Abstract
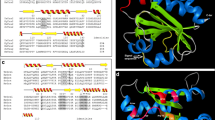
The thioredoxin system is a redox machinery widely distributed in nature and involved in several cellular functions. It is constituted of thioredoxin reductase (Trx-B), its protein substrate thioredoxin (Trx-A) and NADPH. We have previously characterised a Trx-B from the hyperthermophile Sulfolobus solfataricus (SsTrx-B3) (Ruocco et al. in Biochimie 86:883–892, 2004). As in the genome of this archaeon, the gene coding for another Trx-B (SsTrx-B2) and for two Trx-A (SsTrx-A1, SsTrx-A2) have been putatively identified, these proteins were obtained as recombinant forms and characterised. SsTrx-B2, different from SsTrx-B3, did not elicit a thioredoxin reductase activity. S. solfataricus possessed only one Trx-B (SsTrx-B3), which had two thioredoxins (SsTrx-A1 and SsTrx-A2) as substrates. These latter showed a homodimeric structure and catalysed insulin reduction using either DTT or NADPH/SsTrx-B3 as electron donors. In addition, the electron transfer between SsTrx-B3 and either SsTrx-A1 or SsTrx-A2 was fully reversible, thus allowing the determination of the redox potential of the thioredoxin system in S. solfataricus. Among the two thioredoxins, SsTrx-A2 appeared slightly more active and stable than SsTrx-A1. These data, besides shedding light on thioredoxin system in S. solfataricus, will contribute to add further information on this key enzyme system in Archaea.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Trx-A:
-
Thioredoxin
- Trx-B:
-
Thioredoxin reductase
- Ss :
-
Sulfolobus solfataricus
- DTNB:
-
5,5'-Dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)
References
Arcari P, Masullo L, Masullo M, Catanzano F, Bocchini V (2000) A NAD(P)H oxidase isolated from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus is not homologous with another NADH oxidase present in the same microorganism. Biochemical characterization of the enzyme and cloning of the encoding gene. J Biol Chem 275:895–900
Arner ES, Holmgren A (2000) Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem 267:6102–6109
Bao R, Chen Y, Tang YJ, Janin J, Zhou CZ (2007) Crystal structure of the yeast cytoplasmic thioredoxin Trx2. Proteins 66:246–249
Becker K, Gromer S, Schirmer RH, Muller S (2000) Thioredoxin reductase as a pathophysiological factor and drug target. Eur J Biochem 267:6118–6125
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
De Rosa M, Gambacorta A, Gliozzi A (1986) Structure, biosynthesis, and physicochemical properties of archaebacterial lipids. Microbiol Rev 50:70–80
Dello Russo A, Rullo R, Nitti G, Masullo M, Bocchini V (1997) Iron superoxide dismutase from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus: average hydrophobicity and amino acid weight are involved in the adaptation of proteins to extreme environments. Biochim Biophys Acta 1343:23–30
Fusi P, Tedeschi G, Aliverti A, Ronchi S, Tortora P, Guerritore A (1993) Ribonucleases from the extreme thermophilic archaebacterium S. solfataricus. Eur J Biocehm 211:305–310
Gromer S, Merkle H, Schirmer RH, Becker K (2002) Human placenta thioredoxin reductase: preparation and inhibitor studies. Methods Enzymol 347:382–394
Guagliardi A, Nobile V, Bartolucci S, Rossi M (1994) A thioredoxin from the extreme thermophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. Int J Biochem 26:375–380
Hirt RP, Muller S, Embley TM, Coombs GH (2002) The diversity and evolution of thioredoxin reductase: new perspectives. Trends Parasitol 18:302–308
Holmgren A (1979a) Reduction of disulfides by thioredoxin. J Biol Chem 254:9113–9119
Holmgren A (1979b) Thioredoxin catalyzes the reduction of insulin disulfides by dithiothreitol and dihydrolipoamide. J Biol Chem 254:9627–9632
Jeon SJ, Ishikawa K (2002) Identification and characterization of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase from Aeropyrum pernix K1. Eur J Biochem 269:5423–5430
Jin J, Chen X, Zhou Y, Bartlam M, Guo Q, Liu Y, Sun Y, Gao Y, Ye S, Li G, Rao Z, Qiang B, Yuan J (2002) Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of a human thioredoxin-like protein. Eur J Biochem 269:2060–2068
