Abstract
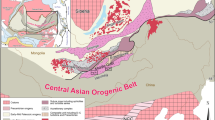
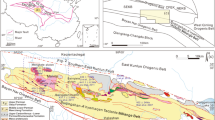
This paper presents new SHRIMP zircon U–Pb chronology, major and trace element, and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic data of two Early Paleozoic granitic plutons (Yierba and North Kudi) from the western Kunlun orogen, in attempt to further constrain the Proto-Tethys evolution. SHRIMP zircon U–Pb dating shows that the Yierba pluton was emplaced in the Middle Cambrian (513 ± 7 Ma) and the North Kudi pluton was emplaced in the Late Silurian (420.6 ± 6.3 Ma). The Yierba pluton consists of quartz monzodiorite, quartz monzonite and granodiorite. These granitoids are metaluminous and potassic, with initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios of 0.7072–0.7096, εNd (T) of −0.2 to −1.6 and εHf (T) (in-situ zircon) of −1.2. Elemental and isotopic data suggest that they were formed by partial melting of subducted sediments, with subsequent melts interacting with the overlying mantle wedge in an oceanic island arc setting in response to the intra-oceanic subduction of Proto-Tethys. The North Kudi pluton consists of syenogranite and alkali-feldspar granite. These granites are metaluminous to weakly peraluminous and potassic. They show an affinity of A1 subtype granite, with initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios of 0.7077–0.7101, εNd (T) of −3.5 to −4.0 and εHf (T) (in-situ zircon) of −3.9. Elemental and isotopic data suggest that they were formed by partial melting of the Precambrian metamorphic basement at a shallow depth (<30 km) during the post-orogenic regime caused by Proto-Tethyan oceanic slab break-off. Our new data suggest that the subduction of the Proto-Tethyan oceanic crust was as early as Middle Cambrian (∼513 Ma) and the final closure of Proto-Tethys was not later than Late Silurian (∼421 Ma), most probably in Middle Silurian.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud NO, Brunel M, Cantagrel JM, Tapponnier P (1993) High cooling and denudation rates at Kongur Shan, Eastern Pamir (Xinjiang, China) revealed by 40Ar/39Ar Alkali Feldspar Thermochronology. Tectonics 12:1335–1346
Bonin B (1990) From orogenic to anorogenic settings: evolution of granitoid suites after a major orogenesis. Geol J 25:261–270
Bouvier A, Vervoort JD, Patchett PJ (2008) The Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd isotopic composition of CHUR: Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets. Earth Planet Sci Lett 273:48–57
Boynton WV (1984) Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed) Rare earth element geochemistry. Developments in Geochemistry 2:63–114
Brunel M, Arnaud N, Tapponnier P, Pan Y, Wang Y (1994) Kongur Shan normal fault: type example of mountain building assisted by extension (Karakoram fault, eastern Pamir). Geology 22:707–710
Collins WJ, Beams SD, White AJR (1982) Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contrib Mineral Petrol 80:189–200
Ding DG, Wang DX, Liu WX (1996) The Western Kunlun Orogenic Belt and Basin (in Chinese). Geol Publ House, Beijing 36:1–224
Eby GN (1992) Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology 20:641–644
Gao JF, Lu JJ, Lai MY, Lin YP, Pu W (2003) Analysis of trace elements in rock samples using HR-ICPMS. J Nanjing Univ (Natural Sci) 39:844–850 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Green TH, Watson EB (1982) Crystallization of apatite in natural magmas under high pressure, hydrous conditions, with particular reference to ‘Orogenic’ rock series. Contrib Mineral Petrol 79:96–105
Hermann J, Spandler CJ (2008) Sediment melts at sub-arc depths: an experimental study. J Petrol 49:717–740
Hou KJ, Li YH, Zou TR, Qu XM, Shi YR, Xie GQ (2007) Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications. Acta Petrol Sin 23:2595–2604 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hsü K, Pan GT, Sengör A (1995) Tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau: a working hypothesis based on the archipelago model of orogenesis. Int Geol Rev 37:473–508
Ionov DA, O’Reilly SY, Griffin WL (1997) Volatile-bearing minerals and lithophile trace elements in the upper mantle. Chem Geol 141:153–184
Jia RY, Jiang YH, Liu Z, Zhao P, Zhou Q (2013) Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of early Silurian high-K calc-alkaline granites and their potassic microgranular enclaves, western Kunlun orogen, NW Tibetan Plateau. Int Geol Rev. doi:10.1080/00206814.2012.755766
Jiang CF, Yang JS, Feng BG, Zhu Z (1992) Opening and closing tectonics of the Kunlun Mountains (in Chinese). Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Ling HF, Zhou XR, Rui XJ, Yang WZ (2002) Petrology and geochemistry of shoshonitic plutons from the western Kunlun orogenic belt, Xinjiang, northwestern China: implications for granitoid geneses. Lithos 63:165–187
