Abstract
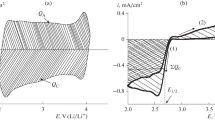
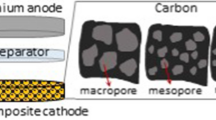
The electrochemical characteristics of carbonaceous materials differing in their specific surface area and porosity are studied by the method of cyclic voltammetry in 0.25 М LiClO4/DMSO electrolyte, both in inert and oxygen atmosphere. The value of the electrochemically active surface area that was estimated from cyclic voltammograms as the polarization capacitance was shown to increase with increase in the BET specific surface area. The efficiency in the oxygen reaction, measured in the oxygen atmosphere and expressed as the charge consumed for the formation of Li2O2 (QC) in the oxygen reduction reaction (the cathodic segment), and the process reversibility, expressed as the ratio of the charge consumed for oxygen evolution (QA) (the anodic segment) to QC, are mainly determined by the electrochemically active surface area and the porosity of the carbonaceous material.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kraytsberg, A. and Ein-Eli, Y., Review on Li–air batteries—Opportunities, limitations and perspective, J. Power Sources, 2011, vol. 196, p. 886.
Ding, N., Chien, S.W., Hor, T.S.A., Lum, R., Zong, Y., and Liu, Z., Influence of carbon pore size on the discharge capacity of Li–O2 batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A., 2014, vol. 2, p. 12433.
Kim, M., Yoo, E., Ahn, W.-S., and Shim, S.E., Controlling porosity of porous carbon cathode for lithium oxygen batteries: Influence of micro and meso porosity, J. Power Sources, 2018, vol. 389, p. 20.
Meini, S., Piana, M., Beyer, H., Schwaemmlein, J., and Gasteiger, H.A., Effect of carbon surface area on first discharge capacity of Li–O2 cathodes and cycle-life behavior in ether-based electrolytes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2012, vol. 159, p. A2135.
Chervin, C.N., Wattendorf, M.J., Long, J.W., Kucko, N.W., and Rolison, D.R., Carbon nanofoam-based cathodes for Li–O2 batteries: correlation of pore solid architecture and electrochemical performance, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2013, vol. 160, p. A1510.
Tan, P., Shyy, W., Wei, Z.H., An, L., and Zhao, T.S., A carbon powder-nanotube composite cathode for non-aqueous lithium-air batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 147, p. 1.
Zhang, G.Q., Zheng, J.P., Liang, R., Zhang, C., Wang, B., Hendrickson, M., and Plichta, E.J., Lithium–air batteries using SWNT/CNF buckypapers as air electrodes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, vol. 157, p. A953.
Sahapatsombut, U., Cheng, H., and Scott, K., Modelling the micro–macro homogeneous cycling behaviour of a lithium–air battery, J. Power Sources, 2013, vol. 227, p. 243.
Yoo, K., Banerjee, S., and Dutta, P., Modeling of volume change phenomena in a Li–air battery, J. Power Sources, 2014, vol. 258, p. 340.
Jung, C.Y., Zhao, T.S., and An, L., Modeling of lithium–oxygen batteries with the discharge product treated as a discontinuous deposit layer, J. Power Sources, 2015, vol. 273, p.440.
Wang, L., Zhao, X., Lu, Y., Xu, M., Zhang, D., Ruoff, R.S., Stevenson, K.J., and Goodenough, J.B., CoMn2O4 spinel nanoparticles grown on graphene as bifunctional catalyst for lithium-air batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, vol. 158, p. A1379.
Li, L. and Manthiram, A., Decoupled bifunctional air electrodes for highperformance hybrid lithium-air batteries, Nano Energy, 2014, vol. 9, p. 94.
Li, L., Liu, C., He, G., Fan, D., and Manthiram, A., Hierarchical pore-in-pore and wire-inwire catalysts for rechargeable Zn– and Li–air batteries with ultra-long cycle life and high cell efficiency, Energy Environ Sci., 2015, vol. 8, p. 3274.
