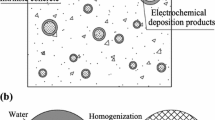
Abstract
A stochastic micromechanical framework is proposed to quantitatively characterize the probabilistic behavior of the saturated concrete healed by the electrochemical deposition method (EDM). Multiphase micromechanical representation for the healed saturated concrete is presented based on the material’s microstructures. Differential scheme-based multilevel homogenization procedures are proposed to quantitatively predict the effective properties of the repaired concrete. The material microstructures are characterized by the non-stationary random process and random variables. The probabilistic behavior for the repaired concrete is reached with high computational efficiency by incorporating the dimensional decomposition method and Newton interpolations. The predictions obtained by the proposed stochastic micromechanical framework are then compared with the available experimental data, existing models, and direct Monte Carlo simulations, which indicates that the presented stochastic micromechanical framework is computationally efficient and capable of characterizing for the probabilistic behavior of saturated concrete repaired by EDM considering the inherent randomness. Finally, the influences of the deposition products and healing degrees on the probabilistic behavior of repaired concrete are discussed based on the proposed models.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrante, F., Graham-Brady, L.: Stochastic simulation of non-Gaussian/non-stationary properties in a functionally graded plate. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 194, 1675–1692 (2005)
Ferrante, F., Brady, L., Acton, K., Arwade, S.: An overview of micromechanics-based techniques for the analysis of microstructural randomness in functionally graded materials. AIP Conf. Proc. 973, 190–195 (2008)
Zhu, H.H., Chen, Q., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G., Guo, F., Wang, Y.Q., Jiang, Z.W., Zhou, S., Wu, B.: Maximum entropy based stochastic micromechanical model for a two-phase composite considering the inter-particle interaction effect. Acta Mech. 226(9), 3069–3084 (2015)
Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Guo, F., Wang, L.B., Yan, Z.G., Deng, T., Zhou, S.: A stochastic micromechanical model for multiphase composite containing spherical inhomogeneities. Acta Mech. 226(6), 1861–1880 (2015)
Sun, W.J., Wang, L.B.: Mechanical properties of rock materials with related to mineralogical characteristics and grain size through experimental investigation: a comprehensive review. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 11, 322–328 (2018)
Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Jiang, Z.W., Yan, Z.G., Li, H.X.: Stochastic micromechanical predictions for the effective properties of concrete considering the interfacial transition zone effects. Int. J. Damage Mech. 27(8), 1252–1271 (2018)
Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G., Wang, C.H., Jiang, Z.W.: A stochastic micromechanical model for fiber-reinforced concrete using maximum entropy principle. Acta Mech. 229(7), 2719–2735 (2018)
Jiang, Z.W., Yang, X.J., Yan, Z.G., Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Wang, C.H., Ju, J.W., Fang, Z.H., Li, H.X.: A stochastic micromechanical model for hybrid fiber-reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 102, 39–54 (2019)
Rahman, S., Chakraborty, A.: A stochastic micromechanical model for elastic properties of functionally graded materials. Mech. Mater. 39, 548–563 (2007)
Tomar, S.S., Zafar, S., Talha, M., Gao, W., Hui, D.: State of the art of composite structures in non-deterministic framework: a review. Thin Walled Struct. 132, 700–716 (2018)
Otsuki, N., Hisada, M., Ryu, J.S., Banshoya, E.J.: Rehabilitation of concrete cracks by electrodeposition. Concr. Int. 21(3), 58–62 (1999)
Ryu, J.S., Otsuki, N.: Crack closure of reinforced concrete by electro deposition technique. Cem. Concr. Res. 32(1), 159–264 (2002)
Mohankumar, G.: Concrete repair by electrodeposition. Indian Concr. J. 79(8), 57–60 (2005)
Chen, Q.: The stochastic micromechanical models of the multiphase materials and their applications for the concrete repaired by electrochemical deposition method. Ph.D. Dissertation, Tongji University (2014)
Ryu, J.S.: New waterproofing technique for leaking concrete. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 22, 1023–1025 (2003)
Ryu, J.S., Otsuki, N.: Experimental study on repair of concrete structural members by electrochemical method. Scr. Mater. 52, 1123–1127 (2005)
Zhu, H.H., Chen, Q., Yan, Z.G., Ju, J.W., Zhou, S.: Micromechanical model for saturated concrete repaired by electrochemical deposition method. Mater. Struct. 47, 1067–1082 (2014)
Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Yan, Z.G., Deng, T., Zhou, S.: Micro-scale description of the saturated concrete repaired by electrochemical deposition method based on Mori–Tanaka method. J. Build. Struct. 36(1), 98–103 (2015)
Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Yan, Z.G., Ju, J.W., Deng, T., Zhou, S.: Micro-scale description of the saturated concrete repaired by electrochemical deposition method based on self-consistent method. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 47(2), 367–371 (2015)
Chen, Q., Jiang, Z.W., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G.: Micromechanical framework for saturated concrete repaired by the electrochemical deposition method with interfacial transition zone effects. Int. J. Damage Mech. 26(2), 210–228 (2017)
Yan, Z.G., Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Zhou, S., Jiang, Z.W.: A multiphase micromechanical model for unsaturated concrete repaired by electrochemical deposition method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 50(24), 3875–3885 (2013)
Chen, Q., Jiang, Z.W., Yang, H., Zhu, H., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G., Li, H.X.: The effective properties of saturated concrete healed by EDMwith the ITZs. Comput. Concr. 21(1), 67–74 (2018)
