Abstract
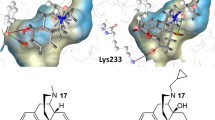
To probe the selective mechanism of agonists binding to three opioid receptor subtypes, ligand-based and receptor-based methods were implemented together and subtype characteristics of opioid agonists were clearly described. Three pharmacophore models of opioid agonists were generated by the Catalyst/HypoGen program. The best pharmacophore models for μ, δ and κ agonists contained four, five and five features, respectively. Meanwhile, the three-dimensional structures of three receptor subtypes were modeled on the basis of the crystal structure of β2-adrenergic receptor, and molecular docking was conducted further. According to these pharmacophore models and docking results, the similarities and differences among agonists of three subtypes were identified. μ or δ agonists, for example, could form one hydrogen bond separately with Tyr129 and Tyr150 at TMIII, whereas κ ones formed a π-π interaction in that place. These findings may be crucial for the development of novel selective analgesic drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang AZ, Pasternak GW (1981) Ontogeny of opioid pharmacology and receptors: high and low affinity site differences. Eur J Pharmacol 73:29–40
Pasternak GW (2001) Insights into mu opioid pharmacology the role of mu opioid receptor subtypes. Life Sci 68:2213–2219
Martin TJ, Eisenach JC (2001) Pharmacology of opioid and nonopioid analgesics in chronic pain states. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:811–817
Trescot AM, Datta S, Lee M, Hansen H (2008) Opioid pharmacology. Pain Physician 11:S133–S153
Zhu Y, King MA, Schuller AG et al (1999) Retention of supraspinal delta-like analgesia and loss of morphine tolerance in delta opioid receptor knockout mice. Neuron 24:243–252
Cahill CM, Morinville A, Hoffert C, O'Donnell D, Beaudet A (2003) Up-regulation and trafficking of delta opioid receptor in a model of chronic inflammation: implications for pain control. Pain 101:199–208
Bao L, Jin SX, Zhang C et al (2003) Activation of delta opioid receptors induces receptor insertion and neuropeptide secretion. Neuron 37:121–133
DeHaven-Hudkins DL, Dolle RE (2004) Peripherally restricted opioid agonists as novel analgesic agents. Curr Pharm Des 10:743–757
Holzgrabe U, Brandt W (2003) Mechanism of action of the diazabicyclononanone-type kappa-agonists. J Med Chem 46:1383–1389
Soukara S, Maier CA, Predoiu U, Ehret A, Jackisch R, Wunsch B (2001) Methylated analogues of methyl (R)-4-(3, 4-dichlorophenylacetyl)- 3-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (GR-89, 696) as highly potent kappa-receptor agonists: stereoselective synthesis, opioid-receptor affinity, receptor selectivity, and functional studies. J Med Chem 44:2814–2826
Johnson H (1978) Quantitative stereo-structure-activity relationships I. Opiate receptor binding. NIDA Res Monogr 146–158
Ray SK, Basak SC, Raychaudhury C, Roy AB, Ghosh JJ (1982) A quantitative structure-activity relationship study of N-alkylnorketobemidones and triazinones using structural information content. Arzneimittelforschung 32:322–325
Podlogar BL, Poda GI, Demeter DA et al. (2000) Synthesis and evaluation of 4-(N, N-diarylamino)piperidines with high selectivity to the delta-opioid receptor: a combined 3D-QSAR and ligand docking study. Drug Des Discov 17:34–50
Huang XQ, Jiang HL, Luo XM et al (2000) Molecular modeling on solvent effect and interaction mechanism of fentanyl analogs to mu-opioid receptor. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21:46–54
Peng Y, Keenan SM, Zhang Q, Welsh WJ (2005) 3D-QSAR comparative molecular field analysis on delta opioid receptor agonist SNC80 and its analogs. J Mol Graph Model 24:25–33
Wang XH, Tang Y, Xie Q, Qiu ZB (2006) QSAR study of 4-phenylpiperidine derivatives as mu opioid agonists by neural network method. Eur J Med Chem 41:226–232
Li W, Tang Y, Xie Q, Sheng W, Qiu ZB (2006) 3D-QSAR studies of orvinol analogs as kappa-opioid agonists. J Mol Model 12:877–884
Greiner E, Spetea M, Krassnig R et al. (2003) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 14-alkoxymorphinans. 18. N-substituted 14-phenylpropyloxymorphinan-6-ones with unanticipated agonist properties: extending the scope of common structure-activity relationships. J Med Chem 46:1758–1763
Carson JR, Coats SJ, Codd EE et al. (2004) N, N-dialkyl-4-[(8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]-oct-3-ylidene)phenylmethyl]benzamides, potent, selective delta opioid agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14:2109–2112
