Abstract
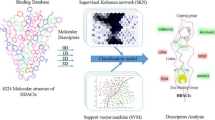
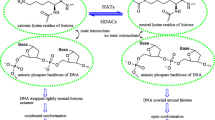
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors have gained attention over the past three decades because of their potential in the treatment of different diseases including various forms of cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, autoimmune, inflammatory diseases, and other metabolic disorders. To date, 5 HDAC inhibitor drugs are marketed for the treatment of hematological malignancies and several drug-candidate HDAC inhibitors are at different stages of clinical trials. However, due to the toxic side effects of these drugs resulting from the lack of target selectivity, active studies are ongoing to design and develop either class-selective or isoform-selective inhibitors. Computational methods have aided the discovery of HDAC inhibitors with the desired potency and/or selectivity. These methods include ligand-based approaches such as scaffold hopping, pharmacophore modeling, three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationships (3D-QSAR); and structure-based virtual screening (molecular docking). The current trends involve the application of the combination of these methods and incorporating molecular dynamics simulations coupled with Poisson–Boltzmann/molecular mechanics generalized Born surface area (MM-PBSA/MM-GBSA) to improve the prediction of ligand binding affinity. This review aimed at understanding the current trends in applying these multilayered strategies and their contribution to the design/identification of HDAC inhibitors.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Any data will be available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
AbdElmoniem N, H. Abdallah M, M. Mukhtar R, Moutasim F, Rafie Ahmed A, Edris A, Ibraheem W, Makki AA, M. Elshamly E, Elhag R, Osman W, A. Mothana R, Alzain AA (2023) Identification of Novel Natural Dual HDAC and Hsp90 Inhibitors for Metastatic TNBC Using e-Pharmacophore Modeling, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Studies. Molecules 28 (4). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041771
Abdizadeh T, Ghodsi R, Hadizadeh F (2017) 3D-QSAR (CoMFA, CoMSIA) and Molecular Docking Studies on Histone Deacetylase 1 Selective Inhibitors. Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery 12 (4). doi:https://doi.org/10.2174/1574892812666170508125927
Agarwal R, Pattarawat P, Duff MR (2022) Wang H-CR, Baudry J. Smith JC. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.31.494169
Aldana-Masangkay GI, Sakamoto KM (2011) The role of HDAC6 in cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/875824
Alseksek RK, Ramadan WS, Saleh E, El-Awady R (2022) The role of HDACs in the response of cancer cells to cellular stress and the potential for therapeutic intervention. Int J Mol Sci 23(15). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158141
Amin SA, Trivedi P, Adhikari N, Routholla G, Vijayasarathi D, Das S, Ghosh B, Jha T (2021) Quantitative activity–activity relationship (QAAR) driven design to develop hydroxamate derivatives of pentanoic acids as selective HDAC8 inhibitors: synthesis, biological evaluation and binding mode of interaction studies. New J Chem 45(37):17149–17162. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nj02636d
Amin SA, Kumar J, Khatun S, Das S, Qureshi IA, Jha T, Gayen S (2022) Binary quantitative activity-activity relationship (QAAR) studies to explore selective HDAC8 inhibitors: In light of mathematical models, DFT-based calculation and molecular dynamic simulation studies. J Mol Struct. 1260. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132833
Anh DT, Hai P-T, Huy LD, Ngoc HB, Ngoc TTM, Dung DTM, Park EJ, Song IK, Kang JS, Kwon J-H, Tung TT, Han S-B, Nam N-H (2021) Novel 4-oxoquinazoline-based N-hydroxypropenamides as histone deacetylase inhibitors: design, synthesis, and biological evaluation. ACS Omega 6(7):4907–4920. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05870
Banerjee S, Adhikari N, Amin SA, Jha T (2019) Structural exploration of tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives as HDAC8 inhibitors through multi-QSAR modeling study. J Biomol Struct Dyn 38(5):1551–1564. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2019.1617782
Basant N, Lin X, Reid T-E, Karla P, Wang X (2015) Discovery of a Novel HDAC2 Inhibitor by a Scaffold-Merging Hybrid Query. Comb Chem High Throughput Screening 18(7):693–700. https://doi.org/10.2174/1386207318666150706103918
Bhaskara S (2015) Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 regulate DNA replication and DNA repair: potential targets for genome stability-mechanism-based therapeutics for a subset of cancers. Cell Cycle 14(12):1779–1785. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2015.1042634
