Abstract
Objective
To monitor the cytokine release patterns in the peri-implant crevicular fluid (PICF) and to investigate which factors affect the success rate of narrow diameter implants (NDI) during the first year.
Material and methods
Mandibular implant overdentures (IOD) retained by 2 NDI were installed in 16 clinically atrophic edentulous patients. The following parameters were monitored during the first year: (i) peri-implant health parameters (plaque index (PI), calculus presence (CP), gingival index (GI), probing depth (PD) and bleeding on probing (BoP); (ii) cytokine concentrations in the PICF (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10); (iii) implant stability quotient (ISQ); (iv) marginal bone level (MBL) and bone level change (BLC); (v) implant success. The insertion torque, bone type, mandibular atrophy, time since edentulism, and smoking habits were also recorded. All data were analyzed using multivariable multilevel mixed-effects regression models.
Results
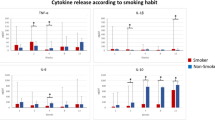
The variability in the TNF-α release patterns temporarily reduced at weeks (w) 8–12, while the IL-1β concentrations remained low until they peaked at w48 [p < 0.05; + 177.55 pg/μl (+ 96.13 − + 258.97)]. Conversely, IL-10 release decreased significantly at w48 [p < 0.05; − 456.24 pg/μl (− 644.41 − − 268.07)]. The PD and ISQ decreased significantly (p < 0.05) over the follow-up period, while the MBL was stable after w48 with a BLC of 0.12 ± 0.71 mm. The overall success rate was 81.3%, and was influenced by TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10, PI, GI, PD, smoking, and time since edentulism.
Conclusion
Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine release was balanced during the first 24 weeks. The GI, smoking, and time since edentulism are the most important factors determining the implant success.
Clinical relevance
The study contributes to the understanding of the osseointegration process in a clinically atrophic population rehabilitated with IOD, and highlights the importance of monitoring clinical peri-implant health-related parameters, smoking habit, and time since edentulism to predict implant success rates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klein MO, Schiegnitz E, Al-Nawas B (2014) Systematic review on success of narrow-diameter dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 29 Suppl:43–54
Al-Johany SS, Al Amri MD, Alsaeed S, Alalola B (2017) Dental implant length and diameter: a proposed classification scheme. J Prosthodont 26:252–260
Schiegnitz E, Al-Nawas B (2018) Narrow-diameter implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 29:21–40
El-Sheikh AM, Shihabuddin OF, Ghoraba SMF (2012) Two versus three narrow-diameter implants with locator attachments supporting mandibular overdentures: a two-year prospective study. Int J Dent 2012:285684
Degidi M, Piattelli A, Carinci F (2008) Clinical outcome of narrow diameter implants: a retrospective study of 510 implants. J Periodontol 79:49–54
Allum SR, Tomlinson RA, Joshi R (2008) The impact of loads on standard diameter, small diameter and mini implants: a comparative laboratory study. Clin Oral Implants Res 19:553–559
Lee JH, Frias V, Lee KW, Wright RF (2005) Effect of implant size and shape on implant success rates: a literature review. J Prosthet Dent 94:377–381
Bidra AS, Almas K (2013) Mini implants for definitive prosthodontic treatment: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent 109:156–164
Pan S, Dagenais M, Thomason JM, Awad M, Emami E, Kimoto S, Wollin SD, Feine JS (2010) Does mandibular edentulous bone height affect prosthetic treatment success? J Dent 38:899–907
Marcello-Machado RM, Bielemann AM, Nascimento GG, Pinto LR, del Bel Cury AA, Faot F (2017) Masticatory function parameters in patients with varying degree of mandibular bone resorption. J Prosthodont Res 61:315–323
Marcello-Machado RM, Faot F, Schuster AJ, Bielemann AM, Chagas Júnior OL, del Bel Cury AA (2017) How does mandibular bone atrophy influence the masticatory function, OHRQoL and satisfaction in overdenture wearers? Clinical results until 1-year post-loading. J Oral Rehabil 44:850–859
Buser D, von Arx T (2000) Surgical procedures in partially edentulous patients with ITI implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 11(Suppl 1):83–100
Akça K, Cehreli MC, Iplikçioğlu H (2003) Evaluation of the mechanical characteristics of the implant-abutment complex of a reduced-diameter morse-taper implant. A nonlinear finite element stress analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 14:444–454
Albrektsson T, Johansson C (2001) Osteoinduction, osteoconduction and osseointegration. Eur Spine J 10(Suppl 2):S96–S101
Trindade R, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2015) Current concepts for the biological basis of dental implants: foreign body equilibrium and osseointegration dynamics. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 27:175–183
