Abstract
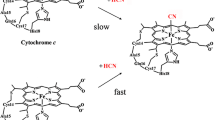
High-resolution Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry is employed to gain thorough kinetics and thermodynamics information on the reaction of free and ligated heme-type ions with selected ligands, with the aim of obtaining an insight into the coordination environment of the prosthetic group in a variety of biomolecular ions. Adopting a stepwise approach towards systems of increasing complexity, we examined the reactivity of free gaseous iron(III) protoporphyrin IX ions, Fe(III)-heme+, of the charged species from microperoxidase-11 (MP11) (covalently peptide bound heme), and of the multiply charged ions from heme proteins, namely, cytochrome c (cyt c) and myoglobin (examples of noncovalently protein bound hemes). Among an array of test compounds allowed to react with Fe(III)-heme+, OP(OMe)3 and P(OMe)3 proved to be similarly efficient ligands in the first addition step, yet displayed markedly distinct reactivity towards heme iron already engaged in axial coordination. The ease with which P(OMe)3 acts as a second axial ligand is exploited to probe structural and conformational features of biomolecular ions. In this way, circumstantial evidence is gained of a folded conformation of +2 charge state ions from MP11 and an elongated one for the +3 charge state ions. Similarly, both the general reaction pattern and detailed kinetics and thermodynamics data point to a regiospecific addition reaction of P(OMe)3 directed at the heme iron within multiply charged ions from cyt c. This unprecedented example of ion–molecule reaction which specifically involves a prosthetic group belonging to protein ions stands in contrast to the multiple, nonspecific interactions established by OP(OMe)3 molecules with the protonated sites of multiply charged cyt c and apomyoglobin ions. This finding may develop and provide sensitive probes of the structure and bonding features of protein ions in the gas phase.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The association of a neutral ligand (L) to Fe(III)-heme+ ions (Eq. 1) at the low operating pressures of the FT-ICR cell is possible in a regime of thermal equilibration of the adduct ion [Fe(III)-heme(L)+] whose excess energy gained in the formation process may be released by IR radiative emission [44, 50]. The rate of radiative emission is expected to increase with increasing size of the ion, and species as large as protein ions are found to undergo a rapid IR cooling [51].
Abbreviations
- CSD:
-
Charge state distribution
- Cyt c :
-
Cytochrome c
- ESI:
-
Electrospray ionization
- Fe(III)-heme+ :
-
Iron(III) protoporphyrin IX ion
- FT-ICR:
-
Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance
- GB:
-
Gas-phase basicity
- HCB:
-
Heme cation basicity
- MP11:
-
Microperoxidase-11
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
References
Dobson CM (2003) Nature 426:884–890
Eaton WA, Munoz V, Thompson PA, Henry ER, Hofrichter J (1998) Acc Chem Res 31:745–754
Rumbley J, Hoang L, Mayne L, Englander SW (2001) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:105–112
Royer CA (2006) Chem Rev 106:1769–1784
Bertini I, Calderone V, Cosenza M, Fragai M, Lee YM, Luchinat C, Mangani S, Terni B, Turano P (2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5334–5339
Katta V, Chait BT (1991) J Am Chem Soc 113:8534–8535
Wood TD, Chorush RA, Wampler FM III, Little DP, O’Connor PB, McLafferty FW (1995) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:2451–2454
Gross DS, Schnier PD, Rodriguez-Cruz SE, Fagerquist CK, Williams ER (1996) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3143–3148
Ogorzalek Loo RR, Smith RD (1995) J Mass Spectrom 30:339–347
Jarrold MF (1999) Acc Chem Res 32:360–367
Konermann L, Simmons DA (2003) Mass Spectrom Rev 22:1–26
Fenn JB, Mann M, Meng CK, Wong SF, Whitehouse CM (1989) Science 246:64–71
Cole RB (ed) (1997) Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, fundamentals, instrumentation and applications. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Kebarle PJ (2000) J Mass Spectrom 35:804–817
Konermann L, Douglas DJ (1997) Biochemistry 36:12296–12302
Konermann L, Douglas DJ (1998) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 9:1248–1254
Grandori R (2003) Curr Org Chem 7:1589–1603
Kaltashov IA, Eyles SJ (2002) Mass Spectrom Rev 21:37–71
Loo JA (2000) Int J Mass Spectrom 200:175–186