Bondarev AD, Attwood MM, Jonsson J, Chubarev VN, Tarasov VV, Schiöth HB (2021) Recent developments of HDAC inhibitors: Emerging indications and novel molecules. Br J Clin Pharmacol 87(12):4577–4597. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.14889
Bora-Singhal N, Mohankumar D, Saha B, Colin CM, Lee JY, Martin MW, Zheng X, Coppola D, Chellappan S (2020) Novel HDAC11 inhibitors suppress lung adenocarcinoma stem cell self-renewal and overcome drug resistance by suppressing Sox2. Scientific Reports 10 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61295-6
Bornelöv S, Reynolds N, Xenophontos M, Gharbi S, Johnstone E, Floyd R, Ralser M, Signolet J, Loos R, Dietmann S, Bertone P, Hendrich B (2018) The Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylation Complex Modulates Chromatin Structure at Sites of Active Transcription to Fine-Tune Gene Expression. Mol Cell 71(1):56-72.e54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.003
Boyes J, Byfield P, Nakatani Y, Ogryzko V (1998) Regulation of activity of the transcription factor GATA-1 by acetylation. Nature 396(6711):594–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/25166
Bui HTB, Nguyen PH, Pham QM, Tran HP, Tran DQ, Jung H, Hong QV, Nguyen QC, Nguyen QP, Le HT, Yang S-G (2022) Target Design of Novel Histone Deacetylase 6 Selective Inhibitors with 2-Mercaptoquinazolinone as the Cap Moiety. Molecules 27 (7). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072204
Cai J-Y, Xu T-T, Wang Y, Chang J-J, Li J, Chen X-Y, Chen X, Yin Y-F, Ni X-J (2018) Histone deacetylase HDAC4 promotes the proliferation and invasion of glioma cells. Int J Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4564
Cao GP, Arooj M, Thangapandian S, Park C, Arulalapperumal V, Kim Y, Kwon YJ, Kim HH, Suh JK, Lee KW (2015) A lazy learning-based QSAR classification study for screening potential histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) inhibitors. SAR QSAR Environ Res 26(5):397–420. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062936x.2015.1040453
Cao GP, Thangapandian S, Son M, Kumar R, Choi YJ, Kim Y, Kwon YJ, Kim HH, Suh JK, Lee KW (2016) QSAR modeling to design selective histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) inhibitors. Arch Pharm Res 39(10):1356–1369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0705-5
Cao F, Zwinderman M, Dekker F (2018) The Process and Strategy for Developing Selective Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors. Molecules 23 (3). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030551
Chen Y-d, Jiang Y-J, Zhou J-W, Yu Q-S, You Q-D (2008) Identification of ligand features essential for HDACs inhibitors by pharmacophore modeling. J Mol Graph Model 26(7):1160–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2007.10.007
Chiaradonna F, Cirulli C, Palorini R, Votta G, Alberghina L (2015) New Insights into the Connection Between Histone Deacetylases, Cell Metabolism, and Cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal 23(1):30–50. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2014.5854
Cohen HY, Lavu S, Bitterman KJ, Hekking B, Imahiyerobo TA, Miller C, Frye R, Ploegh H, Kessler BM, Sinclair DA (2004) Acetylation of the C Terminus of Ku70 by CBP and PCAF Controls Bax-Mediated Apoptosis. Mol Cell 13(5):627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00094-2
Daśko M, de Pascual-Teresa B, Ortín I, Ramos A (2022) HDAC Inhibitors: Innovative Strategies for Their Design and Applications. Molecules 27 (3). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030715
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M, Hrabeta J (2017) Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18 (7). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071414
Elmezayen AD, Kemal Y (2021) Structure-based virtual screening for novel potential selective inhibitors of class IIa histone deacetylases for cancer treatment. Computational Biology and Chemistry 92. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2021.107491
Frühauf A, Meyer-Almes F-J (2021) Non-Hydroxamate Zinc-Binding Groups as Warheads for Histone Deacetylases. Molecules 26 (17). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175151
Gaetano C, Venturelli S, Berger A, Böcker A, Busch C, Weiland T, Noor S, Leischner C, Schleicher S, Mayer M, Weiss TS, Bischoff SC, Lauer UM, Bitzer M (2013) Resveratrol as a Pan-HDAC Inhibitor Alters the Acetylation Status of Jistone Proteins in Human-Derived Hepatoblastoma Cells. PLoS ONE 8 (8). doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073097
Ganai SA, Abdullah E, Rashid R, Altaf M (2017) Combinatorial In Silico Strategy towards Identifying Potential Hotspots during Inhibition of Structurally Identical HDAC1 and HDAC2 Enzymes for Effective Chemotherapy against Neurological Disorders. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 10. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00357
