Abstract
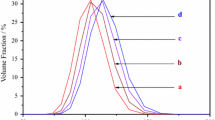
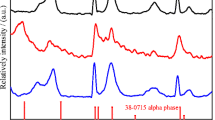
Nanoparticles of α-phase nickel hydroxide were synthesized by a single-step hydrothermal method using urea as the hydrolytic agent. Precipitated powders were of pure turbostratic α-phase as confirmed by x-ray diffraction profile. The ageing of α-Ni(OH)2 in 1.0 M alkali solutions is investigated for pure non-intercalated α-Ni(OH)2 and thiourea intercalated/absorbed α-phase nanomaterials. The α-Ni(OH)2 powder immobilized on the surface of graphite electrodes shows a gradual α→β phase transformation with continuous voltammetric cycling, and the concentration gradient of water that exists in the layered-double-hydroxide-like interlayers of α-phase and the solution was shown to play a crucial role on the high electrochemical activity of this phase nickel hydroxide. To understand the role of water in the ageing process, concomitant entries of non-aqueous solvents like ethanol and acetonitrile along with thiourea were effected. Cyclic voltammetric measurements of thiourea-treated α-Ni(OH)2 samples revealed that hydroxyl ion influx during the anodic oxidation depends on the counter flux of solvent molecules, and if the intercalated the solvent is acetonitrile, then the electrochemical activity of α-Ni(OH)2 reduced drastically; Q a/Q c>1 for water as solvent in the interlayers α-Ni(OH)2 and Q a/Q c<1 for ethanol and acetonitrile as solvents. The α-phase gets stabilized in the presence of thiourea with water and ethanol as co-intercalates. Transmission electron microscope images of α-Ni(OH)2 and thiourea-treated samples show a change in particle size and morphology. Elemental CHNS analysis confirms the presence of sulphur in the thiourea intercalated samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hana XJ, Xua P, Xua CQ, Zhaoa L, Moa ZB, Liu T (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:2763
Meyer M, Bée A, Talbot D, Cabuil V, Boyer JM, Répetti B, Garrigos R (2004) J Colloid Interface Sci 277:309
Liu X, Yu L (2004) Mater Lett 58:1327
Carter JC, Khulbe PK, Gray J, Van Zee JW, Angel SM (2004) Anal Chim Acta 514:241
Srinivasan V, Weidner JW, White RE (2000) J Solid State Electrochem 4:367
Le Bihan S, Guenot J, Figlarz M (1970) C R Acad Sci Ser C 270:2131
McEwen RS (1971) J Phys Chem 75:1782
Oliva P, Leonardi J, Laurent JF, Delmas C, Braconnier JJ, Figlarz M, Fiev F, Deguibert A (1982) J Power Sources 8:229
O’Grady WE, Pandya KI, Swider KE, Corrigan DA (1996) J Electrochem Soc 143:1613
Ganesh Kumar V, Munichandraiah N, Vishnu Kamath P, Shukla AK (1995) J Power Sources 56:111
Gonsalves M, Robert Hillman A (1998) J Electroanal Chem 454:183
French HM, Henderson MJ, Hillman AR, Vieil E (2002) Solid State Ionics 150:27
French HM, Henderson MJ, Hillman AR, Vieil E (2001) J Electroanal Chem 500:192
Delahaye-Vidal D, Beaudoin B, Sac-Epee N, Tekaia-Elhsissen K, Audemer A, Figlarz M (1996) Solid State Ionics 84:239
Tessier C, Guerlou-Demourgues L, Faure C, Basterreix M, Nabias G, Delmas C (2000) Solid State Ionics 133:11
Bernard MC, Bernard P, Keddam M, Senyarich S, Takenouti H (1996) Electrochim Acta 41:91
Jayalakshmi M, Venugopal N, Ramachandra Reddy B, Mohan Rao M (2005) J Power Sources 150:272
Genin P, Delahaye-Vidal A, Portemer F, Tekaia-Elhsissen K, Figlarz M (1991) Eur J Solid State Inorg Chem 28:505
Scholz F, Meyer B (1998) Voltammetry of solid microparticles immobilized on electrode surfaces. In: Bard AJ, Rubinstein I (eds) Electroanalytical chemistry, a series of advances, vol 20. Dekker, New York, p 1
Bing L, Huatang Y, Yunshi Z, Zuoxiang Z, Deying S (1999) J Power Sources 79:277
Kostecki R, McLarnon F (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:485
Jeong DJ, Kim WS, Choi YK, Sung YE (2001) J Electroanal Chem 511:79
Kim MS, Hwang KB, Kim J (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:1537
Choudary BM, Swarna Jaya V, Ramachandra Reddy B, Lakshmi Kantam M, Mohan Rao M, Sakunthala Madhavendra S (2005) Chem Mater 17:2740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayalakshmi, M., Radhika, P., Raja, K.P. et al. Solvent and thiourea adsorption/intercalation effects on the solid-state electrochemistry of α-phase nickel hydroxide nanoparticles. J Solid State Electrochem 11, 165–172 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-005-0081-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-005-0081-z