Kumar V, Marella MA, Cortes-Burgos L et al. (2000) Arylacetamides as peripherally restricted kappa opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:2567–2570
Breslin HJ, Cai C, Miskowski TA et al. (2006) Identification of potent phenyl imidazoles as opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:2505–2508
Chu GH, Gu M, Cassel JA et al. (2006) Novel phenylamino acetamide derivatives as potent and selective kappa opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:645–648
Macdougall JM, Zhang XD, Polgar WE, Khroyan TV, Toll L, Cashman JR (2004) Synthesis and biological evaluation of some 6-arylamidomorphines as analogues of morphine-6-glucuronide. Bioorg Med Chem 12:5983–5990
Breslin HJ, Miskowski TA, Rafferty BM et al. (2004) Rationale, design, and synthesis of novel phenyl imidazoles as opioid receptor agonists for gastrointestinal disorders. J Med Chem 47:5009–5020
Anzini M, Canullo L, Braile C et al. (2003) Synthesis, biological evaluation, and receptor docking simulations of 2-[(acylamino)ethyl]-1, 4-benzodiazepines as kappa-opioid receptor agonists endowed with antinociceptive and antiamnesic activity. J Med Chem 46:3853–3864
Jordan AD, Orsini MJ, Middleton SA et al. (2005) 8-(Heteroaryl)phenalkyl-1-phenyl-1, 3, 8-triazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-ones as opioid receptor modulators. Med Chem 1:601–610
Coats SJ, Schulz MJ, Carson JR et al. (2004) Parallel methods for the preparation and SAR exploration of N-ethyl-4-[(8-alkyl-8-aza-bicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-ylidene)-aryl-methyl]-benzam ides, powerful mu and delta opioid agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14:5493–5498
Kumar V, Guo D, Cassel JA et al. (2005) Synthesis and evaluation of novel peripherally restricted kappa-opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:1091–1095
Dardonville C, Fernandez-Fernandez C, Gibbons SL et al. (2006) Synthesis and pharmacological studies of new hybrid derivatives of fentanyl active at the mu-opioid receptor and I2-imidazoline binding sites. Bioorg Med Chem 14:6570–6580
Azzolina O, Collina S, Linati L et al. (2001) Enantiomers of 2-[(Acylamino)ethyl]-1, 4-benzodiazepines, potent ligands of kappa-opioid receptor: chiral chromatographic resolution, configurational assignment and biological activity. Chirality 13:606–612
Hiebel AC, Lee YS, Bilsky E et al. (2007) Probes for narcotic receptor mediated phenomena. 34. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of a potent mu-agonist delta-antagonist and an exceedingly potent antinociceptive in the enantiomeric C9-substituted 5-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-phenylethylmorphan series. J Med Chem 50:3765–3776
Trabanco AA, Aerts N, Alvarez RM et al. (2007) 4-Phenyl-4-[1H-imidazol-2-yl]-piperidine derivatives as non-peptidic selective delta-opioid agonists with potential anxiolytic/antidepressant properties. Part 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:3860–3863
Lattanzi R, Spetea M, Schullner F et al. (2005) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 14-alkoxymorphinans. 22. (1) Influence of the 14-alkoxy group and the substitution in position 5 in 14-alkoxymorphinan-6-ones on in vitro and in vivo activities. J Med Chem 48:3372–3378
Schutz J, Spetea M, Koch M et al. (2003) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 14-alkoxymorphinans. 20. 14-phenylpropoxymetopon: an extremely powerful analgesic. J Med Chem 46:4182–4187
Chu GH, Gu M, Cassel JA et al. (2005) Potent and highly selective kappa opioid receptor agonists incorporating chroman- and 2, 3-dihydrobenzofuran-based constraints. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:5114–5119
Dardonville C, Jagerovic N, Callado LF, Meana JJ (2004) Fentanyl derivatives bearing aliphatic alkaneguanidinium moieties: a new series of hybrid molecules with significant binding affinity for mu-opioid receptors and I2-imidazoline binding sites. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14:491–493
Coop A, Rothman RB, Dersch C et al. (1999) delta Opioid affinity and selectivity of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyindolomorphinan analogues related to naltrindole. J Med Chem 42:1673–1679
Beguin C, Richards MR, Wang Y et al. (2005) Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological evaluation of salvinorin A analogues modified at C(2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:2761–2765