Gao L, Cueto MA, Asselbergs F, Atadja P (2002) Cloning and Functional Characterization of HDAC11, a Novel Member of the Human Histone Deacetylase Family. J Biol Chem 277(28):25748–25755. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111871200
Genheden S, Ryde U (2015) The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin Drug Discov 10(5):449–461. https://doi.org/10.1517/17460441.2015.1032936
Géraldy M, Morgen M, Sehr P, Steimbach RR, Moi D, Ridinger J, Oehme I, Witt O, Malz M, Nogueira MS, Koch O, Gunkel N, Miller AK (2019) Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 10: Hydrogen Bonding to the Gatekeeper Residue is Implicated. J Med Chem 62(9):4426–4443. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01936
Gregoretti I, Lee Y-M, Goodson HV (2004) Molecular Evolution of the Histone Deacetylase Family: Functional Implications of Phylogenetic Analysis. J Mol Biol 338(1):17–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.02.006
Grönroos E, Hellman U, Heldin C-H, Ericsson J (2002) Control of Smad7 Stability by Competition between Acetylation and Ubiquitination. Mol Cell 10(3):483–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00639-1
Gu W, Roeder RG (1997) Activation of p53 Sequence-Specific DNA Binding by Acetylation of the p53 C-Terminal Domain. Cell 90(4):595–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80521-8
Guan H-P, Ishizuka T, Chui PC, Lehrke M, Lazar MA (2005) Corepressors selectively control the transcriptional activity of PPARγ in adipocytes. Genes Dev 19(4):453–461. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1263305
Guedes IA, Pereira FSS, Dardenne LE (2018) Empirical Scoring Functions for Structure-Based Virtual Screening: Applications, Critical Aspects, and Challenges. Frontiers in Pharmacology 9. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01089
Guenther MG, Barak O, Lazar MA (2001) The SMRT and N-CoR Corepressors Are Activating Cofactors for Histone Deacetylase 3. Mol Cell Biol 21(18):6091–6101. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.21.18.6091-6101.2001
Guo Y, Xiao J, Guo Z, Chu F, Cheng Y, Wu S (2005) Exploration of a binding mode of indole amide analogues as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors and 3D-QSAR analyses. Bioorg Med Chem 13(18):5424–5434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2005.05.016
Gurevich I, Flores AM, Aneskievich BJ (2007) Corepressors of agonist-bound nuclear receptors. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 223(3):288–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2007.05.019
Hai Y, Shinsky SA, Porter NJ, Christianson DW (2017) Histone deacetylase 10 structure and molecular function as a polyamine deacetylase. Nature Communications 8 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15368
Hayakawa F, Towatari M, Ozawa Y, Tomita A, Privalsky ML, Saito H (2004) Functional regulation of GATA-2 by acetylation. J Leukoc Biol 75(3):529–540. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0603389
Herbst-Gervasoni CJ, Christianson DW (2021) X-ray Crystallographic Snapshots of Substrate Binding in the Active Site of Histone Deacetylase 10. Biochemistry 60(4):303–313. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00936
Ho TCS, Chan AHY, Ganesan A (2020) Thirty Years of HDAC Inhibitors: 2020 Insight and Hindsight. J Med Chem 63(21):12460–12484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00830
Hopfinger AJ, Wang S, Tokarski JS, Jin B, Albuquerque M, Madhav PJ, Duraiswami C (1997) Construction of 3D-QSAR Models Using the 4D-QSAR Analysis Formalism. J Am Chem Soc 119(43):10509–10524. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9718937
Hosseinzadeh P, Watson PR, Craven TW, Li X, Rettie S, Pardo-Avila F, Bera AK, Mulligan VK, Lu P, Ford AS, Weitzner BD, Stewart LJ, Moyer AP, Di Piazza M, Whalen JG, Greisen P, Christianson DW, Baker D (2021) Anchor extension: a structure-guided approach to design cyclic peptides targeting enzyme active sites. Nature Communications 12 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23609-8
Hsu K-C, Liu C-Y, Lin TE, Hsieh J-H, Sung T-Y, Tseng H-J, Yang J-M, Huang W-J (2017) Novel Class IIa-Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Discovered Using an in Silico Virtual Screening Approach. Scientific Reports 7 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03417-1
Hu E, Chen Z, Fredrickson T, Zhu Y, Kirkpatrick R, Zhang G-F, Johanson K, Sung C-M, Liu R, Winkler J (2000) Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Human Class I Histone Deacetylase That Functions as a Transcription Repressor. J Biol Chem 275(20):15254–15264. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M908988199
Hu E, Dul E, Sung C-M, Chen Z, Kirkpatrick R, Zhang G-F, Johanson K, Liu R, Lago A, Hofmann G, Macarron R, De Los FM, Perez P, Krawiec J, Winkler J, Jaye M (2003) Identification of Novel Isoform-Selective Inhibitors within Class I Histone Deacetylases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307(2):720–728. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.103.055541
