Abstract
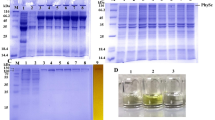
Archaeal A1AO ATP synthase/ATPase operons are highly conserved among species and comprise at least nine genes encoding structural proteins. However, all A1AO ATPase preparations reported to date contained only three to six subunits and, therefore, the study of this unique class of secondary energy converters is still in its infancy. To improve the quality of A1AO ATPase preparations, we chose the hyperthermophilic, methanogenic archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii as a model organism. Individual subunits of the A1AO ATPase from M. jannaschii were produced in E. coli, purified, and antibodies were raised. The antibodies enabled the development of a protocol ensuring purification of the entire nine-subunit A1AO ATPase. The ATPase was solubilized from membranes of M. jannaschii by Triton X-100 and purified to apparent homogeneity by sucrose density gradient centrifugation, ion exchange chromatography, and gel filtration. Electron micrographs revealed the A1 and AO domains and the central stalk, but also additional masses which could represent a second stalk. Inhibitor studies were used to demonstrate that the A1 and AO domains are functionally coupled. This is the first description of an A1AO ATPase preparation in which the two domains (A1 and AO) are fully conserved and functionally coupled.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams JP, Leslie AGW, Lutter R, Walker JE (1994) Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 370:621–628
Aris JP, Klionsky DJ, Simoni RD (1985) The FO subunits of the Escherichia coli F1FO-ATP synthase are sufficient to form a functional proton pore. J Biol Chem 260:11207–11215
Becher B, Müller V (1994) \( \Delta \tilde \mu _{{\rm{Na}}} \)drives the synthesis of ATP via an \( \Delta \tilde \mu _{{\rm{Na}}^{\rm{ + }} } \)translocating F1FO-ATP synthase in membrane vesicles of the archaeon Methanosarcina mazei Gö1. J Bacteriol 176:2543–2550
Boekema EJ, Ubbink-Kok T, Lolkema JS, Brisson A, Konings WN (1997) Visualization of a peripheral stalk in V-type ATPase: evidence for the stator structure essential for rotational catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14291–14293
Böttcher B, Gräber P (2000) The structure of the H+-ATP synthase from chloroplasts and its subcomplexes as revealed by electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1458:404–416
Chen W, Konisky J (1993) Characterization of a membrane-associated ATPase from Methanococcus voltae, a methanogenic member of the Archaea. J Bacteriol 175:5677–5682
Chien LF, Wu JJ, Tzeng CM, Pan RL (1993) ATPase of Rhodospirillum rubrum requires three functional copies of β-subunit as determined by radiation inactivation analysis. Biochem Mol Biol Int 31:13–18
Coskun Ü, Grüber G, Koch MH, Godovac-Zimmermann J, Lemker T, Müller V (2002) Crosstalk in the A1-ATPase from Methanosarcina mazei Gö1 due to nucleotide-binding. J Biol Chem 277:17327–17333
Deppenmeier U, Müller V, Gottschalk G (1996) Pathways of energy conservation in methanogenic archaea. Arch Microbiol 165:149–163
Dimroth P (1997) Primary sodium ion translocating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1318:11–51
Fillingame RH (2000) Getting to the bottom of the F1-ATPase. Nat Struct Biol 7:1002–1004
Fillingame RH, Jiang W, Dmitriev OY (2000) Coupling H+ transport to rotary catalysis in F-type ATP synthases: structure and organization of the transmembrane rotary motor. J Exp Biol 203:9–17
Forgac M (1999) Structure and properties of the vacuolar H+-ATPases. J Biol Chem 274:12951–12954
Forgac M (2000) Structure, mechanism and regulation of the clathrin-coated vesicle and yeast vacuolar H+-ATPases. J Exp Biol 203:71–80
Futai M, Omote H, Maeda M (1995) Escherichia coli H+-ATPase (ATP synthase): catalytic site and roles of subunit interactions in energy coupling. Biochem Soc Trans 23:785–789