Lim, H.D., Song, H., Gwon, H., Park, K.-Y., Kim, J., Bae, Y., Kim, H., Jung, S.-K., Kim, T., Kim, Y.H., Lepró, X., Ovalle-Robles, R., Baughmand, R.H., and Kang, K., A new catalyst-embedded hierarchical air electrode for high-performance Li–O2 batteries, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, vol. 6, p. 3570.
Marinaro, M., Riek, U., Moorthy, S.K.E., Bernhard, J., Kaiser, U., Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M., and Jörissen, L., Au-coated carbon cathodes for improved oxygen reduction and evolution kinetics in aprotic Li–O2 batteries, Electrochem. Commun., 2013, vol.37, p. 53.
Zhu, D., Zhang, L., Song, M., Wang, X., and Chen, Y., An in situ formed Pd nanolayer as a bifunctional catalyst for Li–air batteries in ambient or simulated air, Electrochem. Commun., 2013, vol. 49, p. 9573.
Zhang, Z., Su, L., Yang, M., Hu, M., Bao, J., Wei, J., and Zhou, Z., A composite of Co nanoparticles highly dispersed on N-rich carbon substrates: an efficient electrocatalyst for Li–O2 battery cathodes, Chem. Commun., 2014, vol. 50, p. 776.
Huang, X., Yu, H., Tan, H., Zhu, J., Zhang, W., Wang, C., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Lv, Y., Zeng, Z., Liu, D., Ding, J., Zhang, Q., Srinivasan, M., Ajayan, P.M., Hoon, H., and Yan, Q., Carbon nanotube encapsulated noble metal nanoparticle hybrid as a cathode material for Li–oxygen batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, vol. 24, p. 6516.
Tan, P., Jiang, H.R., Zhu, X.B., An, L., Jung, C.Y., Wu, M.C., Shi, L., Shyy, W., and Zhao, T.S., Advances and challenges in lithium–air batteries, Applied Energy, 2017, vol. 204, p. 780.
Ma, S., Wu, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yan, X., Wei, Y., Liu, P., Wang, J., Jiang, K., Fan, S., Xu, Y., and Peng, Z., Reversibility of noble metal-catalyzed aprotic Li–O2 batteries, Nano Lett., 2015, vol. 15, p. 8084.
McCloskey, B.D., Speidel, A., Scheffler, R., Miller, D.C., Viswanathan, V., Hummelshoj, J.S., Nørskov, J.K., and Luntz, A.C., Twin problems of interfacial carbonate formation in nonaqueous Li–O2 batteries, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2012, vol. 3, p. 997.
Itkis, D.M., Semenenko, D.A., Kataev, E.Yu., Belova, A.I., Neudachina, V.S., Sirotina, A.P., Hävecker, M., Teschner, D., Knop-Gericke, A., Dudin, P., Barinov, A., Goodilin, E.A., Shao-Horn, Y., and Yashina, L.V., Reactivity of carbon in lithium–oxygen battery positive electrodes, Nano Lett., 2013, vol. 13, p. 4697.
Arkhipova, E.A., Ivanov, A.S., Maslakov, K.I., Egorov, A.V., Savilov, S.V., and Lunin, V.V., Mesoporous graphene nanoflakes for high performance supercapacitors with ionic liquid electrolyte, Microporous Mesoporous Materials, 2020, vol. 294, p. 109851.
Bogdanovskaya, V.A., Panchenko, N.V., Radina, M.V., Andreev, V.N., Korchagin, O.V., Tripachev, O.V., and Novikov, V.T., Oxygen reaction at carbonaceous materials with different structure in electrolytes based on lithium perchlorate and aprotic solvents, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2019, vol. 55, p. 878.
Olivares-Marín, M., Aklalouch M., and Tonti, D., Combined influence of meso- and macroporosity of soft-hard templated carbon electrodes on the performance of Li–O2 cells with different configurations, Nanomaterials, 2019, vol. 9, p. 810.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Sciences and Higher Education of the Russian Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by Yu. Pleskov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzov, A.V., Bogdanovskaya, V.A., Emets, V.V. et al. The Effect of Carbonaceous Material Morphology on Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Nonaqueous Electrolyte Containing Lithium Ions. Russ J Electrochem 58, 296–302 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193522040073
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193522040073