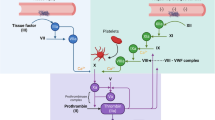
Abstract
Total elevated plasma homocysteine (Hcy) is a risk factor for thromboembolism. Vascular endothelium is important to regulate coagulation, but the impact of Hcy on the clot-promoting activity (CPA) of endothelial cells has not been fully understood. In our study, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were treated with Hcy (8, 20, 80, 200, 800 μmol/L) for 24 h. Annexin V was utilized to detect phosphatidylserine (PS) externalization and endothelial microparticles (MPs) formation. CPA was assessed by recalcification time and purified clotting complex tests. We found that Hcy enhanced the externalized PS and consequent CPA of HUVECs in a dose-dependent fashion, effect of Hcy had statistical significance at 800 μmol/L. In addition, Hcy also increased the shedding of procoagulant endothelial MPs. Blocking of PS with 128 nmol/L annexin V reduced approximately 70% CPA of HUVECs and endothelial MPs, but human anti-tissue factor antibody had little inhibitive effect. Our results showed that Hcy increased CPA of HUVECs via PS externalization and MPs release. Our present study has implications for hyperhomocysteinemia-related hypercoagulability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andree HA, Stuart MC, Hermens WT, Reutelingsperger CP, Hemker HC, Frederik PM, Willems GM (1992) Clustering of lipid-bound annexin V may explain its anticoagulant effect. J Biol Chem 267:17907–17912
Bach RR (2006) Tissue factor encryption. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:456–461
Brumatti G, Sheridan C, Martin SJ (2008) Expression and purification of recombinant annexin V for the detection of membrane alterations on apoptotic cells. Methods 44:235–240
Butenas S, Orfeo T, Mann KG (2009) Tissue factor in coagulation: which? where? when? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1989–1996
Cai B, Shan L, Gong D, Pan Z, Ai J, Xu C, Lu Y, Yang B (2009) Homocysteine modulates sodium channel currents in human atrial myocytes. Toxicology 256:201–206
Chirinos JA, Heresi GA, Velasquez H, Jy W, Jimenez JJ, Ahn E, Horstman LL, Soriano AO, Zambrano JP, Ahn YS (2005) Elevation of endothelial microparticles, platelets, and leukocyte activation in patients with venous thromboembolism. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1467–1471
Chironi GN, Boulanger CM, Simon A, Dignat-George F, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A (2009) Endothelial microparticles in diseases. Cell Tissue Res 335:143–151
Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, Pober JS, Wick TM, Konkle BA, Schwartz BS, Barnathan ES, McCrae KR, Hug BA, Schmidt AM, Stern DM (1998) Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood 91:3527–3561
Combes V, Simon AC, Grau GE, Arnoux D, Camoin L, Sabatier F, Mutin M, Sanmarco M, Sampol J, Dignat-George F (1999) In vitro generation of endothelial microparticles and possible prothrombotic activity in patients with lupus anticoagulant. J Clin Invest 104:93–102
Currò M, Condello S, Caccamo D, Ferlazzo N, Parisi G, Ientile R (2009) Homocysteine-induced toxicity increases TG2 expression in Neuro2a cells. Amino Acids 36:725–730
Dayal S, Wilson KM, Leo L, Arning E, Bottiglieri T, Lentz SR (2006) Enhanced susceptibility to arterial thrombosis in a murine model of hyperhomocysteinemia. Blood 108:2237–2243
den Heijer M, Willems HP, Blom HJ, Gerrits WB, Cattaneo M, Eichinger S, Rosendaal FR, Bos GM (2007) Homocysteine lowering by B vitamins and the secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Blood 109:139–144
Dong F, Zhang X, Li SY, Zhang Z, Ren Q, Culver B, Ren J (2005) Possible involvement of NADPH oxidase and JNK in homocysteine-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol 5:9–20
