Abstract
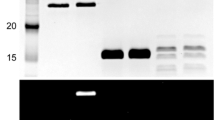
The paper reports the characterization of a protein disulfide oxidoreductase (PDO) from the thermophilic Gram negative bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27, identified as TTC0486 by genome analysis and named TtPDO. PDO members are involved in the oxidative folding, redox balance and detoxification of peroxides in thermophilic prokaryotes. Ttpdo was cloned and expressed in E. coli and the recombinant purified protein was assayed for the dithiol-reductase activity using insulin as substrate and compared with other PDOs characterized so far. In the thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus PDOs work as thiol-reductases constituting a peculiar redox couple with Thioredoxin reductase (SsTr). To get insight into the role of TtPDO, a hybrid redox couple with SsTr, homologous to putative Trs of T. thermophilus, was assayed. The results showed that SsTr was able to reduce TtPDO in a concentration dependent manner with a calculated K M of 34.72 μM, suggesting the existence of a new redox system also in thermophilic bacteria. In addition, structural characterization of TtPDO by light scattering and circular dichroism revealed the monomeric structure and the high thermostability of the protein. The analysis of the genomic environment suggested a possible clustering of Ttpdo with TTC0487 and TTC0488 (tlpA). Accordingly, transcriptional analysis showed that Ttpdo is transcribed as polycistronic messenger. Primer extension analysis allowed the determination of its 5′end and the identification of the promoter region.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard ME, Hamilton AJ, Dankowski T, Heras B, Schembri MS, Edwards JL, Jennings MP, McEwan AG (2009) A periplasmic thioredoxin-like protein plays a role in defense against oxidative stress in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun 77(11):4934–4939. doi:10.1128/IAI.00714-09
Beeby M, O’Connor BD, Ryttersgaard C, Boutz DR, Perry LJ, Yeates TO (2005) The genomics of disulfide bonding and protein stabilization in thermophiles. PLoS Biol 3(9):e309. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030309
Berndt C, Lillig CH, Holmgren A (2008) Thioredoxins and glutaredoxins as facilitators of protein folding. Bba Mol Cell Res 1783(4):641–650. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.02.003
Cabibbo A, Pagani M, Fabbri M, Rocchi M, Farmery MR, Bulleid NJ, Sitia R (2000) ERO1-L, a human protein that favors disulfide bond formation in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 275(7):4827–4833. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.7.4827
Cava F, Hidalgo A, Berenguer J (2009) Thermus thermophilus as biological model. Extremophiles 13(2):213–231. doi:10.1007/s00792-009-0226-6
Cho SH, Parsonage D, Thurston C, Dutton RJ, Poole LB, Collet JF, Beckwith J (2012) A new family of membrane electron transporters and its substrates, including a new cell envelope peroxiredoxin, reveal a broadened reductive capacity of the oxidative bacterial cell envelope. MBio 3(2). doi:10.1128/mBio.00291-11
D’Ambrosio K, Pedone E, Langella E, De Simone G, Rossi M, Pedone C, Bartolucci S (2006) A novel member of the protein disulfide oxidoreductase family from Aeropyrum pernix K1: structure, function and electrostatics. J Mol Biol 362(4):743–752. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.038
Del Giudice I, Limauro D, Pedone E, Bartolucci S, Fiorentino G (2013) A novel arsenate reductase from the bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27: its role in arsenic detoxification. Biochim Biophys Acta 1834(10):2071–2079. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.06.007
Gross E, Sevier CS, Vala A, Kaiser CA, Fass D (2002) A new FAD-binding fold and intersubunit disulfide shuttle in the thiol oxidase Erv2p. Nat Struct Biol 9(1):61–67. doi:10.1038/Nsb740
Gross E, Kastner DB, Kaiser CA, Fass D (2004) Structure of Ero1p, source of disulfide bonds for oxidative protein folding in the cell. Cell 117(5):601–610. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00418-0
