Abstract
Mur ligases are bacterial enzymes involved in the cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis and are viable targets for antibacterial drug discovery. We have performed virtual screening for potential ATP-competitive inhibitors targeting MurC and MurD ligases, using a protocol of consecutive hierarchical filters. Selected compounds were evaluated for inhibition of MurC and MurD ligases, and weak inhibitors possessing dual inhibitory activity have been identified. These compounds represent new scaffolds for further optimisation towards multiple Mur ligase inhibitors with improved inhibitory potency.

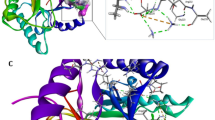
Structure and predicted binding mode of dual 1,3,5-triazine-based inhibitor in E. coli MurC and MurD active sites







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Livermore DM (2003) Bacterial resistance: origins, epidemiology, and impact. Clin Infect Dis 36:11–23
van Heijenoort J (2001) Recent advances in the formation of the bacterial peptidoglycan monomer unit. Nat Prod Rep 18:503–519
Vollmer W, Blanot D, de Pedro MA (2008) Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:149–167
Barreteau H, Kovač A, Boniface A, Sova M, Gobec S, Blanot D (2008) Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:168–207
El Zoeiby A, Sanschagrin F, Levesque RC (2003) Structure and function of the Mur enzymes: development of novel inhibitors. Mol Microbiol 47:1–12
Bertrand JA, Auger G, Martin L, Fanchon E, Blanot D, Le Beller D, van Heijenoort J, Dideberg O (1999) Determination of the MurD mechanism through crystallographic analysis of enzyme complexes. J Mol Biol 289:579–590
Bouhss A, Dementin S, van Heijenoort J, Parquet C, Blanot D (2002) MurC and MurD synthetases of peptidoglycan biosynthesis: borohydride trapping of acyl-phosphate intermediates. Methods Enzymol 354:189–196
Anderson MS, Eveland SS, Onishi HR, Pompliano DL (1996) Kinetic mechanism of the Escherichia coli UDPMurNAc-tripeptide D-alanyl-D-alanine-adding enzyme: use of a glutathione S-transferase fusion. Biochemistry 35:16264–16269
Emanuele JJ, Jin HY, Yanchunas J, Villafranca JJ (1997) Evaluation of the kinetic mechanism of Escherichia coli uridine diphosphate-N-acetylmuramate:L-alanine ligase. Biochemistry 36:7264–7271
Morphy R, Rankovic Z (2009) Designing multiple ligands - medicinal chemistry strategies and challenges. Curr Pharm Des 15:587–600
Csermely P, Agoston V, Pongor S (2005) The efficiency of multi-target drugs: the network approach might help drug design. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:178–182
Silver LL (2007) Multi-targeting by monotherapeutic antibacterials. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:41–55
Tomašić T, Zidar N, Kovač A, Turk S, Simčič M, Blanot D, Müller-Premru M, Filipič M, Grdadolnik SG, Zega A, Anderluh M, Gobec S, Kikelj D, Peterlin Mašič L (2010) 5-Benzylidenethiazolidin-4-ones as multitarget inhibitors of bacterial Mur ligases. ChemMedChem 5:286–295
Bouhss A, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Blanot D, van Heijenoort J, Parquet C (1997) Invariant amino acids in the Mur peptide synthetases of bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis and their modification by site-directed mutagenesis in the UDP-MurNAc:L-alanine ligase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 36:11556–11563
Eveland SS, Pompliano DL, Anderson MS (1997) Conditionally lethal Escherichia coli murein mutants contain point defects that map to regions conserved among murein and folyl poly-gamma-glutamate ligases: identification of a ligase superfamily. Biochemistry 36:6223–6229
Bouhss A, Dementin S, Parquet C, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Bertrand JA, Le Beller D, Dideberg O, van Heijenoort J, Blanot D (1999) Role of the ortholog and paralog amino acid invariants in the active site of the UDP-MurNAc-L-alanine:D-glutamate ligase (MurD). Biochemistry 38:12240–12247
Chappelle EW, Levin GV (1968) Use of the firefly bioluminescent reaction for rapid detection and counting of bacteria. Biochem Med 2:41–52
Traut TW (1994) Physiological concentrations of purines and pyrimidines. Mol Cell Biochem 140:1–22
Škedelj V, Tomašić T, Peterlin Mašič L, Zega A (2011) ATP-binding site of bacterial enzymes as a target for antibacterial drug design. J Med Chem 54:915–929
Konc J, Janežič D (2010) ProBiS: a web server for detection of structurally similar protein binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W436–W440
Konc J, Janežič D (2010) ProBiS algorithm for detection of structurally similar protein binding sites by local structural alignment. Bioinformatics 26:1160–1168
Kitchen DB, Decornez H, Furr JR, Bajorath J (2004) Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: methods and applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:935–949
Turk S, Kovač A, Boniface A, Bostock JM, Chopra I, Blanot D, Gobec S (2009) Discovery of new inhibitors of the bacterial peptidoglycan biosynthesis enzymes MurD and MurF by structure-based virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem 17:1884–1889
Perdih A, Kovač A, Wolber G, Blanot D, Gobec S, Šolmajer T (2009) Discovery of novel benzene 1,3-dicarboxylic acid inhibitors of bacterial MurD and MurE ligases by structure-based virtual screening approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:2668–2673