Fryer RH, Wilson BD, Gubler DB, Fitzgerald LA, Rodgers GM (1993) Homocysteine, a risk factor for premature vascular disease and thrombosis, induces tissue factor activity in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb 13:1327–1333
Fu Y, Zhou J, Li H, Cao F, Su Y, Fan S, Li Y, Wang S, Li L, Gilbert GE, Shi J (2010) Daunorubicin induces procoagulant activity of cultured endothelial cells through phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticles release. Thromb Haemost 104:1235–1241
Hajjar KA (1993) Homocysteine-induced modulation of tissue plasminogen activator binding to its endothelial cell membrane receptor. J Clin Invest 91:2873–2879
Hajjar KA, Jacovina AT (1998) Modulation of annexin II by homocysteine: implications for atherothrombosis. J Investig Med 46:364–369
Hajjar KA, Mauri L, Jacovina AT, Zhong F, Mirza UA, Padovan JC, Chait BT (1998) Tissue plasminogen activator binding to the annexin II tail domain: direct modulation by homocysteine. J Biol Chem 273:9987–9993
Hankey GJ, Eikelboom JW (1999) Homocysteine and vascular disease. Lancet 354:407–413
Hou J, Fu Y, Zhou J, Li W, Xie R, Cao F, Gilbert GE, Shi J (2011) Lactadherin functions as a probe for phosphatidylserine exposure and as an anticoagulant in the study of stored platelets. Vox Sang 100:187–195
Jacovina AT, Deora AB, Ling Q, Broekman MJ, Almeida D, Greenberg CB, Marcus AJ, Smith JD, Hajjar KA (2009) Homocysteine inhibits neoangiogenesis in mice through blockade of annexin A2-dependent fibrinolysis. J Clin Invest 119:3384–3394
Jakubowski H (2011) Quality control in tRNA charging-editing of homocysteine. Acta Biochim Pol 58:149–163
Jakubowski H, Boers GH, Strauss KA (2008) Mutations in cystathionine beta-synthase or methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene increase N-homocysteinylated protein levels in humans. FASEB J 22:4071–4076
Kerkeni M, Tnani M, Chuniaud L, Miled A, Maaroufi K, Trivin F (2006) Comparative study on in vitro effects of homocysteine thiolactone and homocysteine on HUVEC cells: evidence for a stronger proapoptotic and proinflammative homocysteine thiolactone. Mol Cell Biochem 291:119–126
Lambers JW, Cammenga M, König BW, Mertens K, Pannekoek H, van Mourik JA (1987) Activation of human endothelial cell-type plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) by negatively charged phospholipids. J Biol Chem 262:17492–17496
Lee SJ, Kim KM, Namkoong S, Kim CK, Kang YC, Lee H, Ha KS, Han JA, Chung HT, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2005) Nitric oxide inhibition of homocysteine-induced human endothelial cell apoptosis by down-regulation of p53-dependent Noxa expression through the formation of S-nitrosohomocysteine. J Biol Chem 280:5781–5788
Lentz SR, Sadler JE (1991) Inhibition of thrombomodulin surface expression and protein C activation by the thrombogenic agent homocysteine. J Clin Invest 88:1906–1914
Lentz SR, Sadler JE (1993) Homocysteine inhibits von Willebrand factor processing and secretion by preventing transport from the endoplasmic reticulum. Blood 81:683–689
McCully KS (2007) Homocysteine, vitamins, and vascular disease prevention. Am J Clin Nutr 86:1563S–1568S
Mercié P, Garnier O, Lascoste L, Renard M, Closse C, Durrieu F, Marit G, Boisseau RM, Belloc F (2000) Homocysteine-thiolactone induces caspase-independent vascular endothelial cell death with apoptotic features. Apoptosis 5:403–411
Nachman RL (1992) Review: Stratton lecture. Thrombosis and atherogenesis: molecular connections. Blood 79:1897–1906
Nishinaga M, Ozawa T, Shimada K (1993) Homocysteine, a thrombogenic agent, suppresses anticoagulant heparan sulfate expression in cultured porcine aortic endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 92:1381–1386