Gross E, Sevier CS, Heldman N, Vitu E, Bentzur M, Kaiser CA, Thorpe C, Fass D (2006) Generating disulfides enzymatically: reaction products and electron acceptors of the endoplasmic reticulum thiol oxidase Ero1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(2):299–304. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506448103
Gruber CW, Cemazar M, Heras B, Martin JL, Craik DJ (2006) Protein disulfide isomerase: the structure of oxidative folding. Trends Biochem Sci 31(8):455–464. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.06.001
Guagliardi A, Depascale D, Cannio R, Nobile V, Bartolucci S, Rossi M (1995) The purification, cloning, and high-level expression of a glutaredoxin-like protein from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Biol Chem 270(11):5748–5755
Hatahet F, Boyd D, Beckwith J (2014) Disulfide bond formation in prokaryotes: history, diversity and design. Biochim Biophys Acta. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.02.014
Heinemann J, Hamerly T, Maaty WS, Movahed N, Steffens JD, Reeves BD, Hilmer JK, Therien J, Grieco PA, Peters JW, Bothner B (2014) Expanding the paradigm of thiol redox in the thermophilic root of life. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(1):80–85. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.08.009
Henne A, Bruggemann H, Raasch C, Wiezer A, Hartsch T, Liesegang H, Johann A, Lienard T, Gohl O, Martinez-Arias R, Jacobi C, Starkuviene V, Schlenczeck S, Dencker S, Huber R, Klenk HP, Kramer W, Merkl R, Gottschalk G, Fritz HJ (2004) The genome sequence of the extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus. Nat Biotechnol 22(5):547–553. doi:10.1038/nbt956
Holmgren A (1979) Thioredoxin catalyzes the reduction of insulin disulfides by dithiothreitol and dihydrolipoamide. J Biol Chem 254(19):9627–9632
Inaba K (2009) Disulfide bond formation system in Escherichia coli. J Biochem 146(5):591–597. doi:10.1093/Jb/Mvp102
Kashima Y, Ishikawa K (2003) A hyperthermostable novel protein-disulfide oxidoreductase is reduced by thioredoxin reductase from hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii. Arch Biochem Biophys 418(2):179–185. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2003.08.002
Ladenstein R, Ren B (2008) Reconsideration of an early dogma, saying “there is no evidence for disulfide bonds in proteins from archaea”. Extremophiles 12(1):29–38. doi:10.1007/s00792-007-0076-z
Limauro D, Falciatore A, Basso AL, Forlani G, De Felice M (1996) Proline biosynthesis in Streptococcus thermophilus: characterization of the proBA operon and its products. Microbiology 142(Pt 11):3275–3282
Limauro D, Pedone E, Galdi I, Bartolucci S (2008) Peroxiredoxins as cellular guardians in Sulfolobus solfataricus: characterization of Bcp1, Bcp3 and Bcp4. FEBS J 275(9):2067–2077. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06361.x
Limauro D, Saviano M, Galdi I, Rossi M, Bartolucci S, Pedone E (2009) Sulfolobus solfataricus protein disulphide oxidoreductase: insight into the roles of its redox sites. Protein Eng Des Sel 22(1):19–26. doi:10.1093/protein/gzn061
Limauro D, De Simone G, Pirone L, Bartolucci S, D’Ambrosio K, Pedone E (2013) Sulfolobus solfataricus thiol redox puzzle: characterization of an atypical protein disulfide oxidoreductase. Extremophiles. doi:10.1007/s00792-013-0607-8
Lu J, Holmgren A (2013) The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radic Biol Med. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036
Pagani M, Fabbri M, Benedetti C, Fassio A, Pilati S, Bulleid NJ, Cabibbo A, Sitia R (2000) Endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin 1-lbeta (ERO1-Lbeta), a human gene induced in the course of the unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem 275(31):23685–23692. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003061200
Pedone E, Saviano M, Rossi M, Bartolucci S (2001) A single point mutation (Glu85Arg) increases the stability of the thioredoxin from Escherichia coli. Protein Eng 14(4):255–260
Pedone E, Ren B, Ladenstein R, Rossi M, Bartolucci S (2004) Functional properties of the protein disulfide oxidoreductase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: a member of a novel protein family related to protein disulfide-isomerase. Eur J Biochem 271(16):3437–3448. doi:10.1111/j.0014-2956.2004.04282.x