Page D, Nguyen N, Bernard S et al. (2003) New scaffolds in the development of mu opioid-receptor ligands. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:1585–1589
Kim IJ, Ullrich T, Janetka JW et al. (2003) Diaryldimethylpiperazine ligands with mu- and delta-opioid receptor affinity: Synthesis of (+)-4-[(alphaR)-alpha-(4-allyl-(2S, 5S)-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)-(3-hydroxyp henyl)methyl]-N-ethyl-N-phenylbenzamide and (-)-4-[(alphaR)-alpha-(2S, 5S)-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)-(3-hydroxyphenyl)met hyl]-N-ethyl-N-phenylbenzamide. Bioorg Med Chem 11:4761–4768
Chu GH, Gu M, Cassel JA et al. (2007) Novel malonamide derivatives as potent kappa opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:1951–1955
Loriga G, Manca I, Murineddu G et al. (2006) Synthesis of 3, 6-diazabicyclo[3.1.1]heptanes as novel ligands for the opioid receptors. Bioorg Med Chem 14:676–691
Trabanco AA, Pullan S, Alonso JM et al. (2006) 4-Phenyl-4-[1H-imidazol-2-yl]-piperidine derivatives, a novel class of selective delta-opioid agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:146–149
Pinna GA, Cignarella G, Loriga G et al. (2002) N-3(9)-arylpropenyl-N-9(3)-propionyl-3, 9-diazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as mu-opioid receptor agonists. Effects on mu-affinity of arylalkenyl chain modifications. Bioorg Med Chem 10:1929–1937
Grundt P, Williams IA, Lewis JW, Husbands SM (2004) Identification of a new scaffold for opioid receptor antagonism based on the 2-amino-1, 1-dimethyl-7-hydroxytetralin pharmacophore. J Med Chem 47:5069–5075
Ho GD, Bercovici A, Tulshian D et al. (2007) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 4-hydroxy-4-phenylpiperidines as nociceptin receptor ligands: Part 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:3023–3027
Caldwell JP, Matasi JJ, Zhang H, Fawzi A, Tulshian DB (2007) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-substituted spiropiperidines as nociceptin receptor ligands. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:2281–2284
Wentland MP, Sun X, Ye Y, Lou R, Bidlack JM (2003) Redefining the structure-activity relationships of 2, 6-methano-3-benzazocines. Part 2: 8-formamidocyclazocine analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:1911–1914
Wentland MP, Ye Y, Cioffi CL et al. (2003) Syntheses and opioid receptor binding affinities of 8-amino-2, 6-methano-3-benzazocines. J Med Chem 46:838–849
Ho GD, Bercovici A, Tulshian D et al. (2007) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 4-hydroxy-4-phenylpiperidines as nociceptin receptor ligands: Part 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:3028–3033
Palczewski K, Kumasaka T, Hori T et al. (2000) Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289:739–745
Bourne HR, Meng EC (2000) Structure. Rhodopsin sees the light. Science 289:733–734
Luecke H, Schobert B, Lanyi JK, Spudich EN, Spudich JL (2001) Crystal structure of sensory rhodopsin II at 2.4 angstroms: insights into color tuning and transducer interaction. Science 293:1499–1503
Iadanza M, Holtje M, Ronsisvalle G, Holtje HD (2002) Kappa-opioid receptor model in a phospholipid bilayer: molecular dynamics simulation. J Med Chem 45:4838–4846
Fowler CB, Pogozheva ID, LeVine H 3rd, Mosberg HI (2004) Refinement of a homology model of the mu-opioid receptor using distance constraints from intrinsic and engineered zinc-binding sites. Biochemistry 43:8700–8710
Aburi M, Smith PE (2004) Modeling and simulation of the human delta opioid receptor. Protein Sci 13:1997–2008
Zhang Y, Sham YY, Rajamani R, Gao J, Portoghese PS (2005) Homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulations of the mu opioid receptor in a membrane-aqueous system. Chembiochem 6:853–859
Li W, Tang Y, Zheng YL, Qiu ZB (2006) Molecular modeling and 3D-QSAR studies of indolomorphinan derivatives as kappa opioid antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 14:601–610
Cherezov V, Rosenbaum DM, Hanson MA et al (2007) High-resolution crystal structure of an engineered human beta2-adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor. Science 318:1258–1265
Rosenbaum DM, Cherezov V, Hanson MA et al (2007) GPCR engineering yields high-resolution structural insights into beta2-adrenergic receptor function. Science 318:1266–1273
