Abstract
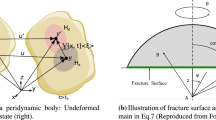
An ordinary state-based peridynamic (PD) model based on the Mindlin plate theory is presented to deal with fracture mechanics problems. Static and dynamic stress resultant intensity factors regarded as the primary fracture parameters for plate structures are evaluated by the displacement extrapolation method. Owing to the PD surface effect, however, the accuracy of the displacement field near crack surfaces is significantly affected. Therefore, the arbitrary horizon domain method is adopted to correct the surface effect. It derives the variable PD parameters to properly describe mechanical behaviors for each material point. Several numerical examples are investigated to examine the performance of the presented method. It indicates that the PD Mindlin plate model incorporated with the arbitrary horizon domain method validly minimizes the influence of the PD surface effect and provides an effective approach to evaluate static and dynamic moment intensity factors.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silling, S.A.: Reformulation of elasticity theory for discontinuities and long-range forces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48, 175–209 (2000)
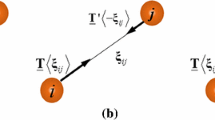
Silling, S.A., Epton, M., Weckner, O., Xu, J., Askari, E.: Peridynamic states and constitutive modeling. J. Elast. 88, 151–184 (2007)
O’Grady, J., Foster, J.: Peridynamic plates and flat shells: a non-ordinary, state-based model. Int. J. Solids Struct. 51, 4572–4579 (2014)
O’Grady, J., Foster, J.: A meshfree method for bending and failure in non-ordinary peridynamic shells. Comput. Mech. 57, 921–929 (2016)
Diyaroglu, C., Oterkus, E., Oterkus, S., Madenci, E.: Peridynamics for bending of beams and plates with transverse shear deformation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 69–70, 152–168 (2015)
Chowdhury, S.R., Roy, P., Roy, D., Reddy, J.N.: A peridynamic theory for linear elastic shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 84, 110–132 (2016)
Nguyen, C.T., Oterkus, S.: Peridynamics for the thermomechanical behavior of shell structures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 219, 106623 (2019)
Yang, Z., Vazic, B., Diyaroglu, C., Oterkus, E., Oterkus, S.: A Kirchhoff plate formulation in a state-based peridynamic framework. Math. Mech. Solids 25, 727–738 (2020)
Yang, Z., Oterkus, E., Oterkus, S.: Peridynamic formulation for higher-order plate theory. J. Peridyn. Nonlocal Model. 3, 1–26 (2020)
Zhang, Q., Li, S., Zhang, A., Peng, Y., Yan, J.: A peridynamic Reissner-Mindlin shell theory. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 122, 122–147 (2021)
Nguyen, C.T., Oterkus, S.: Ordinary state-based peridynamics for geometrically nonlinear analysis of plates. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 112, 102877 (2021)
Shen, G., Xia, Y., Hu, P., Zheng, G.: Construction of peridynamic beam and shell models on the basis of the micro-beam bond obtained via interpolation method. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 86, 104174 (2021)
Shen, G., Xia, Y., Li, W., Zheng, G., Hu, P.: Modeling of peridynamic beams and shells with transverse shear effect via interpolation method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 378, 113716 (2021)
Zhang, Q., Li, S., Zhang, A., Peng, Y.: On nonlocal geometrically exact shell theory and modeling fracture in shell structures. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 386, 114074 (2021)
Le, Q.V., Bobaru, F.: Surface corrections for peridynamic models in elasticity and fracture. Comput. Mech. 61, 499–518 (2018)
Queiruga, A.F., Moridis, G.: Numerical experiments on the convergence properties of state-based peridynamic laws and influence functions in two-dimensional problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 322, 97–122 (2017)
Chen, K.C.: The development of coupled peridynamics and ISO-geometric analysis method for modeling of crack propagation on ship-hull panels. Master Thesis, National Taiwan Ocean University (2020) (in Chinese)
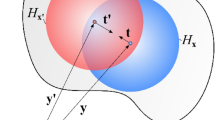
Dai, M.J., Tanaka, S., Guan, P.C., Oterkus, S., Oterkus, E.: Ordinary state-based peridynamic shell model with arbitrary horizon domains for surface effect correction. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 115, 103068 (2021)
Silling, S.A., Lehoucq, R.B.: Peridynamic theory of solid mechanics. Adv. Appl. Mech. 44, 73–168 (2010)
Hu, W., Ha, Y.D., Bobaru, F., Silling, S.A.: The formulation and computation of the nonlocal J-integral in bond-based peridynamics. Int. J. Fract. 176, 195–206 (2012)
Stenstrom, C., Eriksson, K.: The J-contour integral in peridynamics via displacements. Int. J. Fract. 216, 173–183 (2019)
Stenstrom, C., Eriksson, K.: The J-area integral applied in peridynamics. Int. J. Fract. 228, 127–142 (2021)
Imachi, M., Tanaka, S., Bui, T.Q.: Mixed-mode dynamic stress intensity factors evaluation using ordinary state-based peridynamics. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 93, 97–104 (2018)
Imachi, M., Takei, T., Ozdemir, M., Tanaka, S., Oterkus, S., Oterkus, E.: A smoothed variable horizon peridynamics and its application to the fracture parameters evaluation. Acta Mech. 232, 533–553 (2021)
Dai, M.J., Tanaka, S., Oterkus, S., Oterkus, E.: Mixed-mode stress intensity factors evaluation of flat shells under in-plane loading employing ordinary state-based peridynamics. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 112, 102841 (2021)
