Abstract
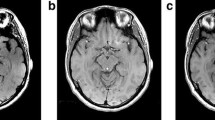
Biopsies revealed an increased iron content in the dopaminergic neurons of nigrosomes in substantia nigra for Parkinson’s disease. In gradient echoes paramagnetic iron leads to a negative phase shift in the complex signal. The combination of magnitude and phase images allows to obtain susceptibility-weighted images (SWI) and quantitative susceptibility maps (QSM) which highlight the resulting susceptibility changes and allow selective imaging of the substantia nigra. The pigment neuromelanin in substantia nigra can be imaged separately by magnetization transfer. Both methods serve as biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease and confirm the disintegration of neuromelanin by iron compounds as the origin of the disease. Another application of MRI in Parkinson’s disease is the control of the localization of implanted electrodes for therapy using deep brain stimulation.


Reproduced from Wikipedia “Susceptibility—questions and answers in MRI”

Reproduced from Ref. [4]

(reproduced from Ref. [5])

(reproduced from Ref. [4]) (Color figure online)

(reproduced from Ref. [10]) (Color figure online)

reproduced from Ref. [11]

(reproduced from Ref. [4])

Reproduced from Ref. [10]

Reproduced from Ref. [17]


Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.M. Haacke, S. Mittal, Z. Wu, J. Neelavalli, Y.-C.N. Cheng, Am. J. Neuroradiol. 30(1), 19 (2009)
S. Mittal, Z. Wu, J. Neelavalli, E.M. Haacke, Am. J. Neuroradiol. 30, 232 (2009)
E.M. Haacke, Y. Xu, Y.-C.N. Cheng, J.R. Reichenbach, Mag. Reson. Med. 52, 612–618 (2004)
C. Liu, H. Wei, N.-J. Gong, M. Cronin, R. Dibb, K. Decker, Tomography 1(1), 3–17 (2015)
J. Liu, T. Liu, L. de Rochefort, J. Ledoux, I. Khalidov, W. Chen, A.J. Tiouris, C. Wisnieff, P. Spincemaille, M.R. Prince, Y. Wang, Neuroimage 59(3), 2560–2568 (2012)
F. Schweser, A. Deistung, B.W. Lehr, J.R. Eciehnbach, Neuroimage 54, 2789 (2011)
A. Warton, R. Bowtell, Neuroimage 53, 515 (2010)
N. Krebs et al., Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 18, 702 (2010)
G. Du, T. Liu, M.M. Lewis, J. Vesek, L. Kon, M. Styner, Q.X. Yang, X. Huang, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 22, 1912 (2014)
M. Brammerloh, E. Kirilina, R. Sibgatulin, K.-H. Herrmann, T. Reinert, C. Jäger, Pelicon, P. Vavpetič, K.J. Pine, A. Deistung, M. Morawski, J.R. Reichenbach, N. Weiskopf, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 28, 0160 (2020)
K. Mi Lee, H.-G. Kim, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 24, 1249 (2016)
Z. Cheng, Y. Li, M. Jokar, S.K. Sethi, W. Chen, S. Chen, F. Yan, E.M. Haacke, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 28, 0201 (2020)
P.J. Basser, C. Pierpaoli, J. Magn. Reson. ser. B 111, 209–219 (1996)
R. Patriat, J. Kaplan, J.J. Niederer, S.A. Huffmaster, M. Petrucci, N. Harel, C. McKinnon, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 26, 0425 (2018)
S.M. Smith, J. Andersson, E.J. Auerbach, C.F. Beckmann, J. Bijsterbosch, G. Douaud, E. Duff, D.A. Feinberg, L. Griffanti, Ludovica NeuroImage 80, 168 (2013)
U. Eichhoff, Appl. Magn. Reson. 49, 579–587 (2018)
K.R. Sreenivasan, E. Bayram, V. Mishra, Z. Yang, C. Bird, X. Zhuang, D. Cordes, B. BluettProc, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 26, 0426 (2018)
K.S. Choi, P.R. Posse, P.E. Holtzheimer, C.C. McIntyre, X.P. Hu, H.S. Mayberg, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 21, 1183 (2013)
J.R. Younce, H.-Y. Lai, Y. Yu, I. Shih, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 21, 0751 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eichhoff, U. Advanced MRI-Methods for Evaluation of Parkinson’s Disease. Appl Magn Reson 52, 1707–1719 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01365-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01365-8