Przybylski M, Glocker MO (1996) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 35:806–826
Schnier PD, Gross DS, Williams ER (1995) J Am Chem Soc 117:6747–6757
Shelimov KB, Clemmer DE, Hudgins RR, Jarrold MF (1997) J Am Chem Soc 119:2240–2248
Gronert S (1999) Int J Mass Spectrom 185–187:351–357
Peschke M, Blades A, Kebarle P (2002) J Am Chem Soc 124:11519–11530
Suckau D, Shi Y, Beu SC, Senko MW, Quinn JP, Wampler FM III, McLafferty FW (1993) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:790–793
McLafferty FW, Guan Z, Haupts UH, Wood TD, Kelleher N (1998) J Am Chem Soc 120:4732–4740
Cassady CJ, Carr SR (1996) J Mass Spectrom 31:247–254
Camara E, Green MK, Penn SG, Lebrilla CB (1996) J Am Chem Soc 118:8751–8752
Fye JL, Woenckhaus J, Jarrold MF (1998) J Am Chem Soc 120:1327–1328
Marshall AG, Hendrickson CL, Jackson GS (1998) Mass Spectrom Rev 17:1–35
Laude DA, Stevenson E, Robinson JM (1997) In: Cole RB (ed) Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Wiley, New York, pp 291–319
Bogdanov B, Smith RD (2005) Mass Spectrom Rev 24:168–200
Scott RA, Mauk AG (eds) (1996) Cytochrome c: a multidisciplinary approach. University Science Books, Sausalito
Jiang X, Wang X (2004) Annu Rev Biochem 73:87–106
Pettigrew GW, Moore GR (eds) (1987) Cytochromes c; biological aspects. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Winkler JR (2004) Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:169–174
Bertini I, Cavallaro G, Rosato A (2006) Chem. Rev 106:90–115
Pletneva EV, Gray HB, Winkler JR (2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18397–18402
Bren KL, Kellogg JA, Kaur R, Wen X (2004) Inorg Chem 43:7934–7944
McLuckey SA, Van Berkel GJ, Glish GL (1990) J Am Chem Soc 112:5668–5670
Gong S, Camara E, He F, Green MK, Lebrilla CB (1999) Int J Mass Spectrom 185–187:401–412
Stephenson JL Jr, Schaaff TG, McLuckey SA (1999) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 10:552–556
Woenckhaus J, Hudgins RR, Jarrold MF (1997) J Am Chem Soc 119:9586–9587
Angelelli F, Chiavarino B, Crestoni ME, Fornarini S (2005) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 16:589–598
Meot-Ner M (1979) In: Bowers MT (ed) Gas-phase ion chemistry, vol 1. Academic, New York
Bartmess JE, Georgiadis RM (1983) Vacuum 33:149–153
Su T, Chesnavich WJ (1982) J Chem Phys 76:5183–5185
Schroder D, Schwarz H, Clemmer DE, Chen Y, Armentrout PB, Baranov VI, Bohme DK (1997) Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Process 161:175–191
Nicoll JB, Dearden DV (1997) KinFit, v.1.0. Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Brigham Young University, Provo
Horn DM, Breuker K, Frank AJ, McLafferty FW (2001) J Am Chem Soc 123:9792–9799
Hunter EP, Lias SG (2005) In: Linstrom PJ, Mallard WG (eds) NIST chemistry webbook, NIST standard reference database number 69. http://webbook.nist.gov
Ryzhov V, Dunbar RC (1999) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 10:862–868
Loew GH, Harris DL (2000) Chem Rev 100:407–419
Reedy CJ, Gibney BR (2004) Chem Rev 104:617–649
Rovira C, Karel Kunc K, Hutter J, Ballone P, Parrinello M (1997) J Phys Chem A 101:8914–8925
Lombardi A, Nastri F, Pavone V (2001) Chem Rev 101:3165–3189
Dallacosta C, Casella L, Monzani E (2003) J Biol Inorg Chem 8:770–776
Baldwin DA, Marques HM, Pratt JM (1987) J Inorg Biochem 30:203–217
Raffa D, Leung KT, Battaglini F (2003) Anal Chem 75:4983–4987
Melchionna S, Barteri M, Ciccotti G (1995) J Comput Aided Mater Des 2:9–22
Melchionna S, Barteri M, Ciccotti G (1996) J Phys Chem 100:19241–19250
Marques HM, Brown KL (2002) Coord Chem Rev 225:123–158
Di Teodoro C, Aschi M, Amadei A, Roccatano D, Malatesta F, Ottaviano L (2005) Chem Phys Chem 6:681–668
Meot-Ner M (2005) Chem Rev 105:213–284
Chowdhury SK, Katta V, Chait BT (1990) J Am Chem Soc 112:9012–9013
Hunter CL, Mauk AG, Douglas DJ (1997) Biochemistry 36:1018–1025
Konishi’ Y, Fengt R (1994) Biochemistry 33:9706–9710
Upmacis RK, Hajjar DP, Chait BT, Mirza UA (1997) J Am Chem Soc 119:10424–10429
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge the Italian Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca Scientifica for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crestoni, M.E., Fornarini, S. Heme-peptide/protein ions and phosphorous ligands: search for site-specific addition reactions. J Biol Inorg Chem 12, 22–35 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-006-0159-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-006-0159-9