Abstract
Context
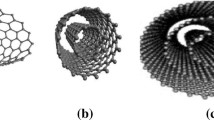
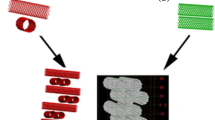
Nanoscrolls are tube-shaped structures formed when a sheet or ribbon of material is rolled into a cylinder, creating a hollow tube with a diameter on the nanoscale, similar to the papyrus. Carbon nanoscrolls have unique properties that make them useful in various applications, such as energy storage, catalysis, and drug delivery. In this study, we employed classical molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the formation and stability of nanoscrolls composed of graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) nanoribbons. Using a carbon nanotube (CNT) as a template to trigger their collapsing, we found that graphene/graphene, graphene/hBN, and hBN/hBN could form CNT-wrapped nanoscrolls at ultrafast speeds. We also confirmed that these nanoscrolls are thermally stable and discussed the other products formed from the interaction of these complexes and their temperature dependence. Gr/Gr and hBN/Gr nanoscrolls exhibit similar interlayer distances, while hBN/hBN nanoscrolls have wider interlayer distances than the other two composite nanoscrolls. These features suggest that hBN/hBN composite nanoscrolls could more efficiently capture small molecules because of their greater interlayer spacing.
Methods
We conducted molecular dynamics simulations using the Forcite package in the Biovia Materials Studio software, which employs the Universal and Dreiding force fields. We considered an NVT ensemble with a fixed time step of 1.0 fs for a duration of 500 ps. The velocity Verlet algorithm was adopted to integrate the equations of motion of the entire system. We employed the Nosé-Hoover-Langevin thermostat to control the system temperature. The simulations were carried out without periodic boundary conditions, so there was no pressure coupling.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
N/A
Code availability
N/A
References
Liu H, Le T, Zhang L, Xu M (2018) J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29:18891
Perim E, Machado LD, Galvao DS (2014) Frontiers in Materials 1:31
Viculis LM, Mack JJ, Kaner RB (2003) Science 299(5611):1361
Xie X, Ju L, Feng X, Sun Y, Zhou R, Liu K, Fan S, Li Q, Jiang K (2009) Nano Lett 9(7):2565
Shi X, Pugno NM, Gao H (2010) Acta Mech Solida Sin 23(6):484
Braga SF, Coluci VR, Legoas SB, Giro R, Galvão DS, Baughman RH (2004) Nano Lett 4(5):881
Mpourmpakis G, Tylianakis E, Froudakis GE (2007) Nano Lett 7(7):1893
Coluci V, Braga S, Baughman R, Galvao D (2007) Phys Rev B 75(12):125404
Hai-Zhen Z, Halidan M, Pei-Shuai Z, Li-Rong F, Jin-Yan S (2021) J Nanopart Res 24(2)
Shi X, Cheng Y, Pugno NM, Gao H (2010) Small 6(6):739
Shi X, Pugno NM, Cheng Y, Gao H (2009) Appl Phys Lett 95(16):163113
Zhang Z, Li T (2011) Nanoscale Res Lett 6:1
Zhou HQ, Qiu CY, Yang HC, Yu F, Chen MJ, Hu LJ, Guo YJ, Sun LF (2011) Chem Phys Lett 501(4–6):475
Lin SY, Chang SL, Chiang CR, Li WB, Liu HY, Lin MF (2021) Nanomaterials 11(6):1372
Pan H, Feng Y, Lin J (2005) Phys Rev B 72(8):085415
Chen Y, Lu J, Gao Z (2007) J Phys Chem C 111(4):1625
Junior MLP, da Cunha WF, Galvão DS, Junior LAR (2021) Phys Chem Chem Phys 23(15):9089
Cheng G, Calizo I, Liang X, Sperling BA, Johnston-Peck AC, Li W, Maslar JE, Richter CA, Walker ARH (2014) Carbon 76:257
Xu Z, Zheng B, Chen J, Gao C (2014) Chem Mater 26(23):6811
Zhao J, Yang B, Yang Z, Zhang P, Zheng Z, Ren W, Yan X (2014) Carbon 79:470
Jayasena B, Subbiah S, Reddy C (2012) In: 2012 12th IEEE International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO). IEEE, pp 1–5
Skrabalak SE (2009) Phys Chem Chem Phys 11(25):4930
Gao Y, Chen X, Xu H, Zou Y, Gu R, Xu M, Jen AKY, Chen H (2010) Carbon 48(15):4475
Perim E, Paupitz R, Galvao DS (2013) J Appl Phys 113(5):054306
