acid solution. Electrochim Acta 51:5853–5857
Mohanapriya S, Tintula KK, Bhat SD, Pitchumani S, Sridhar P (2012) A novel multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWNT)-based nanocomposite for PEFC electrodes. Bull Mater Sci 35:297–303
Li L, Xing Y (2006) Electrochemical durability of carbon nanotubes in noncatalyzed and catalyzed oxidations. J Electrochem Soc 153:A1823–A1828
Kim KH, Oh HS, Kim H (2009) Use of a carbon nanocage as a catalyst support in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Electrochem Commun 11:1131–1134
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Science 354:56–58
Steen E, Prinsloo FF (2002) Comparison of preparation methods for carbon nanotubes supported iron Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. Catal Today 71:327–334
Liu Z, Lin X, Lee JY, Zhang W, Han M, Gan LM (2002) Preparation and characterization of platinum-based electrocatalysts on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Langmuir 18:4054–4060
Xia BY, Ding S, Wu HB, Wang X, Wen X (2012) Hierarchically structured Pt/CNT@ TiO2 nanocatalysts with ultrahigh stability for low-temperature fuel cells. RSC Adv 2:792–796
Kraemer SV, Wikander K, Lindbergh G, Lundblad A, Palmqvist AEC (2008) Evaluation of TiO2 as catalyst support in Pt-TiO2/C composite cathodes for the proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J Power Sources 180:185–190
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107:2891–2959
Brewer L (1968) Bonding and structures of transition metals. Science 161:115–122
Jakšić MM (1984) Electrocatalysis of hydrogen evolution in the light of the Brewer-Engel theory for bonding in metals and intermetallic phases. Electrochim Acta 29:1539–1550
Tauster SJ, Fung SC, Baker RTK, Horsley JA (1981) Strong interactions in supported-metal catalysts. Science 211:1121–1125
Neophytides SG, Murase K, Zafeiratos S, Papakonstantinou G, Paloukis FE, Krstajic NV, Jaksic MM (2006) Composite hypo-hyper-d-intermetallic and interionic phases as supported interactive electrocatalysts. J Phys Chem B 110:3030–3042
Haarstrick A, Ku OM, Heinzle E (1996) TiO2-assisted degradation of environmentally relevant organic compounds in wastewater using a novel fluidized bed photoreactor. Environ Sci Technol 30:817–824
Shim J, Lee CR, Lee HK, Lee JS, Cairns EJ (2001) Electrochemical characteristics of Pt–WO3/C and Pt–TiO2/C electrocatalysts in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J Power Sources 102:172–177
De Luca L, Donato A, Santangelo S, Faggio G, Messina G, Donato N, Neri G (2012) Hydrogen sensing characteristics of Pt/TiO2/MWCNTs composites. Int J Hydr Energy 37:1842–1851
Xing Y (2004) Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of uniformly-dispersed high loading Pt nanoparticles on sonochemically-treated carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 108:19255–19259
Selvarani G, Vinod Selvaganesh S, Krishnamurthy S, Kiruthika GVM, Sridhar P, Pitchumani S, Shukla AK (2009) A methanol-tolerant carbon-supported Pt−Au alloy cathode catalyst for direct methanol fuel cells and its evaluation by DFT. J Phys Chem C 113:7461–7468
Liu SW, Yu JG, Mann S (2009) Synergetic codoping in fluorinated Ti1−xZrxO2 hollow microspheres. J Phys Chem C 113:10712–10717
Hu GJ, Meng XF, Feng XY, Ding YF, Zhang SM, Yang MS (2007) Anatase TiO2 nanoparticles/carbon nanotubes nanofibers: preparation, characterization and photocatalytic properties. J Mater Sci 42:7162–7170
Yu J, Ma T, Liu S (2011) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2 aggregates by embedding carbon nanotubes as electron-transfer channel. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:3491–3501
Vinod Selvaganesh S, Selvarani G, Sridhar P, Pitchumani S, Shukla AK (2010) A durable PEFC with carbon-supported Pt–TiO2 cathode: a cause and effect study. J Electrochem Soc 157:B1000–B1007
Guidong Y, Zheng J, Huahong S, Tiancun X, Zifeng Y (2010) Preparation of highly visible light active N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. J Mater Chem 20:5301–5309
