Abstract
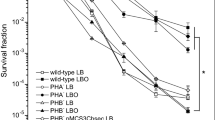
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are highly reduced bacterial storage compounds that increase fitness in changing environments. We have previously shown that phaRBAC genes from the Antarctic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. 14-3 are located in a genomic island containing other genes probably related with its adaptability to cold environments. In this paper, Pseudomonas sp. 14-3 and its PHA synthase-minus mutant (phaC) were used to asses the effect of PHA accumulation on the adaptability to cold conditions. The phaC mutant was unable to grow at 10°C and was more susceptible to freezing than its parent strain. PHA was necessary for the development of the oxidative stress response induced by cold treatment. Addition of reduced compounds cystine and gluthathione suppressed the cold sensitive phenotype of the phaC mutant. Cold shock produced very rapid degradation of PHA in the wild type strain. The NADH/NAD ratio and NADPH content, estimated by diamide sensitivity, decreased strongly in the mutant after cold shock while only minor changes were observed in the wild type. Accordingly, the level of lipid peroxidation in the mutant strain was 25-fold higher after temperature downshift. We propose that PHA metabolism modulates the availability of reducing equivalents, contributing to alleviate the oxidative stress produced by low temperature.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayub ND, Pettinari MJ, Ruiz JA, López NI (2004) A polyhydroxybutyrate-producing Pseudomonas sp. isolated from Antarctic environments with high stress resistance. Curr Microbiol 49:170–174
Ayub ND, Pettinari MJ, Méndez BS, López NI (2006) Impaired polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis from glucose in Pseudomonas sp. 14-3 is due to a defective β-ketothiolase gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett 264:125–131
Ayub ND, Pettinari MJ, Méndez BS, López NI (2007) The polyhydroxyalkanoate genes of a stress resistant Antarctic Pseudomonas are situated within a genomic island. Plasmid 58:240–248
Braunegg G, Sonnleitner B, Lafferty RM (1978) A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of poly-ß-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Eur J Appl Microbial Biotechnol 6:29–37
Butler MJ, Bruheim P, Jovetic S, Marinelli F, Postma PW, Bibb MJ (2002) Engineering of primary carbon metabolism for improved antibiotic production in Streptomyces lividans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4731–4739
D’Amico S, Collins T, Marx JC, Feller G, Gerday C (2006) Psychrophilic microorganisms: challenges for life. EMBO Rep 7:385–389
Franklin FCH, Bagdasarian M, Bagdasarian MM, Timmis KN (1981) Molecular and functional analysis of the TOL plasmid pWW0 from Pseudomonas putida and cloning of genes for the entire regulated aromatic ring meta-cleavage pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:7458–7462
Gocheva YG, Krumova ET, Slokoska LS, Miteva JG, Vassilev SV, Angelova MB (2006) Cell response of Antarctic and temperate strains of Penicillium spp. to different growth temperature. Mycol Res 110:1347–1354
Hirsch P, Gallikowski CA, Siebert J, Peissl K, Kroppenstedt R, Schumann P, Stackebrandt E, Anderson R (2004) Deinococcus frigens sp. nov., Deinococcus saxicola sp.nov., and Deinococcus marmoris sp.nov., low temperature and draught tolerating, UV-resistant bacteria from continental Antarctica. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:636–645
Huisman GW, Wonink E, Meima R, Kazemier B, Terpstra P, Witholt B (1991) Metabolism of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) (PHAs) by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Identification and sequences of genes and function of the encoded proteins in the synthesis and degradation of PHA. J Biol Chem 266:2191–2198
Huisman GW, Wonink E, de Koning G, Preusting H, Witholt B (1992) Synthesis of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) by mutant and recombinant Pseudomonas strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1–5
Kadouri D, Jurkevitch D, Okon Y (2003) Poly β-hydroxybutyrate depolymerase (PhaZ) in Azospirillum brasilense and characterization of a phaZ mutant. Arch Microbiol 180:309–318
Kadouri D, Jurkevitch E, Okon Y, Castro-Sowinski S (2005) Ecological and agricultural significance of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Crit Rev Microbiol 31:55–67
Kane DO, Gill V, Boyd P, Burdon R (1996) Chilling, oxidative stress and antioxidant responses in Arabidopsis thaliana callus. Planta 198:371–377
Kato C, Li L, Nogi Y, Nakamura Y, Tamaoka J, Horikoshi K (1998) Extremelly barophilic bacteria isolated from the Mariana Trench, Challenger Deep, at a depth of 11, 000 meters. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1510–1513
Koonin EV, Makarova KS, Aravind L (2001) Horizontal gene transfer in Prokaryotes: quantification and classification. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:709–742