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Ling HF, Dai BZ (2006) Low-degree melting of a metasomatized lithospheric mantle for the origin of Cenozoic Yulong monzogranite-porphyry, east Tibet: geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf isotopic constraints. Earth Planet Sci Lett 241:617–633
Jiang YH, Liao SY, Yang WZ, Shen WZ (2008) An island arc origin of plagiogranites at Oytag, western Kunlun orogen, northwest China: SHRIMP zircon U–Pb chronology, elemental and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic geochemistry and Paleozoic tectonic implications. Lithos 106:323–335
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Dai BZ, Liao SY, Zhao KD, Ling HF (2009) Middle to late Jurassic felsic and mafic magmatism in southern Hunan Provience, Southeast China: implications for a continental arc to rifting. Lithos 107:185–204
Jiang YH, Liu Z, Jia RY, Liao SY, Zhou Q, Zhao P (2012) Miocene potassic granite-syenite association in western Tibetan Plateau: implications for shoshonitic and high Ba–Sr granite genesis. Lithos 134–135:146–162
Jiang YH, Jia RY, Liu Z, Liao SY, Zhao P, Zhou Q (2013) Origin of Middle Triassic high-K calc-alkaline granitoids and their potassic microgranular enclaves from the western Kunlun orogen, northwest China: a record of the closure of Paleo-Tethys. Lithos 156–159:13–30
Kay RW, MahlburgKay S (1993) Delamination and delamination magmatism. Tectonophysics 219:177–189
Liao SY, Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Yang WZ, Zhou Q, Jin GD, Zhao P (2010) Subducting sediment-derived arc granitoids: evidence from the Datong pluton and its quenched enclaves in the western Kunlun orogen, northwest China. Miner Petrol 100:55–74
Ludwig KR (2001a) Squid 1.02, in a user manual. Berkeley Geochronological Center Special Publication, Berkeley, pp 1–219
Ludwig KR (2001b) Using Isoplot/EX, version 2.49. A geochronological toolkit for microsoft excel. Berkeley Geochronological Center Special Publication, Berkeley, pp 1–55
Martin H, Smithies RH, Rapp R, Moyen JF, Champion D (2005) An overview of adakite, tonalite–trondhjemite–granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos 79:1–24
Matte P, Tapponnier P, Arnaud N, Bourjot L, Avouac JP, Vidal P, Qing L, Pan YS, Yi W (1996) Tectonics of Western Tibet, between the Tarim and the Indus. Earth Planet Sci Lett 142:311–330
Mattern F, Schneider W (2000) Suturing of the Proto-and Paleo-Tethyan oceans in the western Kunlun (Xinjiang, China). J Asian Earth Sci 18:637–650
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1985) Isotopic and geochemical systematics in Tertiary-Recent basalts from southeastern Australia and implication for the sub-continental lithosphere. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49:2051–2067
Pan YS (1990) Tectonic features and evolution of the western Kunlun mountain region. Sci Geol Sin 25:224–232
Pan YS (1996) Geological evolution of the Karakoram and Kunlun Mountains. Seismological Press, Beijing, p 288
Pan YS, Wang Y (1994) Tectonic evolution along the geotraverse from Yecheng to Shiquanhe. Acta Geol Sin 68:295–307
Patino Douce AE, Johnston AD (1991) Phase equilibria and melt productivity in the politic system: implication for the origin of peraluminous granitoids and aluminous granulites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 107:202–218
Pearce JA, Harris NBW, Tindle AG (1984) Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J Petrol 25:956–983
Pu W, Zhao K, Ling H, Jiang S (2004) High precision Nd isotope measurement by means of Triton TI mass spectrometry. Acta Geol Sin 25:271–274 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Pu W, Gao JF, Zhao KD, Ling H, Jiang S (2005) Separation method of Rb–Sr, Sm–Nd using DCTA and HIBA. J Nanjing Univ (Natural Sci) 41:445–450 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Rapp RP, Watson EB (1995) Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8 32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling. J Petrol 36:891–931
Rapp RP, Shimizu N, Norman MD, Applegate GS (1999) Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: experimental constraints at 3.8 Ga. Chem Geol 160:335–356
Schmidt MW, Vielzeuf D, Auzanneau E (2004) Melting and dissolution of subducting crust at high pressures: the key role of white mica. Earth Planet Sci Lett 228:65–84
Sisson TW, Ratajeski K, Hankins WB, Glazner AF (2005) Voluminous granitic magmas from common basaltic sources. Contrib Mineral Petrol 148:635–661
Song B, Zhang YH, Wan YS (2002) Mounting and analytical procedure of zircon SHRIMP dating. Geol Rev 48:26–30 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Streckeisen A, Le Maitre RW (1979) A chemical approximation to the model QAPF classification of the igneous rocks. Neues Jahrbuch Mineralogie Abteilung 136:169–206