Galagan JE, Nusbaum C, Roy A, Endrizzi MG, Macdonald P, FitzHugh W, Calvo S, Engels R, Smirnov S, Atnoor D, Brown A, Allen N, Naylor J, Stange-Thomann N, DeArellano K, Johnson R, Linton L, McEwan P, McKernan K, Talamas J, Tirrell A, Ye W, Zimmer A, Barber RD, Cann I, Graham DE, Grahame DA, Guss AM, Hedderich R, Ingram-Smith C, Kuettner HC, Krzycki JA, Leigh JA, Li W, Liu J, Mukhopadhyay B, Reeve JN, Smith K, Springer TA, Umayam LA, White O, White RH, Conway de Macario E, Ferry JG, Jarrell KF, Jing H, Macario AJ, Paulsen I, Pritchett M, Sowers KR, Swanson RV, Zinder SH, Lander E, Metcalf WW, Birren B (2002) The genome of Methanosarcina acetivorans reveals extensive metabolic and physiological diversity. Genome Res 12:532–542
Gallagher S, Winston SE, Fuller SA, Hurrell JGR (1993). Analysis of proteins In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Gogarten JP, Taiz L (1992) Evolution of proton pumping ATPases: rooting the tree of life. Photosynth Res 33:137–146
Grüber G, Svergun DI, Coskun Ü, Lemker T, Koch MH, Schägger H, Müller V (2001a) Structural insights into the A1 ATPase from the archaeon, Methanosarcina mazei Gö1. Biochemistry 40:1890–1896
Grüber G, Wieczorek H, Harvey WR, Müller V (2001b) Structure–function relationships of A-, F- and V-ATPases. J Exp Biol 204:2597–2605
Heinonen JE, Lahti RJ (1981) A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal Biochem 113:313–317
Hochstein LI, Kristjansson H, Altekar W (1987) The purification and subunit structure of a membrane-bound ATPase from the Archaebacterium Halobacterium saccharovorum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 147:295–300
Ihara K, Watanabe S, Sugimura K, Mukohata Y (1997) Identification of proteolipid from an extremely halophilic archaeon Halobacterium salinarum as an N′,N′-dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide binding subunit of ATP synthase. Arch Biochem Biophys 341:267–272
Inatomi KI (1986) Characterization and purification of the membrane-bound ATPase of the archaebacterium Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol 167:837–841
Inatomi KI, Kamagata Y, Nakamura K (1993) Membrane ATPase from the aceticlastic methanogen Methanothrix thermophila. J Bacteriol 175:80–84
Jones WJ, Leigh JA, Mayer F, Woese CR, Wolfe RS (1983) Methanococcus jannaschii sp. nov., an extremely thermophilic methanogen from a submarine hydrothermal vent. Arch Microbiol 136:254–261
Kane PM (1995) Disassembly and reassembly of the yeast vacuolar H+-ATPase in vivo. J Biol Chem 270:17025–17032
Laubinger W, Dimroth P (1988) Characterization of the ATP synthase of Propionigenium modestum as a primary sodium pump. Biochemistry 27:7531–7537
Lemker T, Ruppert C, Stöger H, Wimmers S, Müller V (2001) Overproduction of a functional A1 ATPase from the archaeon Methanosarcina mazei Gö1 in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 268:3744–3750
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lübben M, Schäfer G (1989) Chemiosmotic energy conservation of the thermoacidophile Sulfolobus acidocaldarius: oxidative phosphorylation and the presence of an FO-related N′,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding proteolipid. J Bacteriol 171:6106–6116
Lübben M, Lünsdorf H, Schäfer G (1987) A plasma membrane ATPase of the thermophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius: purification and immunological relationships to F1-ATPases. Eur J Biochem 167:211–219
Menz RI, Walker JE, Leslie AG (2001) Structure of bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase with nucleotide bound to all three catalytic sites: implications for the mechanism of rotary catalysis. Cell 106:331–341
Michel H, Oesterhelt D (1980) Electrochemical proton gradient across the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium: comparison of the light-induced increase with the increase of intracellular adenosine triphosphate under steady-state illumination. Biochemistry 19:4615–4619
Mountfort DO (1978) Evidence for ATP synthesis driven by a proton gradient in Methanosarcina barkeri. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 85:1346–1350
Mukohata Y, Ihara K (1990). Situation of archaebacterial ATPase among ion-translocating ATPase In: Kim CH, Ozawa T (eds) Bioenergetics. Plenum, New York, pp 205–216
Müller V, Ruppert C, Lemker T (1999) Structure and function of the A1AO ATPases from methanogenic archaea. J Bioenerg Biomembrane 31:15–28
