Abstract
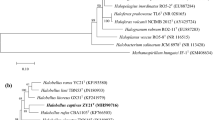
Two extreme halophilic archaeal strains, SYSUA9-0T and SYSUA9-1, were isolated from Ebi lake of Xinjiang, China. The colonies were Gram-negative, coccoid, and non-motile. Strains were aerobic and grew at 25–50 °C (optimum at 37 °C), in the presence of 10–35% (w/v) NaCl (optimum at 20–22%), and pH 6.0–8.0 (optimum at 7.0). The 16S rRNA gene sequence result revealed that the two strains were closely related to Haloprofundus marisrubri SB9T (92.7% similarity). The DNA–DNA hybridization value (97% ± 1%) suggested that SYSUA9-0T and SYSUA9-1 were similar; however, their sequence similarities with other archaeal members suggested that they were novel candidates. The genomic G + C content of SYSUA9-0T was 66.9%. The average nucleotide identity value between SYSU A9-0T and Haloprofundus marisrubri SB9T was 69.1%, which was far below the cutoff value (95–96%) proposed to define the species boundary. The polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylglycerolphosphate methylester (PGP-Me), sulfated mannosyl glucosyl diether, mannosyl glucosyldiether, and four unidentified glycolipids. Phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and comparative genome analysis suggested that SYSU A9-0T and SYSU A9-1 represent a novel species of a new genus within the family Haloferacaceae, for which the name Halegenticoccus soli gen. nov., sp. nov., is proposed. The type strain is SYAUA9-0T (= KCTC4241T = CGMCC 1.15765T).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbes M, Baati H, Guermazi S, Messina C, Santulli A, Gharsallah N, Ammar E (2013) Biological properties of carotenoids extracted from Halobacterium halobium isolated from a tunisian solar saltern. BMC Complement Altern Med 13:1–8
Amoozegar MA, Makhdoumi-Kakhki A, Mehrshad M, Fazeli SA, Sproer C, Ventosa A (2014) Halorientalis persicus sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a salt lake and emended description of the genus Halorientalis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:940–944
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Barrow GI, Feltham RKA (1993) Cowan and steel’s manual for the identification of medical bacteria, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Brock TD (1997) The value of basic research: discovery of Thermus aquaticus and other extreme thermophiles. Genetics 146:1207–1210
Christensen H, Angen O, Mutters R, Olsen JE, Bisgaard M (2000) DNA-DNA hybridization determined in micro-wells using covalent attachment of DNA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1095–1102
Cui HL, Gao X, Sun FF, Dong Y, Xu XW, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Oren A, Zhou PJ (2010a) Halogranum rubrum gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1366–1371
Cui HL, Li XY, Gao X, Xu XW, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Oren A, Zhou PJ (2010b) Halopelagius inordinatus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2089–2093
Cui HL, Sun FF, Gao X, Dong Y, Xu XW, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Oren A, Zhou PJ (2010c) Haladaptatus litoreus sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a marine solar saltern, and emended description of the genus Haladaptatus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1085–1089
Cui H-L, Gao X, Yang X, Xu X-W (2010d) Halorussus rarus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Extremophiles 14:493–499
Dussault HP (1955) An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 70:484–485
Elshahed MS, Najar FZ, Roe BA, Oren A, Dewers TA, Krumholz LR (2004) Survey of archaeal diversity reveals an abundance of halophilic Archaea in a low-salt, sulfide- and sulfur rich spring. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2230–2239
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid–deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–789
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW (2012) The archaea and the deeply branching and phototrophic bacteria. Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, Volume 1. Springer-Verlag, New York
Genderjahn S, Alawi M, Mangelsdorf K, Horn F, Wagner D (2018) Desiccation- and saline-tolerant bacteria and archaea in kalahari pan sediments. Front Microbiol 9:2082
Gupta RS, Naushad S, Baker S (2015) Phylogenomic analyses and molecular signatures for the class Halobacteria and its two major clades: a proposal for division of the class Halobacteria into an emended order Halobacteriales and two new orders, Haloferacales ord. nov. and Natrialbales ord. nov., containing the novel families Haloferacaceae fam. nov.and Natrialbaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1050–1069
Gutierrez MC, Castillo AM, Kamekura M, Ventosa A (2008) Haloterrigena salina sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a saltlake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2880–2884
Jehlicka J, Edwards HG, Oren A (2013) Bacterioruberin and salinixanthin carotenoids of extremely halophilic archaea and bacteria: a raman spectroscopic study. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 106:99–103
Kates M (2010) Techniques of lipidology: isolation, analysis, and identification of lipids, 3rd edn. Newport Somerville, Limited
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108
