Abstract
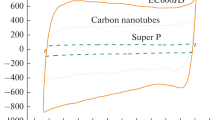
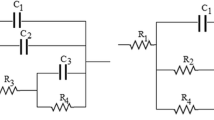
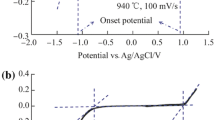
The difficulties in the use of carbon paste electrodes to quantify the electrochemical adsorption of hydrogen in nanocarbon materials are described. Chronoamperometry studies using a Ferro/Ferri redox couple were performed to obtain the electrochemical active area of paste electrodes prepared by dispersion of differing samples of carbon blacks (CB) within silicon oil. This electrochemical active area was combined with the BET-surface area of the carbon blacks, to obtain the mass of superficial carbon involved in the electrochemical processes. To assure equal conditions for comparison, the electronic conductivity of the paste was equivalent in all the samples. From our results it appears that cyclic voltammetry, combined with carbon paste electrodes and nitrogen adsorption isotherms, provides a simple and less expensive route for the qualitative evaluation of the electrochemical hydrogen uptake of novel carbon materials. Still, for quantitative measurements, some issues remain unsolved in highly structured carbons, where the lack of penetration of the bulky Ferro/Ferri redox couple in the micropores of the CB and the occurrence of solid-state diffusion cause the underestimation of the mass involved in hydrogen adsorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kinoshita K (2003) Carbon, electrochemical and physicochemical properties. Wiley, New York
Ye Y, Ahn CC, Witham C, Fultz B, Liu J, Rinzler AG, Colbert D, Smith KA, Smalley RE (1999) Appl Phys Lett 74:2307
Dillon AC, Bekkedahl TA, Jones KM, Heben MJ (1999) Fullerenes 3:716
Wu HB, Chen P, Lin J, Tan KL (2000) Int J Hydrogen Energy 25:261
Yang RT (2000) Carbon 38:623
Yin YF, Mays T, McEnaney B (2000) Langmuir 103:10521
Barisci JN, Wallace GG, Baughman RH (2000) J Electroanal Chem 488:92
Rajalakshmi N, Dhathathreyan KS, Govindaraj A, Satishkumar BC (2000) Electrochim Acta 45:4511
Lee SM, Park KS, Choi YC, Park YS, Bok JM, Bae DJ, Nahm KS, Choi YG, Yu SC, Kim N, Frauenheim T, Lee YH (2000) Synthetic Metals 113:209
Qin X, Gao XP, Liu H, Yuan HT, Yan DY, Gong WL, Song DY (2000) Electrochem Solid State Lett 3:532
Jurewicz K, Frackowiak E, Béguin F (2001) Electrochem Solid State Lett 4:A27
Gao XP, Lan Y, Pan GL, Wu F, Qu JQ, Song DY, Shen PW (2001) Electrochem Solid State Lett 4:A173
Frackowiak E, Béguin F (2002) Carbon 40:1775
Züttel A, Sudan P, Mauron P, Kiyobayashi T, Emmenegger C, Schlapbach L (2002) Int J Hydrogen Energy 27:203
Youn HS, Ryu H, Cho TH, Choi WK (2002) Int J Hydrogen Energy 27:937
Darkrim FL, Malbrunot P, Tartaglia GP (2002) Int J Hydrogen Energy 27:193
Yan X, Gao X, Li Y, Liu Z, Wu F, Shen Y, Son D (2003) Chem Phys Lett 372:336
Miranda-Hernández M, Ayala JA, Rincón ME (2003) J Solid State Electrochem 7:264
Miranda-Hernández M, Ayala JA, Rincón ME (2003) J Solid State Electrochem 7:264
Buchholz DB, Doherty SP, Chang RPH (2003) Carbon 41:1625
Fujiwara A, Ishii K, Suematsu H, Kataura H, Maniwa Y, Suzuki S, Achiba Y (2001) Chem Phys Lett 336:205
Strømme M, Niklasson GA, Granqvist CG (1995) Phys Rev B 52:14192
Groszek AJ (1987) Carbon 25:717
Qu D (2002) J Power Sources 109:403
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to M.E. Trujillo-Camacho and R. Moran for technical assistance, to DGAPA-UNAM and CONACYT-MEXICO for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miranda-Hernández, M., Rincón, M.E. Carbon paste electrodes: correlation between the electrochemical hydrogen storage capacity and the physicochemical properties of carbon blacks. J Solid State Electrochem 9, 646–652 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-004-0639-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-004-0639-1