Hu Y, Stumpfe D, Bajorath J (2016) Recent Advances in Scaffold Hopping. J Med Chem 60(4):1238–1246. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01437
Hu Z, Lin Q, Liu H, Zhao T, Yang B, Tu G (2021) Molecular dynamics-guided receptor-dependent 4D-QSAR studies of HDACs inhibitors. Mol Diversity 26(2):757–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10181-y
Hudson GM, Watson PJ, Fairall L, Jamieson AG, Schwabe JWR (2015) Insights into the Recruitment of Class IIa Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) to the SMRT/NCoR Transcriptional Repression Complex. J Biol Chem 290(29):18237–18244. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.661058
Ibrahim Uba A, Yelekçi K (2019) Homology modeling of human histone deacetylase 10 and design of potential selective inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn 37(14):3627–3636. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2018.1521747
Imhof A, Gajendran C, Tantry SJ, M NS, Mohammed Z, Dewang P, Hallur M, Nair S, Vaithilingam K, Nagayya B, Rajagopal S, Sivanandhan D (2023) Novel dual LSD1/HDAC6 inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Plos One 18 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279063
Ito A, Kawaguchi Y, Lai C-H, Kovacs JJ, Higashimoto Y, Appella E, Yao T-P (2002) MDM2–HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of p53 is required for its degradation. EMBO J 21(22):6236–6245. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdf616
Jeong J-W, Bae M-K, Ahn M-Y, Kim S-H, Sohn T-K, Bae M-H, Yoo M-A, Song EJ, Lee K-J, Kim K-W (2002) Regulation and Destabilization of HIF-1α by ARD1-Mediated Acetylation. Cell 111(5):709–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01085-1
Jung M, Suzuki T, Kasuya Y, Itoh Y, Ota Y, Zhan P, Asamitsu K, Nakagawa H, Okamoto T, Miyata N (2013) Identification of Highly Selective and Potent Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors Using Click Chemistry-Based Combinatorial Fragment Assembly. PLoS ONE 8 (7). doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068669
Juvale DC, Kulkarni VV, Deokar HS, Wagh NK, Padhye SB, Kulkarni VM (2006) 3D-QSAR of histone deacetylase inhibitors: hydroxamate analogues. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 4 (15). doi:https://doi.org/10.1039/b606365a
Kiernan R, Brès V, Ng RWM, Coudart M-P, El Messaoudi S, Sardet C, Jin D-Y, Emiliani S, Benkirane M (2003) Post-activation Turn-off of NF-κB-dependent Transcription Is Regulated by Acetylation of p65. J Biol Chem 278(4):2758–2766. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M209572200
Kleinschek A, Meyners C, Digiorgio E, Brancolini C, Meyer-Almes FJ (2016) Potent and Selective Non-hydroxamate Histone Deacetylase 8 Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 11(23):2598–2606. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201600528
Kovacs JJ, Murphy PJM, Gaillard S, Zhao X, Wu J-T, Nicchitta CV, Yoshida M, Toft DO, Pratt WB, Yao T-P (2005) HDAC6 Regulates Hsp90 Acetylation and Chaperone-Dependent Activation of Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol Cell 18(5):601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.04.021
Krusche CA, Wulfing P, Kersting C, Vloet A, Bocker W, Kiesel L, Beier HM, Alfer J (2005) Histone deacetylase-1 and -3 protein expression in human breast cancer: a tissue microarray analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 90(1):15–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-004-1668-2
Kumbhar N, Nimal S, Barale S, Kamble S, Bavi R, Sonawane K, Gacche R (2022) Identification of novel leads as potent inhibitors of HDAC3 using ligand-based pharmacophore modeling and MD simulation. Scientific Reports 12 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05698-7
Li Y, Shin D, Kwon SH (2012) Histone deacetylase 6 plays a role as a distinct regulator of diverse cellular processes. FEBS journal:n/a-n/a. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12079
Li Y, Zhang X, Zhu S, Dejene EA, Peng W, Sepulveda A, Seto E (2020) HDAC10 Regulates Cancer Stem-Like Cell Properties in KRAS-Driven Lung Adenocarcinoma. Can Res 80(16):3265–3278. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-3613
Li Y, Seto E (2016) HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 6 (10). doi:https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a026831
Liu J, Qian C, Zhu Y, Cai J, He Y, Li J, Wang T, Zhu H, Li Z, Li W, Hu L (2018) Design, synthesis and evaluate of novel dual FGFR1 and HDAC inhibitors bearing an indazole scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem 26(3):747–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.12.041
Liu X, Yan W, Wang S, Lu M, Yang H, Chai X, Shi H, Zhang Y, Jia Q (2023) Discovery of selective HDAC6 inhibitors based on a multi-layer virtual screening strategy. Computers in Biology and Medicine 160. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107036
