Abstract
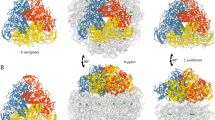
The crystal structure analysis of the aldehyde oxidoreductase from Desulfovibrio gigas was exceptionally revealing with regard to the ligands and structure of the molybdenum site and the mechanism of the hydroxylation reaction catalyzed. The metal is pentacoordinated by two sulfurs of the cis–dithiolene group of the molybdopterin cofactor and by facially arranged sulfido, oxo and water ligands. The latter is in hydrogen-bonding contact with the carboxylate group of Glu 869 and the hydroxyl group of an isopropanol molecule, a substrate analogue inhibitor. This steric arrangement strongly suggests a mechanism for the reductive half-cycle of the reaction with Glu 869 as the base, the metal-bound water as the source of the transferred hydroxyl group, and the sulfido group as the hydride acceptor. The geometry and the proposed mechanism are in agreement with density functional calculations on a model of the molybdenum site. In the oxidative half-reaction, electrons are withdrawn from Morv through the rigidly held pterin ring system, via the iron-sulfur clusters, to the protein surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 June 1997 / Accepted: 20 August 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romão, M., Rösch, N. & Huber, R. The molybdenum site in the xanthine oxidase-related aldehyde oxidoreductase from Desulfovibrio gigas and a catalytic mechanism for this class of enzymes. JBIC 2, 782–785 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050195
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050195