Abstract.
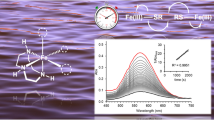
Azotobacter vinelandii produces siderophores with different metal-binding properties, depending on the concentration of Fe(III) and molybdate in the growth medium. The three protonation constants of the mono(catecholamide) siderophore aminochelin were determined by simultaneous spectrophotometric and potentiometric titrations as log K 1=12.1, log K 2=10.22 and log K 3=7.04. Based on the two catechol protonation constants, log K 1 and log K 3, the overall stability constant of the aminochelin iron 3:1 complex was found to be log β3=41.3, resulting in a pFe3+ value of 17.6 at pH 7.45. In order to further investigate the properties of the siderophore, the solubilization of Fe(III) hydroxide by a 8×10–4 M solution of aminochelin at pH 7 and 25 °C was followed spectrophotometrically in the absence and in the presence of molybdate. It was observed that the addition of molybdate resulted in a significant delay in the solubilization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodr, .H., Hider, .R. & Duhme-Klair, .AK. The iron-binding properties of aminochelin, the mono(catecholamide) siderophore of Azotobacter vinelandii . J Biol Inorg Chem 7, 891–896 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-002-0375-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-002-0375-x