Abstract
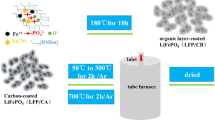
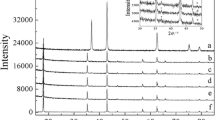
LiFePO4-C nanoparticles were synthesized by a hydrothermal method and subsequent high-energy ball-milling. Different carbon conductive additives including nanosized acetylene black (AB) and multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) were used to enhance the electronic conductivity of LiFePO4. The structural and morphological performance of LiFePO4-C nanoparticles was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of LiFePO4-C/Li batteries were analyzed by cyclic voltammetry and charge/discharge tests. XRD results demonstrate that LiFePO4-C nanoparticles have an orthorhombic olivine-type structure with a space group of Pnma. LiFePO4-C/Li battery with 5 wt% MWCNT displays the best electrochemical properties with a discharge capacity of 142 mAh g−1 at 0.25 C at room temperature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pistoia G, Zane D, Zhang Y (1995) J Electrochem Soc 142:2551
Resimers JN, Dahn JR, von Sacken U (1993) J Electrochem Soc 140:2752
Li W, Resimers JN, Dahn JR (1993) Solid State Ionics 67:123
Dahn JR, von Sacken U, Juzkow MW, Al-Janaby H (1991) J Electrochem Soc 138:2207
Koetschau I, Richard MN, Dahn JR, Soupart JB, Rousche JC (1995) J Electrochem Soc 142:2906
Jeong I-S, Kim J-U, Gu H-B (2001) J Power Sources 102:55
Jin B, Kim J-U, Gu H-B (2003) J Power Sources 117:148
Kim J-U, Jo Y-J, Park G-C, Gu H-B (2003) J Power Sources 119–121:686
Jin B, Jun D-K, Gu H-B (2006) Trans Electr Electron Mater 7:76
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:1188
Bramnik NN, Bramnik KG, Buhrmester T, Baehtz C, Ehrenberg H, Fuess H (2004) J Solid State Electrochem 8:558
Jin B, Gu H-B, Kim K-W (2008) J Solid State Electrochem 12:105
Shiraishi K, Dokko K, Kanamura (2005) J Power Sources 146:555
Myung ST, Komaba S, Hirosaki N, Yashiro H, Kumagai N (2004) Electrochimica Acta 49:4213
Yun NJ, Ha H-W, Jeong KH, Park H-Y, Kim K (2006) J Power Sources 160:1361
Chung S-Y, Bloking JT, Chiang Y-M (2002) Nat Mater 1:123
Yamada A, Chung SC, Hinikuma K (2001) J Electrochem Soc 148:A224
Cho T-H, Chung H-T (2004) J Power Sources 133:272
Yang M-R, Ke W-H, Wu S-H (2005) J Power Sources 146:539
Franger S, Cras FL, Bourbon C, Rouault H (2005) J Power Sources 119–121:252
Jeong W-T, Lee KS (2002) J Power Sources 104:95
Rabanal ME, Gutierrez MC, Garcia-Alvarado F, Gonzalo EC, Arroyo-de Dompablo ME (2006) J Power Sources 160:523
Ni JF, Zhou HH, Chen JT, Zhang XX (2005) Mater Lett 59:2361
Sanchez MAE, Brito GES, Fantini MCA, Goya GF, Matos JR (2006) Solid State Ionics 177:497
Arnold G, Garche J, Hemmer R, Strobele S, Volger C, Wohlfahrt-Mehrens M (2003) J Power Sources 119–121:247
Acknowledgments
This research project received supporting funds from the second-stage Brain Korea 21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, B., Gu, HB., Zhang, W. et al. Effect of different carbon conductive additives on electrochemical properties of LiFePO4-C/Li batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 12, 1549–1554 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0509-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0509-3