Bielemann AM, Marcello-Machado RM, Del Bel Cury AA, Faot F (2018) Systematic review of wound healing biomarkers in peri-implant crevicular fluid during osseointegration. Arch Oral Biol 89:107–128
Bielemann AM, Marcello-Machado RM, Leite FRM, Martinho FC, Chagas-Júnior OL, Antoninha del Bel Cury A, Faot F (2018) Comparison between inflammation-related markers in peri-implant crevicular fluid and clinical parameters during osseointegration in edentulous jaws. Clin Oral Investig 22:531–543
Pivodovaa V, Frankovaa J, Ulrichovaa J (2011) Osteoblast and gingival fibroblast markers in dental implant studies. Biomed Pap 155:109–116
Liskmann S, Vihalemm T, Salum O et al (2005) Correlations between clinical parameters and interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in saliva from totally edentulous patients with peri-implant disease. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 21:543–550
Bastuji-Garin S, Sbidian E, Gaudy-Marqueste C et al (2013) Impact of STROBE statement publication on quality of observational study reporting: interrupted time series versus before-after analysis. PLoS One 8:2–9
Kapur KK (1967) A clinical evaluation of denture adhesives. J Prosthet Dent 18:550–558
Molly L (2006) Bone density and primary stability in implant therapy. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(Suppl 2):124–135
Cawood JI, Howell RA (1988) A classification of the edentulous jaws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 17:232–236
Mombelli A, van Oosten MA, Schurch E, Land NP (1987) The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2:145–151
Guljé F, Raghoebar GM, Ter Meulen JWP et al (2012) Mandibular overdentures supported by 6-mm dental implants: a 1-year prospective cohort study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:59–66
Marcello-Machado RM, Faot F, Schuster AJ, Bielemann AM, Chagas Júnior OL, del Bel Cury AA (2018) One-year clinical outcomes of locking taper Equator attachments retaining mandibular overdentures to narrow diameter implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 20:483–492
Al-Nawas B, Brägger U, Meijer HJA et al (2012) A double-blind randomized controlled trial (RCT) of titanium-13Zirconium versus titanium grade IV small-diameter bone level implants in edentulous mandibles - results from a 1-year observation period. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:896–904
Quirynen M, Al-Nawas B, Meijer HJA et al (2015) Small-diameter titanium Grade IV and titanium-zirconium implants in edentulous mandibles: three-year results from a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:831–840
Misch CE, Perel ML, Wang HL, Sammartino G, Galindo-Moreno P, Trisi P, Steigmann M, Rebaudi A, Palti A, Pikos MA, Schwartz-Arad D, Choukroun J, Gutierrez-Perez JL, Marenzi G, Valavanis DK (2008) Implant success, survival, and failure: the International Congress of Oral Implantologists (ICOI) Pisa Consensus Conference. Implant Dent 17:5–15
Graves DT, Cochran D (2003) The contribution of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor to periodontal tissue destruction. J Periodontol 74:391–401
Petković AB, Matić SM, Stamatović NV, Vojvodić DV, Todorović TM, Lazić ZR, Kozomara RJ (2010) Proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1beta and TNF-alpha) and chemokines (IL-8 and MIP-1alpha) as markers of peri-implant tissue condition. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39:478–485
Wei L, Sun Y, Kong X-F, Zhang C, Yue T, Zhu Q, He DY, Jiang LD (2016) The effects of dopamine receptor 2 expression on B cells on bone metabolism and TNF-α levels in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17:352
Slotte C, Lennerås M, Göthberg C, Suska F, Zoric N, Thomsen P, Nannmark U (2012) Gene expression of inflammation and bone healing in peri-implant crevicular fluid after placement and loading of dental implants. A kinetic clinical pilot study using quantitative real-time PCR. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:723–736
Emecen-Huja P, Eubank TD, Shapiro V, Yildiz V, Tatakis DN, Leblebicioglu B (2013) Peri-implant versus periodontal wound healing. J Clin Periodontol 40:816–824
Gurol C, Kazazoglu E, Dabakoglu B, Korachi M (2011) A comparative study of the role of cytokine polymorphisms interleukin-10 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in susceptibility to implant failure and chronic periodontitis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 26:955–960
Faot F, Nascimento GG, Bielemann AM, Campão TD, Leite FRM, Quirynen M (2015) Can peri-implant crevicular fluid assist in the diagnosis of peri-implantitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Periodontol 86:631–645
Duarte PM, Serrão CR, Miranda TS, Zanatta LCS, Bastos MF, Faveri M, Figueiredo LC, Feres M (2016) Could cytokine levels in the peri-implant crevicular fluid be used to distinguish between healthy implants and implants with peri-implantitis? A systematic review. J Periodontal Res 51:689–698