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Lawrence JG (1999) Gene transfer, speciation, and the evolution of bacterial genomes. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:519–523
Lee SH, Lee SY, Park BC (2005) Cell surface display of lipase in Pseudomonas putida KT2442 using OprF as an anchoring motif and its biocatalytic applications. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8581–8586
Leonardo MR, Dailly Y, Clark DP (1996) Role of NAD in regulating the adhE gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 178:6013–6018
Liu S, Graham JE, Bigelow L, Morse PD, Wilkinson BJ (2002) Identification of Listeria monocytogenes genes expressed in response to growth at low temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1697–1705
López NI, Floccari ME, Garcia AF, Steinbüchel A, Mendez BS (1995) Effect of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate content on the starvation survival of bacteria in natural waters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 16:95–101
Madison LL, Huisman GW (1999) Metabolic engineering of poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates): from DNA to plastic. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:21–53
Margesin R, Neuner G, Storey KB (2007) Cold-loving microbes, plants, and animals—fundamental and applied aspects. Naturwissenschaften 94:77–99
Nelson KE, Weinel C, Paulsen IT, Dodson RJ, Hilbert H, Martins dos Santos VA, Fouts DE, Gill SR, Pop M, Holmes M, Brinkac L, Beanan M, DeBoy RT, Daugherty S, Kolonay J, Madupu R, Nelson W, White O, Peterson J, Khouri H, Hance I, Chris Lee P, Holtzapple E, Scanlan D, Tran K, Moazzez A, Utterback T, Rizzo M, Lee K, Kosack D, Moestl D, Wedler H, Lauber J, Stjepandic D, Hoheisel J, Straetz M, Heim S, Kiewitz C, Eisen JA, Timmis KN, Düsterhöft A, Tümmler B, Fraser CM (2002) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the metabolically versatile Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Microbiol 4:799–808
Ostle A, Holt JG (1982) Nile Blue A as a fluorescent stain for poly-hydroxybutyrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:238–241
Pham TH, Webb JS, Rehm BHA (2004) The role of polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rhamnolipid and alginate production as well as stress tolerance and biofilm formation. Microbiology 150:3405–3413
Reva ON, Weinel C, Weinel M, Böhm K, Stjepandic D, Hoheisel JD, Tümmler B (2006) Functional genomics of stress response in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J Bacteriol 188:4079–4092
Ruiz JA, López NI, Fernández RO, Méndez BS (2001) Polyhydroxyalkanoate degradation is associated with nucleotide accumulation and enhances stress resistance and survival of Pseudomonas oleovorans in natural waters microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:225–230
Ruiz JA, López NI, Méndez BS (2004) rpoS gene expression in carbon starved cultures of the polyhydroxyalkanoate accumulating species Pseudomonas oleovorans. Curr Microbiol 48:396–400
Salahudeen AK, Huang H, Patel P, Jenkins JK (2000) Mechanism and prevention of cold storage-induced human renal tubular cell injury. Transplantation 70:1424–1431
Semchyshyn H, Bagnyukova T, Storey K, Lushchak V (2005) Hydrogen peroxide increases the activities of soxRS regulon enzymes and the levels of oxidized proteins and lipids in Escherichia coli. Cell Biol Int 29:898–902
Smirnova GV, Zakirova ON, Oktyabrskii ON (2001) The role of antioxidant systems in the cold stress response of Escherichia coli. Microbiology 70:45–50
Yan YB, Wu Q, Zhang RQ (2000) Dynamic accumulation and degradation of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) in living cells of Azotobacter vinelandii UWD characterized by 13C NMR. FEMS Microbiol Lett 193:269–273
Zhang L, Onda K, Imai R, Fukuda R, Horiuchi H, Ohtaa A (2003) Growth temperature downshift induces antioxidant response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 307:308–314
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Beatriz Méndez and Dr. M. Julia Pettinari for their helpful comments and critical reading of the manuscript. We also are grateful to Dr. María del Carmen Ríos for her advice with the measurements of lipid peroxidation, and two anonymous reviewers who provided useful criticisms. This work was supported by grants from UBA and CONICET. N.I.L. is a career investigator from CONICET. N.D.A and P.M.T. have a graduate student fellowship from CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Huang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayub, N.D., Tribelli, P.M. & López, N.I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates are essential for maintenance of redox state in the Antarctic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. 14-3 during low temperature adaptation. Extremophiles 13, 59–66 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-008-0197-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-008-0197-z