Dai, M.J., Tanaka, S., Bui, T.Q., Oterkus, S., Oterkus, E.: Fracture parameter analysis of flat shells under out-of-plane loading using ordinary state-based peridynamics. Eng. Fract. Mech. 244, 107560 (2021)
Areias, P.M.A., Belytschko, T.: Non-linear analysis of shells with arbitrary evolving cracks using XFEM. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 62, 384–415 (2005)
Li, J., Khodaei, Z.S., Aliabadi, M.H.: Dynamic dual boundary element analyses for cracked Mindlin plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 152–153, 248–260 (2018)
Bobaru, F., Foster, J.T., Geubelle, P.H., Silling, S.A.: Handbook of Peridynamic Modeling. CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton (2016)
Kilic, B., Madenci, E.: An adaptive dynamic relaxation method for quasi-static simulations using the peridynamic theory. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 53, 194–204 (2010)
Madenci, E., Oterkus, E.: Peridynamic Theory and Its Applications. Springer, New York (2014)
Underwood, P.: Dynamic relaxation. Comput. Methods Trans. Anal. 1, 245–265 (1983)
Liu, Z., Ye, H., Qian, D., Zhang, H., Zheng, Y.: A time-discontinuous peridynamic method for transient problems involving crack propagation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 122, 1824–1845 (2020)
Dirgantara, T., Aliabadi, M.H.: Dual boundary element formulation for fracture mechanics analysis of shear deformable shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38, 7769–7800 (2001)
Belytschko, T., Lu, Y.Y., Gu, L.: Element-free Galerkin methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 37, 229–256 (1994)
Sosa, H.A., Eischen, J.: Computation of stress intensity factors for plate bending via a path-independent integral. Eng. Fract. Mech. 25, 451–462 (1986)
Dolbow, J., Moes, N., Belytschko, T.: Modeling fracture in Mindlin-Reissner plates with the extended finite element method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 37, 7161–7183 (2000)
Guinea, G.V., Planas, J., Elices, M.: \(K_{\rm {I}}\) evaluation by the displacement extrapolation technique. Eng. Fract. Mech. 66, 243–255 (2000)
Zhu, N., Oterkus, E.: Calculation of stress intensity factor using displacement extrapolation method in peridynamic framework. J. Mech. 36, 235–243 (2020)
Han, Q., Wang, Y., Yin, Y., Wang, D.: Determination of stress intensity factor for mode I fatigue crack based on finite element analysis. Eng. Fract. Mech. 138, 118–126 (2015)
Qian, G., Gonzalez-Albuixech, V.F., Niffenegger, M., Giner, E.: Comparison of \(K_{\rm {I}}\) calculation methods. Eng. Fract. Mech. 156, 52–67 (2016)
Madenci, E., Dorduncu, M., Barut, A., Phan, N.: Weak form of peridynamics for nonlocal essential and natural boundary conditions. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 337, 598–631 (2018)
Scabbia, F., Zaccariotto, M., Galvanetto, U.: A novel and effective way to impose boundary conditions and to mitigate the surface effect in state-based peridynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 122, 5773–5811 (2021)
Prudhomme, S., Diehl, P.: On the treatment of boundary conditions for bond-based peridynamic models. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 372, 113391 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The first author gratefully acknowledges financial support from Japan–Taiwan Exchange Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A: Examination of boundary conditions in the nonlocal theory
Appendix A: Examination of boundary conditions in the nonlocal theory
The peridynamic method regarded as a nonlocal continuum theory requires some special treatments to impose boundary conditions, such as the weak form of peridynamics [42], the modified fictitious node method [43], and the variable horizon method [44]. In the present paper, volumetric regions (nonlocal boundary) are employed to implement external load and constraint boundary conditions (see Chap. 2 in Ref. [31]). For external load boundary conditions, the external load computed as body force density is applied on a real material layer along the boundary possessing nonzero volume. For constraint boundary conditions, the prescribed constraint is adopted on a fictitious layer with the particular length scale, \(\delta \), outside the physical boundary. Several numerical examples with constraint boundary conditions are successfully examined in Sect. 4. In “Appendix”, a numerical example with external load and constraint boundary conditions is investigated.
A cantilever square plate with a central crack under dynamic transverse shear load is considered. The length L, width W, and thickness h of the square plate are 2.0, 2.0, and 0.1 m, respectively. The half crack length a is set to 0.1 m. The square plate is subjected to a transverse shear force of \(QH(t)=1.0\) MPa on the right edge with clamped BCs imposed on the left edge (see Fig. 18). Young’s modulus E, Poisson’s ratio \(\nu \), and density \(\rho \) are set to 200 GPa, 0.3, and 7850 kg/\(\mathrm {m}^3\), respectively.
As illustrated in Fig. 19a, b, the displacement nearby the crack tip and dynamic \(F_1\) results are in good agreement between the PD and FEM solutions. It demonstrates that the proposed nonlocal method can well simulate fracture behaviors under different types of boundary conditions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, M.J., Tanaka, S., Oterkus, S. et al. Static and dynamic mechanical behaviors of cracked Mindlin plates in ordinary state-based peridynamic framework. Acta Mech 233, 299–316 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-021-03127-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-021-03127-w