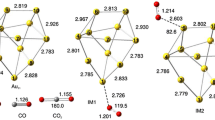
Abstract
The mechanisms for the acetylene hydrochlorination reaction on pristine Au7 and Au8 clusters and on the Si-doped Au clusters Au6Si and Au7Si were systematically investigated via density functional theory using the PBE functional. The band gap (∆Eg) of the Au7Si cluster was found to smaller than that of its undoped equivalent (Au8), thus enhancing its catalytic activity, and Au7Si presented a significantly reduced activation barrier (16.69 kcal mol−1) for the acetylene hydrochlorination reaction compared with the pristine Au8 cluster (21.83 kcal mol−1). On the other hand, the activation barrier for the acetylene hydrochlorination reaction was not lower for the Au6Si cluster than for the pristine Au7 cluster because the band gap (∆Eg) of Au6Si was found to be larger than that of Au7. Hence, the current work shows that the catalytic activities of gold clusters can be systematically modified by doping them. Our findings also suggest how to enhance the acetylene hydrochlorination reaction by doping foreign atoms into Au clusters.

The Si-doped Au7Si cluster showed stronger catalytic activity for the acetylene hydrochlorination reaction compared with the pristine Au8 cluster.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haruta M, Kobayashi T, Sano H, Yamada N (1987) Novel gold catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide at a temperature far below 0 °C. Chem Lett 16:405
Hutchings GJ (1985) Vapor phase hydrochlorination of acetylene: correlation of catalytic activity of supported metal chloride catalysts. J Catal 96:292–295
Yang B, Burch R, Hardacre C, Headdock G, Hu P (2012) Origin of the increase of activity and selectivity of nickel doped by Au, Ag, and Cu for acetylene hydrogenation. ACS Catal 2:1027–1032
Kim HY, Lee HM, Henkelman G (2011) CO oxidation mechanism on CeO2-supported Au nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 134:1560–1570
Boronat M, Leyva-Pérez A, Corma A (2014) Theoretical and experimental insights into the origin of the catalytic activity of subnanometric gold clusters: attempts to predict reactivity with clusters and nanoparticles of gold. Acc Chem Res 47:834–844
Molina LM, Hammer B (2005) Some recent theoretical advances in the understanding of the catalytic activity of Au. Appl Catal A Gen l291:21–31
Manzoor D, Krishnamurty S, Pal S (2014) Effect of silicon doping on the reactivity and catalytic activity of gold clusters. J Phys Chem C 118:7501–7507
Della Pina C, Falletta E, Prati L, Rossi M (2008) Selective oxidation using gold. Chem Soc Rev Chem Soc Rev 37:2077–2095
Choudhary TV, Sivadinarayana C, Datye AK, Kumar D, Goodman DW (2003) Acetylene hydrogenation on Au-based catalysts. Catal Lett 8:1–8
Huang CF, Zhu MY, Kang LH, Dai B (2014) A novel high-stability Au(III)/Schiff-based catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination reaction. Catal Commun 54:61–65
Huang CF, Zhu MY, Kang LH, Li XY, Dai B (2014) Active carbon supported TiO2–AuCl3/AC catalyst with excellent stability for acetylene hydrochlorination reaction. Chem Eng J 242:69–75
Li XY, Pan XL, Yu L, Ren PJ, Wu X, Sun LT, Jiao F, Bao XH (2014) Silicon carbide-derived carbon nanocomposite as a substitute for mercury in the catalytic hydrochlorination of acetylene. Nat Commun 5:3688
Li XY, Zhu MY, Dai B (2013) AuCl3 on polypyrrole-modified carbon nanotubes as acetylene hydrochlorination catalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 142–143:234–240
Bailie JE, Hutchings GJ (1999) Promotion by sulfur of gold catalysts for crotyl alcohol formation from crotonaldehyde hydrogenation. Chem Commun 21:2151–2152
Sakata K, Tada K, Yamada S, Kitagawa Y, Kawakami T, Yamanaka S, Okumura M (2014) DFT calculations for aerobic oxidation of alcohols over neutral Au6 cluster. Mol Phys 112:385–392
Landon P, Collier PJ, Papworth AJ, Kiely CJ, Hutchings GJ (2002) Direct formation of hydrogen peroxide from H2/O2 using a gold catalyst. Chem Commun 18:2058–2059
Fu Q, Saltsburg H, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (2003) Active nonmetallic Au and Pt species on ceria-based water-gas shift catalysts. Science 301:935–938
