Abstract
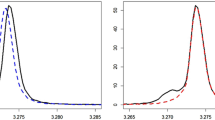
The filter diagonalization method (FDM) was implemented and used instead of fast Fourier transform (FFT) to obtain the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra from the free induction decay (FID) signals. The areas obtained by the FDM, from selected absorption lines, were used as input for a multidimensional method of data analysis. This procedure was applied in a NMR-based metabolomics investigation. In FDM, instead of spectra, the absorption peaks’ specification, such as central frequency, line width, amplitude and relative phases, are estimated and the spectra are built using this information. Therefore, one can select the lines by width and intensity to exclude the broad lines such as baseline, solvent line and albumin peak. Also lines with small amplitude such as noise can be excluded from the spectra. Moreover, the spectra do not suffer from aliasing or baseline problems. These characteristics are fundamental in the metabolomics investigations. To show the superiority of our method over the standard FFT to obtain the spectra, we reconstructed the spectra from simulated FID by both methods. As an example, this new approach is used to analyze the non-small cell lung cancer A549 exposed to different treatments and principal component analysis is used to compare the performance of both methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The defined Hamiltonian is not hermitian, but, is symmetrical, in spite of this fact, it is possible to adapt the theory of quantum mechanics for this symmetric Hamiltonian.
Laboratório Nacional de Biociências.
References
E.D. Lawe, J. Skiling, J. Staunton, S. Sibisi, R. Brereton, J. Magn. Reson. 62, 437–452 (1985)
H. Barkhuijsen, R. Debeer, W.M.M.J. Bovee, J.H.N. Creyghton, D. Vanormondt, Magn. Reson. Med. 2(1), 86–89 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910020111
R.H. Cervantes, S.R. Rabbani, Solid State Commun. 110(4), 215–220 (1999)
S. Haykin (ed.), Nonlinear Methods of Spectral Analysis (Springer, Berlin New York, 1979)
V.A. Mandelshtam, H.S. Taylor, J. Chem. Phys. 107(17), 6756–6769 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.475324
J.H. Chen, V.A. Mandelshtam, A.J. Shaka, J. Magn. Reson. 146(2), 363–368 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1006/jmre.2000.2155
C. Magon, Livre docencia, Instituto de Física da USP de São Carlos (2007)
B. Dai, C.D. Eads, Magn. Reson. Chem. 48(3), 230–234 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.2550
A. Zhang, H. Sun, P. Wang, Y. Han, X. Wang, Analyst 137(2), 293–300 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C1AN15605E
M. Mamas, W.B. Dunn, L. Neyses, R. Goodacre, Arch. Toxicol. 85(1), 5–17 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0609-6
V.N. Kristensen, O.C. Lingjoerde, H.G. Russnes, H.K.M. Vollan, A. Frigessi, A.-L. Borresen-Dale, Nat. Rev. Cancer 14(5), 299–313 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3721
L. Fernandez, A. Rodriguez, P. Garcia, ISME J. 12(5), 1171–1179 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-018-0049-5
T. Young, A.C. Alfaro, Rev. Aquac. 10(1), 26–56 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12146
R. Alcazar, T. Altabella, F. Marco, C. Bortolotti, M. Reymond, C. Koncz, P. Carrasco, A.F. Tiburcio, Planta 231(6), 1237–1249 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1130-0
J.M. Cevallos-Cevallos, J.I. Reyes-De-Corcuera, E. Etxeberria, M.D. Danyluk, G.E. Rodrick, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 20(11–12), 557–566 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2009.07.002
J.G. Bundy, M.P. Davey, M.R. Viant, Metabolomics 5(1), 3–21 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-008-0152-0
R. Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and its Applications. McGraw-Hill Series in Electrical Engineering Circuits and Systems (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1986)
I. Karaman, D.L.S. Ferreira, C.L. Boulangé, M.R. Kaluarachchi, D. Herrington, A.C. Dona, R. Castagné, A. Moayyeri, B. Lehne, M. Loh, P.S. de Vries, A. Dehghan, O.H. Franco, A. Hofman, E. Evangelou, I. Tzoulaki, P. Elliott, J.C. Lindon, T.M.D. Ebbels, J. Proteome Res. 15(12), 4188–4194 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00125
R. Vettukattil, in Methods in Molecular Biology (Springer Nature, 2015), pp. 123–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2377-9_10
D. Neuhauser, J. Chem. Phys. 93(4), 2611–2616 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.458900
M. Goldman, Quantum Description of High-Resolution NMR in Liquids, International Series of Monographs on Chemistry (Oxford University Press, Clarendon, 1991)
Chenomx Inc., Chenomx nmr suite 7.7 (2013). https://www.chenomx.com/
P.S. Bacchi, A.C. Bloise, S.O. Bustos, L. Zimmermann, R. Chammas, S.R. Rabbani, Springerplus 3, 470 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-470
A.B. Martins-Bach, A.C. Bloise, M. Vainzof, S.R. Rabbani, Magn. Reson. Imaging 30(8), 1167–1176 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2012.04.003
A.B. Martins-Bach, A.C. Bloise, S.R. Rabbani, M. Vainzof, Neuromuscul. Disord. 21(9–10), 655–655 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2011.06.805
F. Savorani, G. Tomasi, S.B. Engelsen, J. Magn. Reson. 202(2), 190–202 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2009.11.012
M. Hollander, D.A. Wolfe, E. Chicken, The One-Way Layout (Wiley, New York, 2015), Ch. 6, pp. 202–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119196037.ch6
P.H. Kvam, B. Vidakovic, Designed Experiments (Wiley, New Jersey, 2007), Ch. 8, pp. 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470168707.ch8
I. Jolliffe, Principal Component Analysis (Springer, New York, 2002)
B.B. Misra, S. Mohapatra, Electrophoresis 40(2), 227–246 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201800428
H.U. Zacharias, M. Altenbuchinger, W. Gronwald, Metabolites 8(3), 47 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8030047
Acknowledgements
The author HJC wants to thank Dr. Claudio Jose Magon for the useful discussions about the FDM. The NMR experiments were executed at the Laboratório Nacional de Biociências (LNBIO), part of the Centro Nacional de Pesquisa em Energia e Materiais (CNPEM), project RMN-20606. The authors desire to express gratitude to Sílvia Rocco and Maurício Luís Sforça of the LNBIO for their assistance in NMR measurements. The non-small cell lung cancer, A549 cells line, were cultivated with collaboration of Dr. Roger Chammas group in Cancer Institute of the São Paulo State (ICESP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cervantes, H.J., Kopel, F.M. & Rabbani, S.R. Metabolomics Data Analysis Improvement by Use of the Filter Diagonalization Method. Appl Magn Reson 50, 1369–1380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-019-01158-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-019-01158-0