Lobera M, Madauss KP, Pohlhaus DT, Wright QG, Trocha M, Schmidt DR, Baloglu E, Trump RP, Head MS, Hofmann GA, Murray-Thompson M, Schwartz B, Chakravorty S, Wu Z, Mander PK, Kruidenier L, Reid RA, Burkhart W, Turunen BJ, Rong JX, Wagner C, Moyer MB, Wells C, Hong X, Moore JT, Williams JD, Soler D, Ghosh S, Nolan MA (2013) Selective class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition via a nonchelating zinc-binding group. Nat Chem Biol 9(5):319–325. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1223
Lombardi PM, Cole KE, Dowling DP, Christianson DW (2011) Structure, mechanism, and inhibition of histone deacetylases and related metalloenzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 21(6):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2011.08.004
Luger K, Mäder AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ (1997) Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature 389 (6648):251–260. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/38444
Lührs H, Hock R, Schauber J, Weihrauch M, Harrer M, Melcher R, Scheppach W, Bustin M, Menzel T (2002) Modulation of HMG-N2 binding to chromatin by butyrate-induced acetylation in human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 97(5):567–573. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.10098
Luo Y, Li H (2020) Structure-Based Inhibitor Discovery of Class I Histone Deacetylases (HDACs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21 (22). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228828
Maolanon Alex R, Madsen Andreas S, Olsen Christian A (2016) Innovative Strategies for Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases. Cell Chem Biol 23(7):759–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.06.011
Martínez-Balbás MA, Bauer U-M, Nielsen SJ, Brehm A, Kouzarides T (2000) Regulation of E2F1 activity by acetylation. EMBO J 19(4):662–671. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.4.662
Mason J, Good A, Martin E (2001) 3-D Pharmacophores in Drug Discovery. Curr Pharm Des 7(7):567–597. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612013397843
Melesina J, Simoben CV, Praetorius L, Bülbül EF, Robaa D, Sippl W (2021) Strategies To Design Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 16(9):1336–1359. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202000934
Milazzo G, Mercatelli D, Di Muzio G, Triboli L, De Rosa P, Perini G, Giorgi FM (2020) Histone Deacetylases (HDACs): Evolution, Specificity, Role in Transcriptional Complexes, and Pharmacological Actionability. Genes 11 (5). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050556
Milde T, Oehme I, Korshunov A, Kopp-Schneider A, Remke M, Northcott P, Deubzer HE, Lodrini M, Taylor MD, von Deimling A, Pfister S, Witt O (2010) HDAC5 and HDAC9 in Medulloblastoma: Novel Markers for Risk Stratification and Role in Tumor Cell Growth. Clin Cancer Res 16(12):3240–3252. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-10-0395
Minamiya Y, Ono T, Saito H, Takahashi N, Ito M, Mitsui M, Motoyama S, Ogawa J (2011) Expression of histone deacetylase 1 correlates with a poor prognosis in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 74(2):300–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.02.019
Moi D, Citarella A, Bonanni D, Pinzi L, Passarella D, Silvani A, Giannini C, Rastelli G (2022) Synthesis of potent and selective HDAC6 inhibitors led to unexpected opening of a quinazoline ring. RSC Adv 12(18):11548–11556. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra01753a
Moreno DA, Scrideli CA, Cortez MAA, De Paula QR, Valera ET, Da Silva SV, Yunes JA, Brandalise SR, Tone LG (2010) research paper: Differential expression of HDAC3, HDAC7 and HDAC9 is associated with prognosis and survival in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 150(6):665–673. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08301.x
Munshi N, Merika M, Yie J, Senger K, Chen G, Thanos D (1998) Acetylation of HMG I(Y) by CBP Turns off IFNβ Expression by Disrupting the Enhanceosome. Mol Cell 2(4):457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80145-8
Oehme I, Deubzer HE, Wegener D, Pickert D, Linke J-P, Hero B, Kopp-Schneider A, Westermann F, Ulrich SM, von Deimling A, Fischer M, Witt O (2009) Histone Deacetylase 8 in Neuroblastoma Tumorigenesis. Clin Cancer Res 15(1):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-08-0684
Ononye SN, VanHeyst MD, Oblak EZ, Zhou W, Ammar M, Anderson AC, Wright DL (2013) Tropolones As Lead-Like Natural Products: The Development of Potent and Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 4(8):757–761. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml400158k
Pai P, Kumar A, Shetty MG, Kini SG, Krishna MB, Satyamoorthy K, Babitha KS (2022) Identification of potent HDAC 2 inhibitors using E-pharmacophore modelling, structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamic simulation. Journal of Molecular Modeling 28 (5). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-022-05103-0
