Abstract
Background
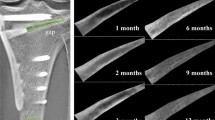
It is important to define callus maturation and corticalization during distraction osteogenesis. Quantitative methods such as ultrasound and Q-computed tomography are sensitive but expensive. The pixel value ratio (PVR) obtained using a PACS (picture archiving and communication system) is a simple and cost-effective investigation tool. Recently, the issue of whether the PVR is correlated with quantitative methods has been studied. We investigated whether serial PVR is a useful technique for predicting corticalization in each callus segment of the regenerate, and can act as a guide for fixator removal in tibial lengthening without intramedullary nailing.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of 30 tibial segments in 18 patients was performed. The mean age of the patients was 18 years (range 5–48 years). There were 6 male patients and 12 female patients, of whom 8 patients were skeletally mature. Indications for limb lengthening were achondroplasia (8 patients), limb length discrepancy (4 patients), and miscellaneous (6 patients). The interobserver variability of the PVR was measured at each callus segment of the regenerate. Serial PVR at each callus segment was classified according to the callus pathway.
Results
The mean interobserver correlation coefficient at the regenerate was high in the posterior callus segment (0.92), the lateral callus segment (0.90), and the medial callus segment (0.70). However, there was low mean interobserver variability in the anterior callus segment (0.49) at the regenerate. A PVR of 1 at the regenerate was achieved first at the lateral callus segment, second at the posterior, third at the medial callus segment, and last at the anterior callus segment. There was no fracture at the regenerate or wire breakage in patients who began fixator removal and full weight bearing when the PVR was 1 in the three callus segments at the regenerate.
Conclusions
In tibial lengthening without nailing, serial measurement of the PVR is a reliable and cost-effective technique to assess the maturity of the callus, especially in the lateral and posterior callus segments, and assessment of the cortical pixel value can safely provide guidelines for fixator removal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eyres KS, Bell MJ, Kanis JA. Methods of assessing new bone formation during limb lengthening. Ultrasonography, dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and radiography compared. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:358–64.
Romanowski CA, Underwood AC, Sprigg A. Reduction of radiation doses in leg lengthening procedures by means of audit and computed tomography scanogram techniques. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:1103–7.
Hazra S, Song HR, Biswal S, Lee SH, Jang KM, Modi HN. Quantitative assessment of mineralization in distraction osteogenesis. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37:843–7.
Lauterburg MT, Exner GU, Jacob HA. Forces involved in lower limb lengthening: an in vivo biomechanical study. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:1815–22.
Li R, Saleh M, Yang L, Coulton L. Radiographic classification of osteogenesis during bone distraction. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:339–47.
Singh S, Song HR, Venkatesh KP, Modi HN, Park MS, Jang KM, Kim SJ. Analysis of callus pattern of tibia lengthening in achondroplasia and a novel method of regeneration assessment using pixel values. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39:261–6.
Zhao L, Fan Q, Venkatesh KP, Park MS, Song HR. Objective guidelines for removing an external fixator after tibial lengthening using pixel value ratio: a pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:3321–6.
Fischgrund J, Paley D, Suter C. Variables affecting time to bone healing during limb lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994:31–7.
Starr KA, Fillman R, Raney EM. Reliability of radiographic assessment of distraction osteogenesis site. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24:26–9.
Danziger MB, Kumar A, DeWeese J. Fractures after femoral lengthening using the Ilizarov method. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15:220–3.
Birch JG, Samchukov ML. Use of the Ilizarov method to correct lower limb deformities in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004;12:144–54.
Paley D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990:81–104.
Eyres KS, Bell MJ, Kanis JA. New bone formation during leg lengthening. Evaluated by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:96–106.
Shim JS, Chung KH, Ahn JM. Value of measuring bone density serial changes on a picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) monitor in distraction osteogenesis. Orthopedics. 2002;25:1269–72.
Song HR, Oh CW, Mattoo R, Park BC, Kim SJ, Park IH, Jeon IH, Ihn JC. Femoral lengthening over an intramedullary nail using the external fixator: risk of infection and knee problems in 22 patients with a follow-up of 2 years or more. Acta Orthop. 2005;76:245–52.
Shyam AK, Singh SU, Modi HN, Song HR, Lee SH, An H. Leg lengthening by distraction osteogenesis using the Ilizarov apparatus: a novel concept of tibia callus subsidence and its influencing factors. Int Orthop. 2009;33:1753–9.
Young JW, Kovelman H, Resnik CS, Paley D. Radiologic assessment of bones after Ilizarov procedures. Radiology. 1990;177:89–93.
Stanitski DF, Shahcheraghi H, Nicker DA, Armstrong PF. Results of tibial lengthening with the Ilizarov technique. J Pediatr Orthop. 1996;16:168–72.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A090084).
Conflict of interest
All authors report that there was no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Song, SH., Sinha, S., Kim, TY. et al. Analysis of corticalization using the pixel value ratio for fixator removal in tibial lengthening. J Orthop Sci 16, 177–183 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-011-0036-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-011-0036-4