Lee I, Ouk Kim Y, Park SC, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100–1103
Liu BB, Tang SK, Zhang YG, Lu XH, Li L, Cheng J, Zhang YM, Zhang LL, Li WJ (2013) Halalkalicoccus paucihalophilus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from lop nur region in Xinjiang, northwest of China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:1007–1014
Liu BB, Zhao WY, Chu X, Hozzein WN, Prabhu DM, Wadaan MAM, Tang SK, Zhang LL, Li WJ (2014) Haladaptatus pallidirubidus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from saline soil samples in Yunnan and Xinjiang, China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 106:901–910
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964
Minegishi H, Kamekura M, Itoh T, Echigo A, Usami R, Hashimoto T (2010) Further refinement of the phylogeny of the Halobacteriaceae based on the full-length RNA polymerase subunit B’ (rpoB’) gene. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2398–2408
Minegishi H, Yamauchi Y, Echigo A, Shimane Y, Kamekura M, Itoh T, Ohkuma M, Usami R (2013) Halarchaeum nitratireducens sp. nov., a moderately acidophilic haloarchaeon isolated from commercial sea salt. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4202–4206
Ng WL, Yang CF, Halladay JT, Arora A, DasSarma S (1995) Protocol 25: Isolation of genomic and plasmid DNAs from Halobacteriumhalobium. In: DasSarma S, Fleischmann EM (eds) Archaea: a laboratory manual: halophiles. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, pp 179–180
Oren A (2000) The order halobacteriales. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes: a handbook on the biology of bacteria, Vol. 3, 3rd edn. Springer, New York, pp 113–164
Oren A, Ventosa A (2011) International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Halobacteriaceae and Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Halomonadaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2792–2795
Oren A, Ventosa A, Grant WD (1997) Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:233–238
Rampelotto PH (2013) Extremophiles and extreme environments. Life (Basel) 3:482–485
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2016) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32:929–931
Roh SW, Lee ML, Bae JW (2010) Haladaptatus cibarius sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from seafood, and emended description of the genus Haladaptatus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1187–1190
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Savage KN, Krumholz LR, Oren A, Elshahed MS (2007) Haladaptatus paucihalophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a low-salt, sulfide-rich spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:19–24
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelhood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Wang ZX, Xu Y, Zhou PJ (2000) Taxonomy of a new species of haloalkalophilic archaeon. Acta Microbiol Sin 40:115–120
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Truper HG (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Xian WD, Narsing Rao MP, Zhou EM, Liu L, Xiao M, Li WJ (2018) Diversity of thermophiles in terrestrial hot springs of Yunnan and Tibet, China. In: Egamberdieva D, Birkeland NK, Panosyan H, Li WJ (ed) Extremophiles in eurasian ecosystems: ecology, diversity, and applications. Microorganisms for sustainability, vol 8, Springer, Singapore, pp 57–79
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Zhang G, Gu J, Zhang R, Rashid M, Haroon MF, Xun W, Ruan Z, Dong X, Stingl U (2017) Haloprofundus marisrubri gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a brine–seawater interface. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:9–16
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Prof. Dr. Yu-Guang Zhou (CGMCC, China) for providing the reference type strains. This research was supported by National Science and Technology Foundation Project (No. 2017FY100300), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 91751206, 31800001), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2015M580748), China Postdoctoral Special Foundation funded project (2016T90811), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2017A030310206) and China Biodiversity Observation Networks (Sino BON). This work was also funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, through the Research Groups Program Grant no. (RGP-1438-0004).
The 16S rRNA gene sequences of strains SYSU A9-0T and SYSU A9-1 have been deposited in GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under the accession numbers KX752787and KX752786. The rpoB’ gene sequences of SYSU A9-0T and SYSU A9-1 has been deposited in GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under the accession numbers KX752788 and KX752789, respectively. The whole genome shotgun project of strain SYSU A9-0T has been deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession PEND00000000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by A. Oren.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, BB., Narsing Rao, M.P., Yin, XQ. et al. Description of Halegenticoccus soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a soil sample of Ebi lake. Extremophiles 23, 521–528 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-019-01104-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-019-01104-9