Greene J, Kahn S, Savoj H, Sprague P, Teig S (1994) Chemical function queries for 3D database search. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 16:1297–1308
Brooks BR, Broccoleri RE, Olafson BD, States DJ, Swaminathan S, Karplus M (1983) CHARMM: a program for macromolecular energy. J Comput Chem 4:187–217
Rollinger JM, Haupt S, Stuppner H, Langer T (2004) Combining ethnopharmacology and virtual screening for lead structure discovery: COX-inhibitors as application example. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 44:480–488
CATALYST, 4.10. Accelrys Inc. http://www.accelrys.com: San Diego, CA
Roy PP, Roy K (2008) On some aspects of variable selection for partial least squares regression models. QSAR Comb Sci 27:302–313
Sali A, Blundell TL (1993) Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234:779–815
Sali A, Overington JP (1994) Derivation of rules for comparative protein modeling from a database of protein structure alignments. Protein Sci 3:1582–1596
Chang G, Still WC, Guida WC (1989) An internal coordinate Monte Carlo method for searching conformational space. J Am Chem Soc 111:4379–4386
Mohamadi F, Richards NGJ, Guida WC et al (1990) Macromodels-An integrated software system for modeling organic and bioorganic molecules using molecular mechanics. J Comput Chem 11:440–467
Glide, 5.0, 2008. Schrödinger, LLC
Prime, 2.0, 2008. Schrödinger, LLC
Zhang J, Yu K, Zhu W, Jiang H (2006) Neuraminidase pharmacophore model derived from diverse classes of inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:3009–3014
Codd EE, Shank RP, Schupsky JJ, Raffa RB (1995) Serotonin and norepinephrine uptake inhibiting activity of centrally acting analgesics: structural determinants and role in antinociception. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:1263–1270
DeHaven-Hudkins DL, Burgos LC, Cassel JA et al. (1999) Loperamide (ADL 2-1294), an opioid antihyperalgesic agent with peripheral selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:494–502
Filizola M, Villar HO, Loew GH (2001) Differentiation of delta, mu, and kappa opioid receptor agonists based on pharmacophore development and computed physicochemical properties. J Comput Aided Mol Des 15:297–307
Singh N, Cheve G, Ferguson DM, McCurdy CR (2006) A combined ligand-based and target-based drug design approach for G-protein coupled receptors: application to salvinorin A, a selective kappa opioid receptor agonist. J Comput Aided Mol Des 20:471–493
Surratt CK, Johnson PS, Moriwaki A et al. (1994) mu opiate receptor. Charged transmembrane domain amino acids are critical for agonist recognition and intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem 269:20548–20553
Fukuda K, Kato S, Mori K (1995) Location of regions of the opioid receptor involved in selective agonist binding. J Biol Chem 270:6702–6709
Sagara T, Egashira H, Okamura M, Fujii I, Shimohigashi Y, Kanematsu K (1996) Ligand recognition in mu opioid receptor: experimentally based modeling of mu opioid receptor binding sites and their testing by ligand docking. Bioorg Med Chem 4:2151–2166
Pogozheva ID, Lomize AL, Mosberg HI (1998) Opioid receptor three-dimensional structures from distance geometry calculations with hydrogen bonding constraints. Biophys J 75:612–634
Subramanian G, Paterlini MG, Larson DL, Portoghese PS, Ferguson DM (1998) Conformational analysis and automated receptor docking of selective arylacetamide-based kappa-opioid agonists. J Med Chem 41:4777–4789
Lavecchia A, Greco G, Novellino E, Vittorio F, Ronsisvalle G (2000) Modeling of kappa-opioid receptor/agonists interactions using pharmacophore-based and docking simulations. J Med Chem 43:2124–2134
Thirstrup K, Hjorth SA, Schwartz TW (1996) In Investigation of the Binding Pocket in the Kappa Opioid Receptor by a Combination of Alanine Substitutions and Steric Hindrance Mutagenesis. 27th Meeting of the International Narcotics Research Conference, Poster M30
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 30600785 and 30973642), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant 0914035) and Key 863 High-Tech Program (Grant 2006AA020404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 806 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, J., Liu, G., Zhang, J. et al. Insights into subtype selectivity of opioid agonists by ligand-based and structure-based methods. J Mol Model 17, 477–493 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0745-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0745-1