Abstract
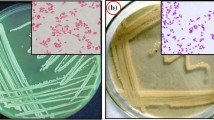
The presence of sulphur in fossil fuels and the natural environment justifies the study of sulphur-utilising bacterial species and genes involved in the biodesulphurisation process. Technology has been developed based on the natural ability of microorganisms to remove sulphur from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon chains. This biotechnology aims to minimise the emission of sulphur oxides into the atmosphere during combustion and prevent the formation of acid rain. In this study, the isolation and characterization of desulphurising microorganisms in rhizosphere and bulk soil samples from Antarctica that were either contaminated with oil or uncontaminated was described. The growth of selected isolates and their capacity to utilise sulphur based on the formation of the terminal product of desulphurisation via the 4S pathway, 2-hydroxybiphenyl, was analysed. DNA was extracted from the isolates and BOX-PCR and DNA sequencing were performed to obtain a genomic diversity profile of cultivable desulphurising bacterial species. Fifty isolates were obtained showing the ability of utilising dibenzothiophene as a substrate and sulphur source for maintenance and growth when plated on selective media. However, only seven genetically diverse isolates tested positive for sulphur removal using the Gibbs assay. DNA sequencing revealed that these isolates were related to the genera Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aislabie JM, Balks MR, Foght JM, Waterhouse EJ (2004) Hydrocarbon spills on Antarctic soil: effect and management. Env Sci Technol 38:1265–1274
Aiyar A (2000) The use of CLUSTAL W and CLUSTAL X for multiple sequence alignment. Methods Mol Biol 132:221–241
Bastiaens L, Springael D, Wattiau P, Harms H, de Wachter R, Verachtert H, Diels L (2000) Isolation of adherent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading bacteria using PAH-sorbing carriers. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1834–1843
Chang JH, Chang YK, Chang HN (1998) Desulfurization of diesel oils by a newly isolated dibenzothiophene-degrading Nocardia sp. strain CYKS2. Biotechnol Prog 14:851–855
Chang JH, Chang YK, Cho KS, Chang HN (2000) Desulfurization of model and diesel oils by resting cells of Gordona sp. Biotechnol Lett 22:193–196
Chen H, Zhang WJ, Chen JM, Cai YB, Li W (2008) Desulfurization of various organic sulfur compounds and the mixture of DBT + 4,6-DMDBT by Mycobacterium sp. ZD–19. Bioresour Technol 99:3630–3634
Denome SA, Olson ES, Young KD (1994) Identification and cloning of genes involved in specific desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2837–2843
Duarte GF, Rosado AS, Seldin L, Araújo W, Van Elsas JD (2001) Analysis of bacterial community structure in sulfurous-oil-containing soils and detection of species carrying dibenzothiophene desulfurization (dsz) genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1052–1062
Embley TM (1991) The linear PCR reaction: a simple and robust method for sequencing amplified rRNA genes. Lett Appl Microbiol 13:171–174
Gascuel O, Steel M (2006) Neighbor-joining revealed. Mol Biol Evol 23(11):1997–2000
Izumi Y, Ohshiro T, Ogino H, Hine Y, Shimao M (1994) Selective desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:223–226
Kayser KJ, Bielaga-Jones BA, Jackowsky K, Odusan O, Kilbane JJ (1993) Utilization of organosulphur compounds by axenic and mixed cultures of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IGTS8. J Gen Microbiol 139:3123–3129
Lynch JM (2002) Resilience of the rhizosphere to anthropogenic disturbance. Biodegradation 13:21–27
Mohebali G, Ball AS, Kaytash A, Rasekh B (2008) Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as the sulfur source for the production of desulfurizing resting cells of Gordonia alkanivorans RIPI90A. Microbiology 154:878–885
Nekodzuka S, Toshiaki N, Nakajima-Kambe T, Nobura N, Lu J, Nakahara Y (1997) Specific desulfurization of debenzothiophene by Mycobacterium strain G3. Biocatal Biotransform 15:21–27
Ohshiro T, Izumi Y (1999) Microbial desulfurization of organic sulfur compounds in petroleum. Biosci Biotechonol Biochem 63:1–9
Olson ES, Stanley DC, Gallagher JR (1993) Characterization of intermediates in the microbial desulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Energy Fuels 7:159–164
Omori T, Monna L, Saiki Y, Kodama T (1992) Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Corynebacterium sp. strain SY1. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:911–915
Orr WL (1978) Oil sand and oil shale chemistry. Chemie, New York
Pointing SB, Chan Y, Lacap DC, Lau MC, Jurgens JA, Farrell RL (2009) Highly specialized microbial diversity in hyper-arid polar desert. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19964–19969
Raheb J, Mohammad JH, Memari B (2010) Increasing of biodesulfurization activity of newly recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 by cloning the flavin reductase gene. Int J Biotechnol Biochem 6:219–229
Saul DJ, Aislabie J, Brown CE, Harris L, Foght JM (2005) Hydrocarbon contamination changes the bacterial diversity of soil from around Scott Base, Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:141–155
Silveira AB (2008) Isolamento e caracterização de linhagens de Bacillus e Paenibacillus promotores de crescimento vegetal em lavouras de arroz e trigo do Rio Grande do Sul. Doctoral thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, pp 113
Sourdis J, Nei M (1988) Relative efficiencies of the maximum parsimony and distance-matrix methods in obtaining the correct phylogenetic tree. Mol Biol Evol 5:298–311
Speight JG (1980) The chemistry and technology of petroleum. Dekker, New York
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA 4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tanaka Y, Matsui T, Konishi J, Maruhashi K, Kurane R (2002) Biodesulfurization of benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene by a newly isolated Rhodococcus strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:325–328
Versalovic J, Schneider M, De Bruijn FJ, Lupski JR (1994) Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria using repetitive sequence-based polymerase chain reaction. Method Mol Cell Biol 5:25–40
Wynn-Williams DD (1996) Antarctic microbial diversity: the basis of polar ecosystem processes. Biodivers Conserv 5:1271–1293
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Alexandre Rosado for providing samples from Antarctica and for relevant information regarding the material, Dr. Raquel Peixoto and Dr. Juliano Cury for the DNA sequencing, and Dr. Silvana Queiroz for the DNA purification. This study received financial and logistic support from the Brazilian Antarctic Program, PROANTAR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Matsunaga.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boniek, D., Figueiredo, D., Pylro, V.S. et al. Characterization of bacterial strains capable of desulphurisation in soil and sediment samples from Antarctica. Extremophiles 14, 475–481 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-010-0326-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-010-0326-3