Pedone E, D’Ambrosio K, De Simone G, Rossi M, Pedone C, Bartolucci S (2006a) Insights on a new PDI-like family: structural and functional analysis of a protein disulfide oxidoreductase from the bacterium Aquifex aeolicus. J Mol Biol 356(1):155–164. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.11.041
Pedone E, Limauro D, D’Alterio R, Rossi M, Bartolucci S (2006b) Characterization of a multifunctional protein disulfide oxidoreductase from Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS J 273(23):5407–5420. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05533.x
Pedone E, Limauro D, D’Ambrosio K, De Simone G, Bartolucci S (2010) Multiple catalytically active thioredoxin folds: a winning strategy for many functions. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(22):3797–3814. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0449-9
Ren B, Tibbelin G, de Pascale D, Rossi M, Bartolucci S, Ladenstein R (1998) A protein disulfide oxidoreductase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus contains two thioredoxin fold units (vol 5, pg 602, 1998). Nat Struct Biol 5(10):924. doi:10.1038/2766
Ruddon RW, Bedows E (1997) Assisted protein folding. J Biol Chem 272(6):3125–3128
Ruggiero A, Masullo M, Ruocco MR, Grimaldi P, Lanzotti MA, Arcari P, Zagari A, Vitagliano L (2009) Structure and stability of a thioredoxin reductase from Sulfolobus solfataricus: a thermostable protein with two functions. Bba-Proteins Proteom 1794(3):554–562. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.11.011
Ruocco MR, Ruggiero A, Masullo L, Arcari P, Masullo M (2004) A 35 kDa NAD(P)H oxidase previously isolated from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus is instead a thioredoxin reductase. Biochimie 86(12):883–892. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2004.10.008
Sanchez R, Roovers M, Glansdorff N (2000) Organization and expression of a Thermus thermophilus arginine cluster: presence of unidentified open reading frames and absence of a Shine-Dalgarno sequence. J Bacteriol 182(20):5911–5915. doi:10.1128/Jb.182.20.5911-5915.2000
Sato Y, Inaba K (2012) Disulfide bond formation network in the three biological kingdoms, bacteria, fungi and mammals. FEBS J 279(13):2262–2271. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08593.x
Sevier CS, Kaiser CA (2006) Disulfide transfer between two conserved cysteine pairs imparts selectivity to protein oxidation by Ero1. Mol Biol Cell 17(5):2256–2266. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-05-0417
Sevier CS, Cuozzo JW, Vala A, Aslund F, Kaiser CA (2001) A flavoprotein oxidase defines a new endoplasmic reticulum pathway for biosynthetic disulphide bond formation. Nat Cell Biol 3(10):874–882. doi:10.1038/ncb1001-874
Tanboon W, Chuchue T, Vattanaviboon P, Mongkolsuk S (2009) Inactivation of thioredoxin-like gene alters oxidative stress resistance and reduces cytochrome c oxidase activity in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. FEMS Microbiol Lett 295(1):110–116. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01591.x
Vala A, Sevier CS, Kaiser CA (2005) Structural determinants of substrate access to the disulfide oxidase Erv2p. J Mol Biol 354(4):952–966. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.09.076
Yang XQ, Ma KS (2010) Characterization of a thioredoxin–thioredoxin reductase system from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima. J Bacteriol 192(5):1370–1376. doi:10.1128/Jb.01035-09
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the grants from MIUR for project FIRB no. RBRN07BMCT and Università Federico II di Napoli and “Compagnia di San Paolo” (Naples Laboratory) for “Programma F.A.R.O, IV° tornata”. We acknowledge Dr. Carmen Sarcinelli for her helpful technical assistance and the grant from POR CAMPANIA FSE 2007/2013 for PROGETTO CARINA CUP B25B09000080007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Robb.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedone, E., Fiorentino, G., Pirone, L. et al. Functional and structural characterization of protein disulfide oxidoreductase from Thermus thermophilus HB27. Extremophiles 18, 723–731 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0652-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0652-y