Vervoort J, Patchett PJ, Blichert-Toft J, Albarede F (1999) Relationships between Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd isotopic systems in the global sedimentary system. Earth Planet Sci Lett 168:79–99
Wang YZ (1983) The age of the Yishak group of Western Kunlun, and tectonic significance. Xinjiang Geol 1:1–8 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang ZH, Sun S, Hou QL, Li JL (2001) Effect of melt-rock interaction on geochemistry in the Kudi ophiolite (western Kunlun Mountains, northwestern China): implication for ophiolite origin. Earth Planet Sci Lett 191:33–48
Wang ZH, Sun S, Li JL, Hou QL (2002) Petrogenesis of tholeiite associations in Kudi ophiolite (western Kunlun Mountains, northwestern China): implications for the evolution of back-arc basins. Contrib Mineral Petrol 143:471–483
Wang Q, Xu JF, Jian P, Bao ZW, Zhao ZH, Li CF, Xiong XL, Ma JL (2006) Petrogenesis of adakitic porphyries in an extensional tectonic setting, Dexing, South China: implications for the genesis of porphyry copper mineralization. J Petrol 47:119–144
Watson EB, Harrison TM (1983) Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth Planet Sci Lett 64:295–304
Whalen JB, Currie KL, Chappell BW (1987) A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib Mineral Petrol 95:407–419
William IS, Buick A, Cartwright I (1996) An extended episode of early Mesoproterozoic metamorphic fluid flow in the Reynold Region, Central Australia. J Metamorph Geol 14:29–47
Wright JB (1969) A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis. Geol Mag 106:370–384
Wu FY, Yang YH, Xie LW, Yang JH, Xu P (2006) Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U–Pb geochronology. Chem Geol 234:105–126
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Hao J, Li JL (2002) Arc-ophiolite obduction in the Western Kunlun Range (China): implications for the Palaeozoic evolution of central Asia. J Geol Soc Lond 159:517–528
Xiao XC, Wang J, Su L, Song SG (2003) A further discussion of the Kuda phiolite, West Kunlun and its tectonic significance. Geol Bull China 22:745–750 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Liu DY, Jian P, Liu CZ, Yuan C, Sun M (2005) Accretionary tectonics of the Western Kunlun Orogen, China: a Paleozoic-early Mesozoic, long-lived active continental margin with implications for the growth of Southern Eurasia. J Geol 113:687–705
Xu R, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Chen F, Vidal P, Arnaud N, Zhang Q, Zhao D (1994) A discovery of an early Palaeozoic tectono-magmatic belt in the Northern part of west Kunlun Shan. Sci Geol Sin 29:313–328 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu JF, Shinjo R, Defant MJ, Wang Q, Rapp RP (2002) Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China: partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust? Geology 30:1111–1114
Yao Y, Hsü KJ (1994) Origin of the Kunlun Mountains by arc-arc and arc-continent collisions. Island Arc 3:75–89
Yuan C, Zhou H, Sun M, Li JL, Hou QL (2000) Geochemical characteristics and tectonic implications of North Kuda pluton, West Kunlun Mountains. Geochemica 29:588–594 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan C, Sun M, Zhou MF, Zhou H, Xiao WJ, Li JL (2002) Tectonic evolution of the West Kunlun: geochronologic and geochemical constraints from Kudi Granitoids. Int Geol Rev 44:653–669
Yuan C, Sun M, Zhou MF, Zhou H, Xiao WJ, Li JL (2003) Absence of Archean basement in the South Kunlun Block: Nd–Sr–O isotopic evidence from granitoids. Island Arc 12:13–21
Yuan C, Sun M, Zhou MF, Xiao WJ, Zhou H (2005) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Yishak Volcanic Sequence, Kudi ophiolite, West Kunlun (NW China): implications for the magmatic evolution in a subduction zone environment. Contrib Mineral Petrol 150:195–211
Zhang CL, Yu HF, Shen JL, Dong YG, Ye HM, Guo KY (2004) Zircon SHRIMP age determination of the giant-crystal gabbro and basalt in Kuda, west Kunlun: dismembering of the Kuda Ophiolite. Geol Rev 50:639–650 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Hang-Qiang Xie for his assistance with SHRIMP zircon U–Pb dating, to Wei Pu for her assistance with measurements of whole-rock Sr and Nd isotopes, and to Ke-Jun Hou for his assistance with measurements of zircon Hf isotope. We thank Yigang Xu (Associate editor) and two anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful reviews and constructive comments. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (40972040; 40572037; 41272083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: Y. Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Jiang, YH., Jia, RY. et al. Origin of Middle Cambrian and Late Silurian potassic granitoids from the western Kunlun orogen, northwest China: a magmatic response to the Proto-Tethys evolution. Miner Petrol 108, 91–110 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-013-0288-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-013-0288-0