Abstract
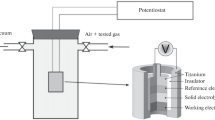
An improved polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell-based amperometric hydrogen sensor has been developed. The sensor operates at room temperature, and the electrolyte used in the sensor is Nafion which is a proton-conducting solid polymer electrolyte. Platinum black is used as both anode and cathode. The sensor functions as a fuel cell, H2/Pt//Nafion//Pt/O2, and a mechanical barrier limits the supply of hydrogen to the sensing side electrode. The limiting current is found to be linearly related to the hydrogen concentration. The sensor can be used to measure hydrogen in argon in parts per million and percentage levels. The basic principle, details of assembly, and response behavior of the sensor are discussed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kordesch K, Gunter S (1996) Fuel cells and their applications. VCH publishers, Inc., New York, USA (Chapter 4)
David L (1984) Handbook of Fuel Cell and Batteries. McGraw-Hill, New York (Chapter 22)
Jung J, Runge H (1988) Proc. 4th Int. Conf. on Liquid Metal Engineering and Technology 3:603–10, Avignon, France
Masse F, Rodriguez G, IWGFR-98 (1997) IAEA IWGFR specialists meeting on sodium removal and disposal from LMFBRs in normal operations and in the framework of decommissioning, Aix en Provence 3–7 November
Rodriguez G, Karpov AV, Nalimov Yu P (2001) Waste Management 21:357–362
DocIIs/IIW-805-85 (1995) Weld World 23(3/40):50–62
Velmurugan S, Rufus AL, Sathyaseelan VS, Padmakumari TV, Narasimhan SV, Mathur PK (1995) Nucl Energy 34(2):103–116
Ramesh C, Murugesan N, Prince AAM, Velmurugan S, Narasimhan SV, Ganesan V (2001) Corros Sci 43:1865–1875
Prince AAM, Velmurugan S, Ramesh C, Murugesan N, Raghavan PS, Gopalan R, Narasimhan SV (2001) J Nucl Mater 289:281–290
Polack AJ, Buhler HJ, Petty Weeks S (1985) Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Solid-State Sensors and Actuators (Transducers’85) Philadelphia, PA, USA, June 11–14 pp 85–88
Miura N, Kato H, Ozawa Y, Yamazoe N, Seiyama T (1983) Chem Letters 12:1573–1576
Miura N, Yamazoe N (1988) Chemical Sensor Technology, vol. 1. Kodansha, Tokyo (pp. 123–139)
Miura N, Kato H, Ozawa Y, Yamazoe N, Seiyama T (1984) Chem Letters 13:1905–1908
Miura N, Harada T, Yamazoe N (1989) J Electrochem Soc 136:215–1219
Remash C, Periaswami G, Albert SK, Shankar P, Murugesan N, Mathews CK, Gill TPS (1997) Indian Patent No. 186660
Ramesh C, Velayutham G, Murugesan N, Ganesan V, Dhathathreyan KS, Periaswami G (2003) J Solid State Electrochem 7:511–516
Velayutham G, Ramesh C, Murugesan N, Manivannan V, Periaswami G (2004) Ionics 10(1–2):50–55
Xianbo L, Shouguo W, Li W, Zhenxi S (2005) Sens Actuators B 107:812–817
Song SQ, Liang ZX, Zhou WJ, Sun GQ, Xin Q, Stregiopoulos V, Tsoadiras P (2005) J Power Sources 145:495–501
Albert SK, Remash C, Murugesan N, Gill TPS, Periasami G, Kulkarni SD (1997) Welding Journal 76:251s–254s
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, C., Murugesan, N., Krishnaiah, M.V. et al. Improved Nafion-based amperometric sensor for hydrogen in argon. J Solid State Electrochem 12, 1109–1116 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-007-0448-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-007-0448-4