Abstract
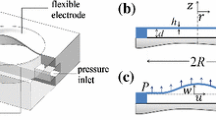
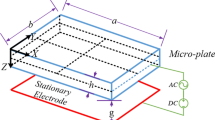
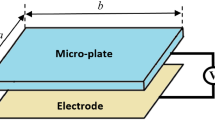
This paper investigates the dynamic behavior of a circular micro-plate interacting with compressible fluid and excited by electrostatic force. Utilizing Kirchhoff’s thin plate theory for the actuating micro-plate and assuming inviscidity for the operating fluid, an eigenvalue problem of the coupled system is derived using Fourier-Bessel expansion. Investigating the change in free vibration properties of the system, a parametric study is done accounting for the variation of physical and geometric properties of the bounded domain. Then considering step input voltages, the response of the coupled system, pull-in time, and pull-in voltages are derived. It is shown that besides the electric permittivity the inertial effect of the contained fluid also changes the transient response significantly. The impact of fluid added mass is observed in the decreased response frequencies and increased pull-in times. In addition, by constructing phase plane diagrams, it is found that the attraction zones of stable fixed points vary for different contained fluids. This could affect the response of the micro-plate qualitatively when there exists an uncertainty in the initial conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miao J., Lin R., Chen L., Zou Q., Lim S.Y., Seah S.H.: Design consideration in micromachined silicon microphones. Microelectron. J. 33, 21–28 (2002)
Liu J., Martinn D.T., Kardirvel , Nishida K.T., Cattafesta L., Sheplak M., Mann B.P.: Nonlinear model and system identification of a capacitive dual-backplate MEMS microphone. J. Sound Vib. 309, 276–292 (2008)
Jiankang W., Lijun L.: Liquid-solid coupled system of micropump. Acta Mech. Solida Sinica 19, 40–49 (2006)
Zengerle R., Ulrich J.: A bi-directional silicon micropump. Sens. Actuators A 50, 81–86 (1995)
Rezazadeh G., Tayefe-Rezaei S., Ghesmati J., Tahmasebi A.: Investigation of the pull-in phenomenon in drug delivery micropump using Galerkin method. Sens. Transducers 78, 1098–1107 (2007)
Vogl G.W., Nayfeh A.H.: A reduced-order model for electrically actuated clamped circular plates. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 684–690 (2005)
Saeedivahdat A., Abdolkarimzadeh F., Feyzi A., Rezazadeh G., Tarverdilo S.: Effect of thermal stresses on stability and frequency response of a capacitive microphone. Microelectron. J. 41, 865–873 (2010)
Wang Y.-G., Lin W.-H., Li X.-M., Feng Z.-J.: Bending and vibration of an electrostatically actuated circular micro-plate in presence of Casimir force. Appl. Math. Model. 35, 2348–2357 (2011)
Batra R.C., Porfiri M., Spinello D.: Reduced-order models for microelectromechanical rectangular and circular plates incorporating the Casimir force. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45, 3558–3583 (2008)
Sun Y., Saka M.: Thermoelastic damping in micro-scale circular plate resonators. J. Sound Vib. 329, 328–337 (2010)
Lin R., Wang W.: Structural dynamics of microsystems-current state of research and future directions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 20, 1015–1043 (2006)
Batra R.C., Porfiri M., Spinello D.: Review of modeling electrostatically actuated microelectromechanical systems. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, R23–R31 (2007)
Li W.-L.: Squeeze film effects on dynamic performance of MEMS l-mirrors-consideration of gas rarefaction and surface roughness. Microsyst. Technol. 14, 315–324 (2008)
Bao M., Yang H.: Squeeze film air damping in MEMS. Sens. Actuators A 136, 3–27 (2007)
Pandey A.K., Pratap R.: Effect of flexural modes on squeeze film damping in MEMS cantilever resonators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 2475–2484 (2007)
Crescini D., Marioli D., Taroni A.: Piezoelectric thick-film fluid density sensor based on resonance vibration. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Technol. Conf. (St. Paul, MN) 2, 1368–1371 (1998)
