Abstract
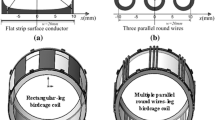
The design and development of dedicated radiofrequency (RF) coils is a fundamental task to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) applications. Coil resistance reduces the SNR and should be minimized by employing conductors of appropriate shape and cross section. At RF, the conductor resistance is increased due to the skin effect, which distributes the current primarily on the surface of the conductor instead of uniformly over the cross section. In particular, in rectangular shape conductors the current density is concentrated in the high-curvature area and increases the conductor resistance, while rounded conductors present lower resistance and demonstrate improvements in performance especially in low-frequency tuned coils. This paper summarizes the different methods for estimating conductor losses in RF coils for NMR applications, whose performance strongly affect quality data. Because the impact to coil loss from conductors with different cross-sectional area is not something generally recognized and nor addressed in many other coil design works, we believe the review could be interesting for researchers working in the field of NMR coil design and development.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Jin, Electromagnetic Analysis and Design in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1999)
D.I. Hoult, R.E. Richards, J. Magn. Reson. 24, 71–85 (1976)
D.I. Hoult, P.C. Lauterbur, J. Magn. Reson. 34, 415–433 (1979)
T. Claasen-Vujcic, H.M. Borsboom, H.J.G. Gaykema, T. Mehlkopf, Magn. Reson. Med. 36, 111–116 (1996)
G. Giovannetti, V. Hartwig, V. Positano, N. Vanello, Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 42(2), 109–134 (2014)
D.I. Hoult, Concepts Magn. Reson. 12, 173–187 (2000)
A. Haase, F. Odoj, M. Von Kienlin, J. Warnking, F. Fidler, A. Weisser, M. Nittka, E. Rommel, T. Lanz, B. Kalusche, M. Griswold, Concepts Magn. Reson. 12(6), 361–388 (2000)
C.E. Hayes, W.A. Edelstein, J.F. Schenck, O.M. Mueller, M. Eash, J. Magn. Reson. 63(3), 622–628 (1985)
W.A. Edelstein, G.H. Glover, C.J. Hardy, R.W. Redington, Magn. Reson. Med. 3, 604–618 (1986)
S.E. Hurlston, G.P. Cofer, G.A. Johnson, Int. J. Imag. Syst. Technol. 8, 277–284 (1997)
C. Chen, D.J. Hoult, Biomedical Magnetic Resonance Technology (IOP, Bristol, 1989)
R.E. Matick, Transmission Lines for Digital and Communication Networks (McGraw–Hill, New York, 1969)
V. Belevitch, Philips Tech. Rev. 32(6/7, 18), 221–231 (1971)
J.W. Carlson, Magn. Reson. Med. 3, 778–790 (1986)
K. Schmidt, Approximate R. F. resistance of rectangular cross section conductors. http://fermi.la.asu.edu/w9cf/articles/equiv/equiv.html. Accessed 10 Jan 2016
F.E. Terman, Radio Engineers’ Handbook (McGraw-Hill Book Comp., New York, London, 1943)
D. Gerling, Approximate analytical calculation of the skin effect in rectangular wires. International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS 2009), 15–18 November 2009, Tokyo, (2009), p. 1–6
J. Guo, D. Kajfez, A.W. Glisson, Electr. Lett. 33(11), 966–967 (1997)
R.A. Sainati, T.J. Moravec, I.E.E.E. Trans, Circuits Syst. 36, 533–540 (1989)
J. Mispelter, M. Lupu, A. Briguet, NMR Probeheads for Biophysical and Biomedical Experiments (Imperial College Press, London, 2015)
R. Faraji-Dana, Y. Chow, in IEE Proceedings, 1990, vol. 137, Pt. H, no. 2
G. Giovannetti, R. Francesconi, L. Landini, M.F. Santarelli, V. Positano, V. Viti, A. Benassi, Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B: Magn. Reson. Eng. 20B, 9–16 (2004)
F.D. Doty, G. Entzminger Jr, C.D. Hauck, J.P. Staab, J. Magn. Reson. 138, 144–154 (1999)
G. Giovannetti, V. Hartwig, L. Landini, M.F. Santarelli, Appl. Magn. Reson. 39, 391–399 (2010)
G. Giovannetti, V. Hartwig, L. Landini, M.F. Santarelli, Conc. Magn. Reson. Part B 41B(2), 57–61 (2012)
A. Kuehne, S. Goluch, P. Waxmann, F. Seifert, B. Ittermann, E. Moser, E. Laistler, Magn. Reson. Med. 74(4), 1165–1176 (2015)
A. Kuehne, H. Waiczies, E. Moser, E. Laistler, in Proceedings of the ISMRM, Milan, Italy, 2014, p. 1363
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giovannetti, G., Tiberi, G. Skin Effect Estimation in Radiofrequency Coils for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Applications. Appl Magn Reson 47, 601–612 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-016-0780-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-016-0780-x