Kadokura H, Katzen F, Beckwith J (2003) Protein disulfide bond formation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem 72:111–135
Kadokura H (2006) Oxidative protein folding: many different ways to introduce disulfide bonds. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:731–733
Ladenstein R, Ren B (2006) Protein disulfides and protein disulfide oxidoreductases in hyperthermophiles. FEBS J 273:4170–4185
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lillig CH, Holmgren A (2007) Thioredoxin and related molecules—from biology to health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:25–47
Mallick P, Boutz DR, Eisenberg D, Yeates TO (2002) Genomic evidence that the intracellular proteins of archaeal microbes contain disulfide bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9679–9684
Masullo M, Raimo G, Parente A, Gambacorta A, De Rosa M, Bocchini V (1991) Properties of the elongation factor 1 alpha in the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. Eur J Biochem 199:529–537
Masullo M, Raimo G, Bocchini V (1993) Resistance of archaebacterial aEF-1 alphaGDP against denaturation by heat and urea. Biochim Biophys Acta 1162:35–39
Masullo M, Raimo G, Dello Russo A, Bocchini V, Bannister JV (1996) Purification and characterization of NADH oxidase from the archaea Sulfolobus acidocaldarius and Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 23:47–54
Pedone E, Limauro D, D’Alterio R, Rossi M, Bartolucci S (2006) Characterization of a multifunctional protein disulfide oxidoreductase from Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS J 273:5407–5420
Pekkari K, Holmgren A (2004) Truncated thioredoxin: physiological functions and mechanism. Antioxid Redox Signal 6:53–61
Raimo G, Masullo M, Parente A, Dello Russo A, Bocchini V (1992) Molecular, functional and structural properties of an archaeabacterial elongation factor 2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1132:127–132
Raimo G, Masullo M, Savino G, Scarano G, Ianniciello G, Parente A, Bocchini V (1996) Archaeal elongation factor 1 beta is a dimer Primary structure, molecular and biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 1293:106–112
Rehse PH, Kumei M, Tahirov TH (2005) Compact reduced thioredoxin structure from the thermophilic bacteria Thermus thermophilus. Proteins 61:1032–1037
Ruggiero A, Ruocco MR, Grimaldi P, Arcari P, Masullo M, Zagari A, Vitagliano L (2005) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of Sulfolobus solfataricus thioredoxin reductase. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 61:906–909
Ruocco MR, Ruggiero A, Masullo L, Arcari P, Masullo M (2004) A 35 kDa NAD(P)H oxidase previously isolated from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus is instead a thioredoxin reductase. Biochimie 86:883–892
Sevier CS, Kaiser CA (2006) Conservation and diversity of the cellular disulphide bond formation pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:797–811
She Q, Singh RK, Confalonieri F, Zivanovic Y, Allard G, Awayez MJ, Chan-Weiher CC, Clausen IG, Curtis BA, De Moors A, Erauso G, Fletcher C, Gordon PM, Heikamp-de Jong I, Jeffries AC, Kozera CJ, Medina N, Peng X, Thi-Ngoc HP, Redder P, Schenk ME, Theriault C, Tolstrup N, Charlebois RL, Doolittle WF, Duguet M, Gaasterland T, Garrett RA, Ragan MA, Sensen CW, Van der Oost J (2001) The complete genome of the crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus P2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7835–7840
Spassov VZ, Karshiokoff AD, Ladenstein R (1994) Optimization of the electrostatic interactions in proteins of different functional and folding type. Protein Sci 3:1556–1569
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Antranikian.
Pasquale Grimaldi and Maria Rosaria Ruocco contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grimaldi, P., Ruocco, M.R., Lanzotti, M.A. et al. Characterisation of the components of the thioredoxin system in the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus . Extremophiles 12, 553–562 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-008-0161-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-008-0161-y