Abstract.
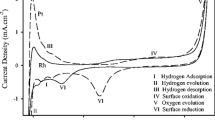
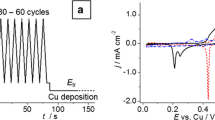
The underpotential deposition of copper onto polycrystalline rhodium was studied as a function of the degree of oxidation of the electrode surface in acidic media using potentiodynamic techniques. Surface oxidation of the rhodium electrode was carried out using a triangular sweep potential between E L (lower limit) and E U (upper limit: 0.94≤E U≤1.4 V). Cu electrodeposition was performed at the same time as the total or partial reduction of the oxidized species. The surface oxides produced at E U≤1.09 V were completely reduced during Cu electrodeposition. In this case, the potentiodynamic I-E patterns for oxidative dissolution of Cu were characterized by three anodic peaks located at 0.41 V (peak I), 0.47 V (peak II) and 0.59 V (peak III) and the coverage degree by Cu, θCu, was on the order of a monolayer. Surface oxides produced at E U>1.09 V were partially reduced during the copper electrodeposition. In this case, the I-E profiles exhibited only two anodic peaks (II and III) and θCu was <1. The Rh-oxygen species that remain on the electrode surface block the active sites of lower energy and modify the binding energy of strongly adsorbed Cu.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salgado, L., Meas, Y. & Trejo, G. Influence of the degree of surface oxidation of polycrystalline Rh electrodes on the underpotential deposition of Cu. J Solid State Electrochem 7, 37–42 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-002-0282-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-002-0282-7