Akhavan O, Azhimirad R, Safa S, Larijani MM (2010) Visible light photo-induced antibacterial activity of CNT-doped TiO2 thin films with various CNT contents. J Mater Chem 20:7386–7392
Li Y, Hwang DS, Lee NH, Kim SJ (2005) Synthesis and characterization of carbon-doped titania as an artificial solar light sensitive photocatalyst. Chem Phys Lett 404:25–29
Ren W, Ai Z, Jia L, Zhang L, Fan X, Zou Z (2007) Low temperature preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of mesoporous carbon-doped crystalline TiO2. Appl Catal B 69:138–144
Dhanasekaran P, Vinod Selvaganesh S, Bhat SD (2016) Nitrogen and carbon doped titanium oxide as an alternative and durable electrocatalyst support in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Power Sources 304(2016):360–372
Xiao Q, Ouyang L (2009) Photocatalytic activity and hydroxyl radical formation of carbon-doped TiO2 nanocrystalline: effect of calcination temperature. Chem Eng J 148:248–253
Zhou C, Wang H, Peng F, Liang J, Yu H, Yang J (2009) MnO2/CNT supported Pt and PtRu nanocatalysts for direct methanol fuel cells. Langmuir 25:7711–7717
Qin YH, Li Y, Lv RL, Wang TL, Wang WG, Wang CW (2015) Enhanced methanol oxidation activity and stability of Pt particles anchored on carbon-doped TiO2 nanocoating support. J Power Sources 278:639–644
Xia BY, Wang B, Wu HB, Liu Z, Wang X, Wen X, Lou (D) (2012) Sandwich-structured TiO2–Pt–graphene ternary hybrid electrocatalysts with high efficiency and stability. J Mater Chem 22:16499–16505
Eder D (2010) Carbon nanotube−inorganic hybrids. Chem Rev 110:1348–1385
Zhang H, Lv X, Li Y, Wang Y, Li J (2010) P25-graphene composite as a high performance photocatalyst. ACS Nano 4:380–386
Dai L, Mau AWH (2000) Surface and interface control of polymeric biomaterials, conjugated polymers, and carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 104:1891–1915
Qu L, Zhang H, Zhu J, Dai L (2005) Template-free electrodeposition of multicomponent metal nanoparticles for region-specific growth of interposed carbon nanotube micropatterns. Nanotechnology 16:2111–2117
Montero-Ocampo C, Vargas Garcia JR, Arce Estrada E (2013) Comparison of TiO2 and TiO2-CNT as cathode catalyst supports for ORR. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:12780–12800
Christensen PA, Curtis TP, Egerton TA (2003) Photoelectrocatalytic and photocatalytic disinfection of E. coli suspensions by titanium dioxide. Appl Catal B Environ 41:371–386
Kannan R, Pillai VK (2009) Applications of carbon nanotubes in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J Indian Inst Sci 89:425–436
Dhanasekaran P, Vinod Selvaganesh S, Giridhar VV, Bhat SD (2016) Iron and nitrogen co-doped titania framework as hybrid catalyst support for improved durability in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Int J Hydr Energy 41:18214–18220
Kinoshita K, Lundquis JT, Stonehart P (1973) Potential cycling effects on platinum electrocatalyst surfaces. Electrochemistry 48:157–166
Avasarala B, Moore R, Haldar P (2010) Surface oxidation of carbon supports due to potential cycling under PEM fuel cell conditions. Electrochim Acta 55:4765–4771
Neophytides SG, Zafeiratos S, Papakonstantinou GD, Jaksic JM, Paloukis FE, Jaksic MM (2005) Extended brewer hypo–hyper-image-interionic bonding theory—I. Theoretical considerations and examples for its experimental confirmation. Int J Hydr Energy 30:131–147
Acknowledgements
Dr. S. D. Bhat CSIR thanks grant (No. DU-MLP-0090) under CSIR-Young Scientist Award Scheme. Dr. S. Vinod Selvaganesh and Mr. P. Dhanasekaran gratefully acknowledge CSIR for Research Associateship. Authors thank the Director and the Head, PPMG, CECRI, for their support and encouragement. We also thank Mr. A. Rathishkumar, Senior Technical Officer, CECRI, for his help in TEM characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinod Selvaganesh, S., Dhanasekaran, P. & Bhat, S.D. Nanocomposite TiO2-f-MWCNTs as durable support for Pt in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Solid State Electrochem 21, 2997–3009 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3628-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3628-x