Pant K, Peixoto E, Richard S, Gradilone SA (2020) Role of Histone Deacetylases in Carcinogenesis: Potential Role in Cholangiocarcinoma. Cells 9 (3). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030780
Patel JH, Du Y, Ard PG, Phillips C, Carella B, Chen C-J, Rakowski C, Chatterjee C, Lieberman PM, Lane WS, Blobel GA, McMahon SB (2004) The c-MYC Oncoprotein Is a Substrate of the Acetyltransferases hGCN5/PCAF and TIP60. Mol Cell Biol 24(24):10826–10834. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.24.24.10826-10834.2004
Patil V, Sodji QH, Kornacki JR, Mrksich M, Oyelere AK (2013) 3-Hydroxypyridin-2-thione as Novel Zinc Binding Group for Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibition. J Med Chem 56(9):3492–3506. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm301769u
Peng Z, Zhao Q, Tian X, Lei T, Xiang R, Chen L, Yang Y (2022) Discovery of Potent and Isoform‐selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Using Structure‐based Virtual Screening and Biological Evaluation. Molecular Informatics 41 (9). doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.202100295
Pharmacophores and Pharmacophore Searches (2006). Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/3527609164
Poonia P, Sharma M, Jha P, Chopra M (2022) Pharmacophore-based virtual screening of ZINC database, molecular modeling and designing new derivatives as potential HDAC6 inhibitors. Mol Diversity. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10540-3
Porter NJ, Christianson DW (2019) Structure, mechanism, and inhibition of the zinc-dependent histone deacetylases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 59:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.01.004
Rajak H, Patel VK, Shirbhate E, Tiwari P, Kore R, Veerasamy R, Mishra A (2023) Multi-targeted HDAC Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: Current
Ruzic D, Djokovic N, Nikolic K (2021) Fragment-Based Drug Design of Selective HDAC6 Inhibitors. In: Protein-Ligand Interactions and Drug Design. Methods in Molecular Biology. pp 155–170. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1209-5_9
Santos KB, Guedes IA, Karl ALM, Dardenne LE (2020) Highly Flexible Ligand Docking: Benchmarking of the DockThor Program on the LEADS-PEP Protein-Peptide Data Set. J Chem Inf Model 60(2):667–683. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00905
Sartorelli V, Puri PL, Hamamori Y, Ogryzko V, Chung G, Nakatani Y, Wang JYJ, Kedes L (1999) Acetylation of MyoD Directed by PCAF Is Necessary for the Execution of the Muscle Program. Mol Cell 4(5):725–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80383-4
Saunders A, Huang X, Fidalgo M, Reimer MH, Faiola F, Ding J, Sánchez-Priego C, Guallar D, Sáenz C, Li D, Wang J (2017) The SIN3A/HDAC Corepressor Complex Functionally Cooperates with NANOG to Promote Pluripotency. Cell Rep 18(7):1713–1726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.055
Schäker-Hübner L, Warstat R, Ahlert H, Mishra P, Kraft FB, Schliehe-Diecks J, Schöler A, Borkhardt A, Breit B, Bhatia S, Hügle M, Günther S, Hansen FK (2021) 4-Acyl Pyrrole Capped HDAC Inhibitors: A New Scaffold for Hybrid Inhibitors of BET Proteins and Histone Deacetylases as Antileukemia Drug Leads. J Med Chem 64(19):14620–14646. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01119
Schlessinger A, Kapla J, Rodríguez-Espigares I, Ballante F, Selent J, Carlsson J (2021) Can molecular dynamics simulations improve the structural accuracy and virtual screening performance of GPCR models? PLOS Computational Biology 17 (5). doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008936
Shukla S, Tekwani BL (2020) Histone Deacetylases Inhibitors in Neurodegenerative Diseases, Neuroprotection and Neuronal Differentiation. Frontiers in Pharmacology 11. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00537
Simões-Pires C, Zwick V, Nurisso A, Schenker E, Carrupt P-A, Cuendet M (2013) HDAC6 as a target for neurodegenerative diseases: what makes it different from the other HDACs? Molecular Neurodegeneration 8 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-8-7
Sirous H, Campiani G, Brogi S, Calderone V, Chemi G (2020) Computer-Driven Development of an in Silico Tool for Finding Selective Histone Deacetylase 1 Inhibitors. Molecules 25 (8). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081952
Sirous H, Campiani G, Calderone V, Brogi S (2021) Discovery of novel hit compounds as potential HDAC1 inhibitors: The case of ligand- and structure-based virtual screening. Computers in Biology and Medicine 137. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104808