Zheng B, Xu Z, Gao C (2016) Nanoscale 8(3):1413
Song H, Geng S, An M, Zha X (2013) J Appl Phys 113(16):164305
Kim JH, Benelmekki M (2018) In: Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles and Architecture Nanostructures. Elsevier, pp 553–574
Wang Y, Zhan H, Yang C, Xiang Y, Zhang Y (2015) Comput Mater Sci 96:300
Zhang D, Yang H (2016) J Mol Struct 1125:282
Zhang Z, Li T (2010) Appl Phys Lett 97(8):081909
Júnior MP, Júnior LR, Galvão DS, De Sousa JM (2021) Chem Phys Lett 780:138919
Patra N, Wang B, Král P (2009) Nano Lett 9(11):3766
Perim E, Galvao DS (2009) Nanotechnology 20(33):335702
Qayyum MS, Hayat H, Matharu RK, Tabish TA, Edirisinghe M (2019) Appl Phys Rev 6(2):021310
Kim JH, Lu TM (2016) RSC Adv 6(21):17179
Li X, Zhang T, Gu S, Kang SZ, Li G, Mu J (2013) Sep Purif Technol 108:139
Ji E, Son J, Kim JH, Lee GH (2018) FlatChem 7:26
Aftab S, Iqbal MZ, Rim YS (2023) Small 19:2205418
Cui X, Kong Z, Gao E, Huang D, Hao Y, Shen H, Di C, Xu Z, Zheng J, Zhu D (2018) Nat Commun 9:1301
Ghosh R, Singh M, Chang LW, Lin HI, Chen YS, Muthu J, Papnai B, Kang YS, Liao YM, Bera KP, Guo GY, Hsieh YP, Hofmann M, Chen YF (2022) ACS Nano 16:5743
Wang L, Yue Q, Pei C, Fan H, Dai J, Huang X, Li H, Huang W (2020) Nano Res 13:959
Deng W, You C, Chen X, Wang Y, Li Y, Feng B, Shi K, Chen Y, Sun L, Zhang Y (2019) Small 15:1970160
Han MY, Özyilmaz B, Zhang Y, Kim P (2007) Phys Rev Lett 98(20):206805
Son YW, Cohen ML, Louie SG (2006) Phys Rev Lett 97(21):216803
Park CH, Louie SG (2008) Nano Lett 8(8):2200
Barone V, Peralta JE (2008) Nano Lett 8(8):2210
Systèmes D (2017) San Diego
Rappe AK, Casewit CJ, Colwell KS, Goddard WAI, Skiff WM (1992) J Am Chem Soc 114:10024
Mayo SL, Olafson BD, Goddard WA (1990) J Phys Chem 94:8897
Senftle TP, Hong S, Islam MM, Kylasa SB, Zheng Y, Shin YK, Junkermeier C, Engel-Herbert R, Janik MJ, Aktulga HM et al (2016) npj Computational Materials 2(1):1
Liang T, Shan TR, Cheng YT, Devine BD, Noordhoek M, Li Y, Lu Z, Phillpot SR, Sinnott SB (2013) Mater Sci Eng R Rep 74(9):255
Tersoff J (1989) Phys Rev B 39(8):5566
Sha H, Zhang S, Faller R (2018) Carbon 132:401
Li X, Jin Y, Xue Q, Zhu L, Xing W, Zheng H, Liu Z (2017) J CO2 Util 18:275
Li X, Xue Q, Chang X, Zhu L, Zheng H (2017) J CO2 Uti 21:429
Daff TD, Collins SP, Dureckova H, Perim E, Skaf MS, Galvão DS, Woo TK (2016) Carbon 101:218
Funding
This work received partial support from Brazilian agencies CAPES, CNPq, and FAPDF. L.A.R.J thanks the financial support from Brazilian Research Council FAP-DF grants \(00193-00000857/2021-14\), \(00193-00000853/2021-28\), and \(00193-00000811/2021-97\), CNPq grants \(302236/2018-0\) and \(350176/2022-1\), and FAPDF-PRONEM grant \(00193.00001247/2021-20\). L.A.R.J also thanks ABIN grant 08/2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.A.L.L.: data curation, formal analysis, methodology, and writing—original draft preparation. L. A. Ribeiro Júnior: conceptualization, funding acquisition, and writing—reviewing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This paper belongs to the Topical Collection on IX Symposium on Electronic Structure and Molecular Dynamics - IX SeedMol.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1 (avi 3718 KB)
Supplementary file 2 (avi 3718 KB)
Supplementary file 3 (avi 3456 KB)
Supplementary file 4 (avi 9817 KB)
Supplementary file 5 (avi 3396 KB)
Supplementary file 6 (avi 5715 KB)
Supplementary file 7 (avi 3966 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, K.A.L., Ribeiro Júnior, L.A. Formation and stability of nanoscrolls composed of graphene and hexagonal boron nitride nanoribbons: insights from molecular dynamics simulations. J Mol Model 29, 339 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-023-05702-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-023-05702-5