Graves DT, Nooh N, Gillen T, Davey M, Patel S, Cottrell D, Amar S (2001) IL-1 plays a critical role in oral, but not dermal, wound healing. J Immunol 167:5316–5320. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.167.9.5316
Khoury SB, Thomas L, Walters JD, Sheridan JF, Leblebicioglu B (2008) Early wound healing following one-stage dental implant placement with and without antibiotic prophylaxis: a pilot study. J Periodontol 79:1904–1912
Schierano G, Bassi F, Gassino G, Mareschi K, Bellone G, Preti G (2000) Cytokine production and bone remodeling in patients wearing overdentures on oral implants. J Dent Res 79:1675–1682
Jawa RS, Anillo S, Huntoon K, Baumann H, Kulaylat M (2011) Analytic review: interleukin-6 in surgery, trauma, and critical care: part I: basic science. J Intensive Care Med 26:3–12
Jawa RS, Anillo S, Huntoon K, Baumann H, Kulaylat M (2011) Interleukin-6 in surgery, trauma, and critical care part II: clinical implications. J Intensive Care Med 26:73–87
Boskey AL, Coleman R (2010) Aging and bone. J Dent Res 89:1333–1348
Davies JE (2003) Understanding peri-implant endosseous healing. J Dent Educ 67:932–949
Sayardoust S, Omar O, Norderyd O, Thomsen P (2017) Clinical, radiological, and gene expression analyses in smokers and non-smokers, part 2: RCT on the late healing phase of osseointegration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 19:901–915
Sasaki H, Hou L, Belani A, Wang CY, Uchiyama T, Müller R, Stashenko P (2000) IL-10, but not IL-4, suppresses infection-stimulated bone resorption in vivo. J Immunol 165:3626–3630
Liu D, Yao S, Wise GE (2006) Effect of interleukin-10 on gene expression of osteoclastogenic regulatory molecules in the rat dental follicle. Eur J Oral Sci 114:42–49
Schierano G, Bellone G, Cassarino E, Pagano M, Preti G, Emanuelli G (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin 10 in oral implant sites in humans. J Dent Res 82:428–432
Negri BM, Pimentel SP, Casati MZ, Cirano FR, Casarin RC, Ribeiro FV (2016) Impact of a chronic smoking habit on the osteo-immunoinflammatory mediators in the peri-implant fluid of clinically healthy dental implants. Arch Oral Biol 70:55–61
Sayardoust S, Omar O, Thomsen P (2017) Gene expression in peri-implant crevicular fluid of smokers and nonsmokers. 1. The early phase of osseointegration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 19:681–693
Gokmenoglu C, Ozmeric N, Erguder I, Elgun S (2014) The effect of light-emitting diode photobiomodulation on implant stability and biochemical markers in peri-implant crevicular fluid. Photomed Laser Surg 32:138–145
Salvi GE, Lang NP (2004) Diagnostic parameters for monitoring peri-implant conditions. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 19(Suppl):116–127
Bouri A, Bissada N, Al-Zahrani MS et al (2008) Width of keratinized gingiva and the health status of the supporting tissues around dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 23:323–326
Lin G-H, Chan H-L, Wang H-L (2013) The significance of keratinized mucosa on implant health: a systematic review. J Periodontol 84:1755–1767
Gobbato L, Avila-Ortiz G, Sohrabi K, Wang CW, Karimbux N (2013) The effect of keratinized mucosa width on peri-implant health: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 28:1536–1545
Souza AB, Tormena M, Matarazzo F, Araújo MG (2016) The influence of peri-implant keratinized mucosa on brushing discomfort and peri-implant tissue health. Clin Oral Implants Res 27:650–655
Kissa J, El Kholti W, Laalou Y, El Farouki M (2017) Augmentation of keratinized gingiva around dental implants. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg 118:156–160
Marcello-Machado RM, Faot F, Schuster AJ, Nascimento GG, del Bel Cury AA (2018) Mini-implants and narrow diameter implants as mandibular overdenture retainers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical and radiographic outcomes. J Oral Rehabil 45:161–183
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Neodent’s Research Support Program for supplying the dental implants and attachments used in the study.
Funding
This study was funded by National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, grant 476170/2013) and was financed in part by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The research protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of School of Dentistry (Report no. 1.267.086), Federal University of Pelotas.
Informed consent
The informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Marcello-Machado RM and Faot F share the first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcello-Machado, R.M., Faot, F., Schuster, A.J. et al. Mapping of inflammatory biomarkers in the peri-implant crevicular fluid before and after the occlusal loading of narrow diameter implants. Clin Oral Invest 24, 1311–1320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03010-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03010-y