Sixto-López Y, Gómez-Vidal JA, de Pedro N, Bello M, Rosales-Hernández MC, Correa-Basurto J (2020) Hydroxamic acid derivatives as HDAC1, HDAC6 and HDAC8 inhibitors with antiproliferative activity in cancer cell lines. Scientific Reports 10 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67112-4
Smith RD, Damm-Ganamet KL, Dunbar JB, Ahmed A, Chinnaswamy K, Delproposto JE, Kubish GM, Tinberg CE, Khare SD, Dou J, Doyle L, Stuckey JA, Baker D, Carlson HA (2015) CSAR Benchmark Exercise 2013: Evaluation of Results from a Combined Computational Protein Design, Docking, and Scoring/Ranking Challenge. J Chem Inf Model 56(6):1022–1031. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00387
Sotriffer CA, Sanschagrin P, Matter H, Klebe G (2008) SFCscore: Scoring functions for affinity prediction of protein-ligand complexes. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 73 (2):395–419. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22058
Spyrakis F, Cavasotto CN (2015) Open challenges in structure-based virtual screening: Receptor modeling, target flexibility consideration and active site water molecules description. Arch Biochem Biophys 583:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2015.08.002
Status and Future Prospective. Current Medicinal Chemistry 30 (24):2762–2795. doi:https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867329666220922105615
Sun H, Li Y, Tian S, Xu L, Hou T (2014) Assessing the performance of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 4. Accuracies of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methodologies evaluated by various simulation protocols using PDBbind data set. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16 (31):16719–16729. doi:https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp01388c
Tang G, Wong JC, Zhang W, Wang Z, Zhang N, Peng Z, Zhang Z, Rong Y, Li S, Zhang M, Yu L, Feng T, Zhang X, Wu X, Wu JZ, Chen L (2014) Identification of a Novel Aminotetralin Class of HDAC6 and HDAC8 Selective Inhibitors. J Med Chem 57(19):8026–8034. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm5008962
Thangapandian S, John S, Lee Y, Kim S, Lee KW (2011) Dynamic Structure-Based Pharmacophore Model Development: A New and Effective Addition in the Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) Inhibitor Discovery. Int J Mol Sci 12(12):9440–9462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12129440
Tyagi R, Singh A, Chaudhary KK, Yadav MK (2022) Pharmacophore modeling and its applications. In: Bioinformatics. pp 269–289. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-89775-4.00009-2
Uba AI, Weako J, Keskin Ö, Gürsoy A, Yelekçi K (2019) Examining the stability of binding modes of the co-crystallized inhibitors of human HDAC8 by molecular dynamics simulation. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics:1–10. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2019.1615989
Uba AI, Yelekçi K (2017) Identification of potential isoform-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors for cancer therapy: a combined approach of structure-based virtual screening, ADMET prediction and molecular dynamics simulation assay. J Biomol Struct Dyn 36(12):3231–3245. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2017.1384402
Uba Aİ, YelekÇİ K (2017) Exploration of the binding pocket of histone deacetylases: the design of potent and isoform-selective inhibitors. Turk J Biol 41:901–918. https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-1701-26
Uba AI, Yelekçi K (2018a) Carboxylic acid derivatives display potential selectivity for human histone deacetylase 6: Structure-based virtual screening, molecular docking and dynamics simulation studies. Comput Biol Chem 75:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.05.004
Uba AI, Yelekçi K (2018b) Pharmacophore-based virtual screening for identification of potential selective inhibitors of human histone deacetylase 6. Comput Biol Chem 77:318–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.10.016
Uba AI, Yelekçi K (2019) Crystallographic structure versus homology model: a case study of molecular dynamics simulation of human and zebrafish histone deacetylase 10. J Biomol Struct Dyn 38(15):4397–4406. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2019.1691658
Urias BS, Pavan AR, Albuquerque GR, Prokopczyk IM, Alves TMF, de Melo TRF, Sartori GR, da Silva JHM, Chin CM, Santos JLD (2022) Optimization of Resveratrol Used as a Scaffold to Design Histone Deacetylase (HDAC-1 and HDAC-2) Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 15 (10). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101260
Vema A, Debnath S, Kalle AM (2022) Identification of novel HDAC8 selective inhibitors through ligand and structure based studies: Exploiting the acetate release channel differences among class I isoforms. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 15 (6). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103863
Volmar C-H, Wahlestedt C (2015) Histone deacetylases (HDACs) and brain function. Neuroepigenetics 1:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepig.2014.10.002