Chen, Q., Jiang, Z.W., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G., Li, H.X., Rabczuk, T.: A multiphase micromechanical model for unsaturated concrete repaired by electrochemical deposition method with the bonding effects. Int. J. Damage Mech. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789518773633
Weng, G.: Some elastic properties of reinforced solids, with special reference to isotropic ones containing spherical inclusions. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 22, 845–856 (1984)
Weng, G.: The theoretical connection between Mori–Tanaka’s theory and the Hashin–Shtrikman–Walpole bounds. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 28, 1111–1120 (1990)
Ju, J.W., Chen, T.M.: Micromechanics and effective moduli of elastic composites containing randomly dispersed ellipsoidal inhomogeneities. Acta Mech. 103, 103–121 (1994)
Ju, J.W., Chen, T.M.: Effective elastic moduli of two-phase composites containing randomly dispersed spherical inhomogeneities. Acta Mech. 103, 123–144 (1994)
Ostoja-Starzewski, M.: Material spatial randomness: from statistical to representative volume element. Probab. Eng. Mech. 21(2), 112–132 (2006)
Mura, T.: Micromechanics of Defects in Solids. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1987)
Norris, A.N.: A differential scheme for the effective modulus of composites. Mech. Mater. 4, 1–16 (1985)
McLaughlin, R.: A study of the differential scheme for composite materials. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 15, 237–244 (1977)
Chen, Q., Jiang, Z.W., Yang, Z.H., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G., Wang, Y.Q.: Differential-scheme based micromechanical framework for saturated concrete repaired by the electrochemical deposition method. Mater. Struct. 49(12), 5183–5193 (2016)
Chen, Q., Jiang, Z.W., Yang, Z.H., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G., Wang, Y.Q.: Differential-scheme based micromechanical framework for unsaturated concrete repaired by the electrochemical deposition method. Acta Mech. 228(2), 415–431 (2017)
Chen, Q., Mousavi, N.M., Fisher, Q., Zhu, H.H.: Multi-scale approach for modeling the transversely isotropic elastic properties of shale considering multi-inclusions and interfacial transition zone. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 84, 95–104 (2016)
Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Yan, Z.G., Ju, J.W., Jiang, Z.W., Wang, Y.Q.: A multiphase micromechanical model for hybrid fiber reinforced concrete considering the aggregate and ITZ effects. Constr. Build. Mater. 114, 839–850 (2016)
Nezhad, M.M., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Chen, Q.: A simplified multiscale damage model for the transversely isotropic shale rocks under tensile loading. Int. J. Damage Mech. 25(5), 705–726 (2016)
Zhu, H.H., Chen, Q.: An approach for predicting the effective properties of multiphase composite with high accuracy. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 1, 41–47 (2017)
Ju, J., Zhang, X.: Micromechanics and effective transverse elastic moduli of composites with randomly located aligned circular fibers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 35, 941–960 (1998)
Ju, J., Sun, L.: A novel formulation for the exterior-point Eshelby’s tensor of an ellipsoidal inclusion. J. Appl. Mech. 66, 570–574 (1999)
Ju, J., Sun, L.: Effective elastoplastic behavior of metal matrix composites containing randomly located aligned spheroidal inhomogeneities. Part I: micromechanics-based formulation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38, 183–201 (2001)
Ju, J., Yanase, K.: Micromechanics and effective elastic moduli of particle-reinforced composites with near-field particle interactions. Acta Mech. 215, 135–153 (2010)
Ju, J., Yanase, K.: Micromechanical effective elastic moduli of continuous fiber-reinforced composites with near-field fiber interactions. Acta Mech. 216, 87–103 (2011)
Sun, L., Ju, J.: Effective elastoplastic behavior of metal matrix composites containing randomly located aligned spheroidal inhomogeneities. Part II: applications. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38, 203–225 (2001)
Sun, L., Ju, J.: Elastoplastic modeling of metal matrix composites containing randomly located and oriented spheroidal particles. J. Appl. Mech. 71, 774–785 (2004)
Yanase, K., Ju, J.W.: Effective elastic moduli of spherical particle reinforced composites containing imperfect interfaces. Int. J. Damage Mech. 21, 97–127 (2012)
Christensen, R.M., Lo, K.H.: Solutions for effective shear properties in three phase sphere and cylinder models. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 27, 315–330 (1979)
Berryman, J.G.: Long-wave propagation in composite elastic media II. Ellipsoidal inclusion. Acoust. Soc. Am. J. 68, 1820–1831 (1980)
Chen, Q., Zhu, H.H., Ju, J.W., Yan, Z.G., Jiang, Z.W., Chen, B., Wang, Y.Q., Fan, Z.H.: Stochastic micromechanical predictions for the probabilistic behavior of saturated concrete repaired by the electrochemical deposition method. Int. J. Damage Mech. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789519860805
Ghanem, P.D., Spanos, P.D.: Stochastic Finite Elements: A Spectral Approach. Springer, New York (1991)
Xu, H., Rahman, S.: Decomposition methods for structural reliability analysis. Probab. Eng. Mech. 20, 239–250 (2005)
Smith, J.C.: Experimental values for the elastic constants of a particulate-filled glassy polymer. J. Res. Natl. Bureau Stand. 80A, 45–49 (1976)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Key Research and Development Plan (2018YFC0705400, 2017YFC0704004). This work is also supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51508404, 51478348, 51278360, 51308407, U1534207), the Funds of Fundamental Research Plan for the Central Universities in Chang’an University (300102218511), the 1000 Talents Plan Short-Term Program by the Organization Department of the Central Committee of the CPC, the Funds of Fundamental Research Plan for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Ma, R., Jiang, Z. et al. Differential scheme-based stochastic micromechanical framework for saturated concrete repaired by EDM. Acta Mech 230, 4287–4301 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-019-02511-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-019-02511-x