Nkosi B, Coville NJ, Hutchings GJ (1988) Reactivation of a supported gold catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 1:71–72
Nkosi B, Adams MD, Coville NJ, Hutchings GJ (1991) Hydrochlorination of acetylene using carbon-supported gold catalysts: a study of catalyst reactivation. J Catal 128:378–386
Wang Y, Zhu MY, Kang LH, Dai B (2014) Neutral Au n (n = 3–10) clusters catalyze acetylene hydrochlorination: a density functional theory study. RSC Adv 4:38466–38473
Pichugina DA, Nikolaev SA, Mukhamedzyanova DF, Kuz’menko NE (2014) Quantum-chemical modeling of ethylene and acetylene adsorption on gold clusters. Rus J Phys Chem A 88:959–964
Ferraro F, Pérez-Torres JF, Hadad CZ (2015) Selective catalytic activation of acetylene by a neutral gold cluster of experimentally known gas-phase geometry. J Phys Chem C 119:7755–7764
Li XB, Wang HY, Yang XD, Zhu ZH, Tang YJ (2007) Size dependence of the structures and energetic and electronic properties of gold clusters. J Chem Phys 126:084505
Li YF, Mao AJ, Li Y, Kuang XY (2012) Density functional study on size-dependent structures, stabilities, electronic and magnetic properties of Au n M (M = Al and Si, n = 1–9) clusters: comparison with pure gold clusters. J Mol Model 18:3061–3072
Bürgel C, Reilly NM, Johnson GE, Mitrić R, Kimble ML, Castleman AW, Bonačić-Koutecký V (2008) Influence of charge state on the mechanism of CO oxidation on gold clusters. J Am Chem Soc 130:1694–1698
Socaciu LD, Hagen J, Bernhardt TM, Wöste L, Heiz U, Häkkinen H, Landman U (2003) Catalytic CO oxidation by free Au2 −: experiment and theory. J Am Chem Soc 125:10437–10445
Conte M, Carley AF, Heirene C, Willock DJ, Johnston P, Herzing AA, Kiely CJ, Hutchings GJ (2007) Hydrochlorination of acetylene using a supported gold catalyst: a study of the reaction mechanism. J Catal 250:231–239
Wang S, Shen B, Song Q (2010) Kinetics of acetylene hydrochlorination over bimetallic Au–Cu/C catalyst. Catal Lett 134:102–109
Gao M, Lyalin A, Taketsugu T (2011) Role of the support effects on the catalytic activity of gold clusters: a density functional theory study. Catalysts 1:18–39
Spivey K, Williams JI, Wang L (2006) Structures of undecagold clusters: ligand effect. Chem Phys Lett 432:163–166
Priyanka BS, Dharamvir K (2013) Structure of small gold clusters with Si doping using DFT (Au n Si, n = 1–10, 19). J Nanopart Res 24:203–212
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li H, Izmaylov A, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery Jr JA, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Keith T, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam JM, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewski VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ (2010) Gaussian 09. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868
Schäfer A, Huber C, Ahlrichs R (1994) Fully optimized contracted Gaussian basis sets of triple zeta valence quality for atoms Li to Kr. J Chem Phys 100:5829
Gonzalez C, Schlegel HB (1989) An improved algorithm for reaction path following. J Chem Phys 90:2154–2161
Gonzalez C, Schlegel HB (1990) Reaction path following in mass-weighted internal coordinates. J Phys Chem 94:5523–5527
Duijneveldt FBV, Lenthe JHV (1994) State of the art in counterpoise theory. Chem Rev 94:1873–1885
Gautam S, Goel N, Dharamvir K (2014) A DFT based prediction of gold fullerene Au92Si12 with the aid of silicon. RSC Adv 4:13927–13933
Pal R, Wang LM, Huang W, Wang LS, Zeng XC (2009) Structural evolution of doped gold clusters: MAu x − (M = Si, Ge, Sn; x = 5−8). J Am Chem Soc 131:3396–3404
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the funding provided by the Science and Technology Fund Projects of Shihezi University (no. 2014ZRKXJQ03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3820 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhao, F. & Kang, L. Catalysis of the acetylene hydrochlorination reaction by Si-doped Au clusters: a DFT study. J Mol Model 24, 61 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-018-3602-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-018-3602-2