Müller V, Aufurth S, Rahlfs S (2001) The Na+ cycle in Acetobacterium woodii: identification and characterization of a Na+ translocating F1FO-ATPase with a mixed oligomer of 8 and 16 kDa proteolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1505:108–120
Neumann S, Matthey U, Kaim G, Dimroth P (1998) Purification and properties of the F1FO ATPase of Ilyobacter tartaricus, a sodium ion pump. J Bacteriol 180:3312–3316
Reidlinger J, Müller V (1994) Purification of ATP synthase from Acetobacterium woodii and identification as a Na+-translocating F1FO-type enzyme. Eur J Biochem 223:275–283
Ruppert C, Wimmers S, Lemker T, Müller V (1998) The A1AO ATPase from Methanosarcina mazei: cloning of the 5′ end of the aha operon encoding the membrane domain and expression of the proteolipid in a membrane-bound form in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 180:3448–3452
Ruppert C, Kavermann H, Wimmers S, Schmid R, Kellermann J, Lottspeich F, Huber H, Stetter KO, Müller V (1999) The proteolipid of the A1AO ATP synthase from Methanococcus jannaschii has six predicted transmembrane helices but only two proton-translocating carboxyl groups. J Biol Chem 274:25281–25284
Ruppert C, Schmid R, Hedderich R, Müller V (2001) Selective extraction of subunit D of the Na+-translocating methyltransferase and subunit c of the A1AO ATPase from the cytoplasmic membrane of methanogenic archaea by chloroform/methanol and characterization of subunit c of Methanothermobacter thermoautotrophicus as a 16-kDa proteolipid. FEMS Microbiol Lett 195:47–51
Schäfer G, Meyering-Vos M (1992) F-Type or V-Type? The chimeric nature of the archaebacterial ATP synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1101:232–235
Schäfer G, Engelhard M, Müller V (1999) Bioenergetics of the Archaea. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:570–620
Scheel E, Schäfer G (1990) Chemiosmotic energy conservation and the membrane ATPase of Methanolobus tindarius. Eur J Biochem 187:727–735
Senior AE, Nadanaciva S, Weber J (2000) Rate acceleration of ATP hydrolysis by F1FO ATP synthase. J Exp Biol 203:35–40
Steinert K, Bickel-Sandkötter S (1996) Isolation, characterization, and substrate specificity of the plasma membrane ATPase of the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii. Z Naturforsch 51:29–39
Steinert K, Wagner V, Kroth-Pancic PG, Bickel-Sandkötter S (1997) Characterization and subunit structure of the ATP synthase of the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii and organization of the ATP synthase genes. J Biol Chem 272:6261–6269
Stock D, Gibbons C, Arechaga I, Leslie AG, Walker JE (2000) The rotary mechanism of ATP synthase. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:672–679
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Valentine RC, Chignell DA (1968) Electron microscopy of muscle phosphorylase molecules: significance of a rhombic shape. Nature 218:950–953
Vik SB, Antonio BJ (1994) A mechanism of proton translocation by F1FO ATP synthases suggested by double mutants of the a subunit. J Biol Chem 269:30364–30369
Wilkens S, Capaldi RA (1998) Electron microscopic evidence of two stalks linking the F1 and FO parts of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1365:93–97
Wilms R, Freiberg C, Wegerle E, Meier I, Mayer F, Müller V (1996) Subunit structure and organization of the genes of the A1AO ATPase from the archaeon Methanosarcina mazei Gö1. J Biol Chem 271:18843–18852
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. We are indebted to Holger Kavermann and Volker Kuhle for their contributions to the expression studies. We thank Thorsten Lemker for his support in protein purification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Antranikian
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lingl, A., Huber, H., Stetter, K.O. et al. Isolation of a complete A1AO ATP synthase comprising nine subunits from the hyperthermophile Methanococcus jannaschii . Extremophiles 7, 249–257 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0318-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0318-7