Wang Y, Stowe Ryan L, Pinello Christie E, Tian G, Madoux F, Li D, Zhao Lisa Y, Li J-L, Wang Y, Wang Y, Ma H, Hodder P, Roush William R, Liao D (2015) Identification of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Benzoylhydrazide Scaffold that Selectively Inhibit Class I Histone Deacetylases. Chem Biol 22(2):273–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.12.015
Wang Y, Fass J, Kaminow B, Herr JE, Rufa D, Zhang I, Pulido I, Henry M, Bruce Macdonald HE, Takaba K, Chodera JD (2022) End-to-end differentiable construction of molecular mechanics force fields. Chem Sci 13(41):12016–12033. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sc02739a
Wang P, Wang Z, Liu J (2020) Role of HDACs in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Molecular Cancer 19 (1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1127-7
Watson PJ, Fairall L, Santos GM, Schwabe JWR (2012) Structure of HDAC3 bound to co-repressor and inositol tetraphosphate. Nature 481(7381):335–340. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10728
Weichert W, Röske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T, Ebert MPA, Pross M, Dietel M, Denkert C, Röcken C (2008a) Association of patterns of class I histone deacetylase expression with patient prognosis in gastric cancer: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 9(2):139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(08)70004-4
Weichert W, Röske A, Niesporek S, Noske A, Buckendahl A-C, Dietel M, Gekeler V, Boehm M, Beckers T, Denkert C (2008b) Class I Histone Deacetylase Expression Has Independent Prognostic Impact in Human Colorectal Cancer: Specific Role of Class I Histone Deacetylases In vitro and In vivo. Clin Cancer Res 14(6):1669–1677. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-07-0990
Wilson AJ, Byun D-S, Nasser S, Murray LB, Ayyanar K, Arango D, Figueroa M, Melnick A, Kao GD, Augenlicht LH, Mariadason JM, Cleveland JL (2008) HDAC4 Promotes Growth of Colon Cancer Cells via Repression of p21. Mol Biol Cell 19(10):4062–4075. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e08-02-0139
Wu R, Wang S, Zhou N, Cao Z, Zhang Y (2010) A Proton-Shuttle Reaction Mechanism for Histone Deacetylase 8 and the Catalytic Role of Metal Ions. J Am Chem Soc 132(27):9471–9479. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja103932d
Yan G, Li D, Zhong X, Liu G, Wang X, Lu Y, Qin F, Guo Y, Duan S, Li D (2020) Identification of HDAC6 selective inhibitors: pharmacophore based virtual screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39(6):1928–1939. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1743760
Yao Y-L, Yang W-M, Seto E (2001) Regulation of Transcription Factor YY1 by Acetylation and Deacetylation. Mol Cell Biol 21(17):5979–5991. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.21.17.5979-5991.2001
You A, Tong JK, Grozinger CM, Schreiber SL (2001) CoREST is an integral component of the CoREST- human histone deacetylase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(4):1454–1458. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.98.4.1454
Yuan Z-l, Guan Y-j, Chatterjee D, Chin YE (2005) Stat3 Dimerization Regulated by Reversible Acetylation of a Single Lysine Residue. Science 307(5707):269–273. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1105166
Zhang Y, Gilquin B, Khochbin S, Matthias P (2006) Two catalytic domains are required for protein deacetylation. J Biol Chem 281(5):2401–2404. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C500241200
Zhang X, Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Yong S, Salas-Burgos A, Koomen J, Olashaw N, Parsons JT, Yang X-J, Dent SR, Yao T-P, Lane WS, Seto E (2007) HDAC6 Modulates Cell Motility by Altering the Acetylation Level of Cortactin. Mol Cell 27(2):197–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.033
Zhang L, Zhang J, Jiang Q, Zhang L, Song W (2018) Zinc binding groups for histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 33(1):714–721. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2017.1417274
Acknowledgements
AIU would like to thank Associate Professor Chun Wu of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Rowan University, NJ, United States for support.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AIU and GZ carried out the study and wrote the manuscript. Both authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Institutional review board statement
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling editor: S. Albrecht.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uba, A.I., Zengin, G. In the quest for histone deacetylase inhibitors: current trends in the application of multilayered computational methods. Amino Acids 55, 1709–1726 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03297-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03297-y