The UniProt Consortium (2011) Ongoing and future developments at the Universal Protein Resource. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D214–D219
Accelrys Discovery Studio is available from Accelrys Inc, San Diego, California 92121, USA
SYBYL Molecular modelling package 7.3. (2006) St. Louis, MO Tripos Inc
UNITY Chemical Information Software (2006) St. Louis, MO Tripos Inc
Gasteiger J, Rudolph C, Sadowski J (1990) Automatic generation of 3D-atomic coordinates for organic molecules. Tetrahedron Comput Method 3:537–547
Goodford PJ (1985) A computational procedure for determining energetically favorable binding sites on biologically important macromolecules. J Med Chem 28:849–857
Pymol is available from Delano Scientific LLC, San Francisco, CA. http://pymol.sourceforge.net
Rarey M, Kramer B, Lengauer T, Klebe G (1996) A fast flexible docking method using an incremental construction algorithm. J Mol Biol 261:470–489
Rarey M, Wefing S, Lengauer T (1996) Placement of medium-sized molecular fragments into active sites of proteins. J Comput Aided Mol Des 10:41–54
Gold v4.1 is available from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, 12 Union Road, Cambridge, CB2 1EZ, UK. www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk
Liger D, Masson A, Blanot D, van Heijenoort J, Parquet C (1995) Over-production, purification and properties of the uridine-diphosphate-N-acetylmuramate:L-alanine ligase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 230:80–87
Auger G, Martin L, Bertrand J, Ferrari P, Fanchon E, Vaganay S, Petillot Y, van Heijenoort J, Blanot D, Dideberg O (1998) Large-scale preparation, purification, and crystallization of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine:D-glutamate ligase from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 13:23–29
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia OA (1979) Improved Assay for Nanomole Amounts of Inorganic-Phosphate. Anal Biochem 100:95–97
Tomašić T, Zidar N, Rupnik V, Kovač A, Blanot D, Gobec S, Kikelj D, Peterlin Mašič L (2009) Synthesis and biological evaluation of new glutamic acid-based inhibitors of MurD ligase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:153–157
Zidar N, Tomašić T, Šink R, Rupnik V, Kovač A, Turk S, Patin D, Blanot D, Contreras Martel C, Dessen A, Müller Premru M, Zega A, Gobec S, Peterlin Mašič L, Kikelj D (2010) Discovery of novel 5-benzylidenerhodanine and 5-benzylidenethiazolidine-2,4-dione inhibitors of MurD ligase. J Med Chem 53:6584–6594
Mol CD, Brooun A, Dougan DR, Hilgers MT, Tari LW, Wijnands RA, Knuth MW, McRee DE, Swanson RV (2003) Crystal structures of active fully assembled substrate- and product-bound complexes of UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid:L-alanine ligase (MurC) from Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol 185:4152–4162
Deva T, Baker EN, Squire CJ, Smith CA (2006) Structure of Escherichia coli UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl:L-alanine ligase (MurC). Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 62:1466–1474
Gordon E, Flouret B, Chantalat L, van Heijenoort J, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Dideberg O (2001) Crystal structure of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate:meso-diaminopimelate ligase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 276:10999–11006
Yan Y, Munshi S, Leiting B, Anderson MS, Chrzas J, Chen Z (2000) Crystal structure of Escherichia coli UDPMurNAc-tripeptide D-alanyl-D-alanine-adding enzyme (MurF) at 2.3 A resolution. J Mol Biol 304:435–445
Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK (2005) ZINC–a free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model 45:177–182
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 46:3–26
Jones G, Willett P, Glen RC, Leach AR, Taylor R (1997) Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J Mol Biol 267:727–748
Gohlke H, Hendlich M, Klebe G (2000) Knowledge-based scoring function to predict protein-ligand interactions. J Mol Biol 295:337–356
Sosič I, Štefane B, Kovač A, Turk S, Blanot D, Gobec S (2010) The synthesis of novel 2,4,6-trisubstituted 1,3,5-triazines: a search for potential MurF enzyme inhibitors. Heterocycles 81:91–115
Ward WHJ, Holdgate GA (2001) 7 Isothermal Titration Calorimetry in Drug Discovery. In: King FD, Oxford AW (eds) Progress in Medicinal Chemistry, vol 38. Elsevier, pp 309–376
O'Shea R, Moser HE (2008) Physicochemical properties of antibacterial compounds: implications for drug discovery. J Med Chem 51:2871–2878
Payne DJ, Gwynn MN, Holmes DJ, Pompliano DL (2007) Drugs for bad bugs: confronting the challenges of antibacterial discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:29–40
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sixth Framework Programme (FP6) Integrated Project Inhibition of New TArgets for Fighting Antibiotic Resistance (EUR-INTAFAR) (Project No. LSHM-CT-2004-512138), by the Slovenian Research Agency (Grant No. P1-0208) and by the World Federation of Scientists. The authors thank Professor Roger Pain for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomašić, T., Kovač, A., Klebe, G. et al. Virtual screening for potential inhibitors of bacterial MurC and MurD ligases. J Mol Model 18, 1063–1072 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1139-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1139-8