Abstract
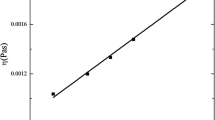
An experimental procedure, based on proton magnetic relaxation, is presented to determine the absolute dynamic viscosity in blood serum (ηS). The blood serum samples were obtained voluntary from whole blood of healthy individuals and patients, and processed by classical methods (centrifugation and decanting). The Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill pulse sequence was employed to determine the transverse proton magnetic relaxation time (T2) in a Tecmag Magnetic Resonance console coupled to a magnet of 0.095 T and the temperature of measurement was 293 K. A theoretical linear behavior of the transverse proton magnetic relaxation rate (1/T2) as a function of ηS was obtained after the consideration of blood serum as an extremely diluted solution of albumin and globulins, and assuming a fast exchange of water molecules between the bound phase and the solvent. A value of ηS = 1.29 ± 0.07 mPa s was obtained in samples belonging to 20 voluntary healthy individuals, which statistically match with the value obtained using the Ostwald viscometer for the same samples (ηS = 1.32 ± 0.04 mPa s, P = 0.104319 > 0.05, α = 0.05). The potential medical utility of the presented proton magnetic resonance procedure was demonstrated in patients with Multiple Myeloma (24) and Sickle Cell Disease (34), in which ηS resulted increased with values of 1.40 ± 0.18 mPa s (P = 0.0137509 < 0.05, α = 0.05) and 1.36 ± 0.10 mPa s (P = 0.00809615 < 0.05, α = 0.05), respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used can be accessed contacting directly to the corresponding author.
References
R. Rosencranz, S.A. Bogen, Am. J. Clin. Pathol.Pathol. A 125, S78 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1309/FFF7U8RRPK26VAPY
M.A. Gertz, Blood A 132, 1379 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-06-846816
M.A. Lores-Guevara, Y. Mengana-Torres, J.C. García-Naranjo, N. Rodríguez-Suárez, L.C. Suárez-Beyries, M.A. Marichal-Feliú, T. Simón-Boada, I.C. Rodríguez-Reyes, J. Phillippé. Appl. Magn. Reson. A 49, 1075 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-018-1026-x
Y. Mengana-Torres, M.A. Lores-Guevara, J.C. García-Naranjo, B.T. Ricardo-Ferro, L.C. Suárez-Beyries, I.C. Rodríguez-Reyes, J. Phillippé, Int. J. Biochem. Biophys. Mol. Biol. A 4, 25 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijbbmb.20190402.12
Z.H. Endre, P.W. Kuchel, Biophys. Chem. A 24, 333 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-4622(86)85039-6
M. Lores, C. Cabal, O. Nascimento, A.M. Gennaro, Appl. Magn. Reson. A30, 121 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166986
R. Hong, M.J. Cima, R. Weissleder, L. Josephson, Magn. Reson. Med. A59, 515 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.21526
L. Peña-Zamora, Graduate Thesis, Universidad de Oriente, Santiago de Cuba, Cuba, 2005
K. Venu, V.P. Denisov, B. Halle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. A 119, 3122 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja963611t
M. Lores, C. Cabal, Appl. Magn. Reson.Reson. A 28, 79 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166995
M.A. Lores-Guevara, J.C. García-Naranjo, C.A. Cabal-Mirabal, Appl. Magn. Reson.Reson. A 50, 541 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-018-1104-0
O.K. Dazkiewic, J.W. Hennel, B. Lubas, T.W. Szczepkowski, Nature A200, 1006 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/2001006a0
R.S. Menon, P.S. Allen, Biophys. J. A 57, 389 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82555-8
P.S. Allen, M.E. Castro, E.O. Treiber, J.A. Lunt, D.P.J. Boisvert, Phys. Med. Biol. A 31, 699 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/31/7/001
K.J. Olszewski, Acta Phys. Polonica A. A 82, 487 (1992). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.82.487
M.A. Lores-Guevara, Y. Rodríguez-Almira, E.R. Pérez-Delfín, Revista Cubana de Química. A XIV, 3 (2002)
D. J. Ernst, L. O. Balance, R. R. Calam, R. McCall, S. S. Smith, D. I. Szamosi, D. J. Warunek, Approved Standard CLSI. A 27 (2007)
Y. Mengana-Torres, PhD Thesis, Universidad de Oriente, Santiago de Cuba, Cuba, 2024
M.A. Lores-Guevara, Aplicaciones Médicas de la Relajación Magnética Nuclear, 1st edn. (Ediciones Universidad de Oriente, Santiago de Cuba, 2023)
S. Meiboom, D. Gill, Rev. Sci. Instrum. A29, 688 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1716296
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Belgian Development Cooperation through VLIR-UOS (Flemish Interuniversity Council-University Cooperation for Development) in the context of the Institutional University Cooperation program with Universidad de Oriente. The authors also want to thank the MRI RESEARCH CENTRE of the University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, Canada, for all the support received to finalize this work.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Yulianela Mengana Torres, Manuel Arsenio Lores Guevara; methodology: Yulianela Mengana Torres, Manuel Arsenio Lores Guevara, Hugo Ferrales Milán, formal analysis and investigation: Yulianela Mengana Torres, Manuel Arsenio Lores Guevara, Hugo Ferrales Milán, Yamirka Alonso Geli; writing—original draft preparation: Manuel Arsenio Lores Guevara; writing—review and editing: Yulianela Mengana Torres, Manuel Arsenio Lores Guevara, Juan Carlos García Naranjo; resources: Lidia Clara Suárez Beyries, Samuel Jorge Rosales Rodríguez, Inocente Rodríguez Reyes; supervision: Yulianela Mengana Torres, Manuel Arsenio Lores Guevara, Juan Carlos García Naranjo.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This research has been performed in agreement with all the ethical rules corresponding to scientific research in human beings in accordance with the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki (1964, updated until 2013) of the World Medical Association. The approval from the ethical committee of the “Juan Bruno Zayas Alfonso” General Hospital was obtained.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial and/or non-financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mengana Torres, Y., Lores Guevara, M.A., Ferrales Milán, H. et al. Dynamic Viscosity of Blood Serum Determined Using Proton Magnetic Relaxation. Appl Magn Reson (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-024-01644-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-024-01644-0