Perła-Kaján J, Twardowski T, Jakubowski H (2007) Mechanisms of homocysteine toxicity in humans. Amino Acids 32:561–572
Piccin A, Murphy WG, Smith OP (2007) Circulating microparticles: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Blood Rev 21:157–171
Reviakine II, Bergsma-Schutter W, Brisson A (1998) Growth of protein 2-D crystals on supported planar lipid bilayers imaged in situ by AFM. J Struct Biol 121:356–361
Rodgers GM, Conn MT (1990) Homocysteine, an atherogenic stimulus, reduces protein C activation by arterial and venous endothelial cells. Blood 75:895–901
Rodgers GM, Kane WH (1986) Activation of endogenous factor V by a homocysteine-induced vascular endothelial cell activator. J Clin Invest 77:1909–1916
Sauls DL, Warren M, Hoffman M (2011) Homocysteinylated fibrinogen forms disulfide-linked complexes with albumin. Thromb Res 127:576–581
Shi J, Shi Y, Waehrens LN, Rasmussen JT, Heegaard CW, Gilbert GE (2006) Lactadherin detects early phosphatidylserine exposure on immortalized leukemia cells undergoing programmed cell death. Cytometry A 69:1193–1201
Suhara T, Fukuo K, Yasuda O, Tsubakimoto M, Takemura Y, Kawamoto H, Yokoi T, Mogi M, Kaimoto T, Ogihara T (2004) Homocysteine enhances endothelial apoptosis via upregulation of Fas-mediated pathways. Hypertension 43:1208–1213
Tait JF, Frankenberry DA, Shiang R, Murray JC, Adler DA, Disteche CM (1991) Chromosomal localization of the human gene for annexin V (placental anticoagulant protein I) to 4q26–q28. Cytogenet Cell Genet 57:187–192
Taube J, McWilliam N, Luddington R, Byrne CD, Baglin T (1999) Activated protein C resistance: effect of platelet activation, platelet-derived microparticles, and atherogenic lipoproteins. Blood 93:3792–3797
Thambyrajah J, Townend JN (2000) Homocysteine and atherothrombosis-mechanisms for injury. Eur Heart J 21:967–974
Undas A, Brozek J, Jankowski M, Siudak Z, Szczeklik A, Jakubowski H (2006) Plasma homocysteine affects fibrin clot permeability and resistance to lysis in human subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1397–1404
Zhang G, Gurtu V, Kain SR, Yan G (1997) Early detection of apoptosis using a fluorescent conjugate of annexin V. Biotechniques 23:525–531
Zhang C, Cai Y, Adachi MT, Oshiro S, Aso T, Kaufman RJ, Kitajima S (2001) Homocysteine induces programmed cell death in human vascular endothelial cells through activation of the unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem 276:35867–35874
Zhou J, Liu S, Ma M, Hou J, Yu H, Lu C, Gilbert GE, Shi J (2009) Procoagulant activity and phosphatidylserine of amniotic fluid cells. Thromb Haemost 101:845–851
Zhou J, Shi J, Hou J, Cao F, Zhang Y, Rasmussen JT, Heegaard CW, Gilbert GE (2010) Phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant activity in acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Thromb Haemost 8:773–782
Zwaal RF, Schroit AJ (1997) Pathophysiologic implications of membrane phospholipid asymmetry in blood cells. Blood 89:1121–1132
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2007CB512000/2007CB512006) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (30973532). The authors thank Li Zhang, Yakun Zhang and Jing Li for excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
J. Zhu and R. Xie equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Xie, R., Piao, X. et al. Homocysteine enhances clot-promoting activity of endothelial cells via phosphatidylserine externalization and microparticles formation. Amino Acids 43, 1243–1250 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1196-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1196-4