Lindholm U.S., Kana D.D., Chu W.H., Abramson H.N.: Elastic vibration characteristics of cantilever plates in water. J. Ship Res. 9, 11–22 (1965)
Minami H.: Added mass of a membrane vibrating at finite amplitude. J. Fluids Struct. 12, 919–932 (1998)
Meyerhoff W.K.: Added masses of thin rectangular plates calculated from potential theory. J. Ship Res. 14, 100–111 (1970)
Ergin A., Ugurlu B.: Linear vibration analysis of cantilever plates partially submerged in fluid. J. Fluids Struct. 17, 927–939 (2003)
Sinha J.K., Sandeep S., Rama R.A.: Added mass and damping of submerged perforated plates. J. Sound Vib. 260, 549–564 (2003)
Yadykin Y., Tenetov V., Levin D.: The added mass of a flexible plate oscillating in a fluid. J. Fluids Struct. 17, 115–123 (2003)
Gorman D.G., Trendafilov I., Mulholland A.J., Horacek J.: Analytical modelling and extraction of the modal behaviour of a cantilever beam in fluid interaction. J. Sound Vib. 308, 231–245 (2007)
Tariverdilo S., Shahmardani M., Mirzapour J., Shabani R.: Asymmetric free vibration of circular plate in contact with incompressible fluid. Appl. Math. Model. 37, 228–239 (2013)
Zhao Y.-P., Wang L.S., Yu T.X.: Mechanics of adhesion in MEMS—a review. J. Adhesion Sci. Technol. 17, 519–546 (2003)
Guo J.-G., Zhou L.-J., Zhao Y.-P.: Instability analysis of torsional MEMS/NEMS actuators under capillary force. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 331, 458–462 (2009)
Lin W.-H., Zhao Y.-P.: Casimir effect on the pull-in parameters of nanometer switches. Microsyst. Technol. 11, 80–85 (2005)
Talebian S., Rezazadeh G., Fathalilou M., Toosi B.: Effect of temperature on pull-in voltage and natural frequency of an electrostatically actuated micro-plate. Mechatronics 20, 666–673 (2010)
Wang Z., Zhao Y.-P.: Self-instability and bending behaviors of nano plates. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica 22, 630–643 (2009)
Rezazadeh G., Fathalilou M., Shabani R., Tarverdilou S., Talebian S.: Dynamic characteristics and forced response of an electrostatically-actuated microbeam subjected to fluid loading. Microsyst. Technol. 15, 1355–1363 (2009)
Sader J.E.: Frequency response of cantilever beams immersed in viscous fluids with applications to the atomic force microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 64–76 (1998)
Harrison C., Tavernier E., Vancauwenberghe O., Donzier E., Hsud K., Goodwin A., Marty F., Mercier B.: On the response of a resonating plate in a liquid near a solid wall. Sens. Actuators A 134, 414–426 (2007)
Moghimi Zand M., Ahmadian M.T.: Characterization of coupled-domain multi-layer micro-plates in pull-in phenomenon, vibrations and dynamics. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 49, 1226–1237 (2007)
Ayela C., Nicu L.: Micromachined piezoelectric membranes with high nominal quality factors in Newtonian liquid media: a Lamb’s model validation at the microscale. Sens. Actuators B 123, 860–868 (2007)
Wang Z., Wang F.-C., Zhao Y.-P.: Tap dance of a water droplet. Proc. R. Soc. A 468, 2485–2495 (2012)
Roman, B., Bico, J.: Elasto-capillarity: deforming an elastic structure with a liquid droplet. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 22 (2010). doi:10.1088/0953-8984/22/49/493101
Tanaka T., Morigami M., Atoda N.: Mechanism of resist pattern collapse during development process. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 6059–6064 (1993)
Chakrapani N., Wei B., Carrillo A., Ajayan P.M., Kane R.S.: Capillarity-driven assembly of two-dimensional cellular carbon nanotube foams. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 4009–4012 (2004)
Ali S.M., Mantell S.C., Longmire E.K.: Mechanical performance of microcantilevers in liquids. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 20, 441–450 (2011)
lnaba S., Akaishi K., Mori T., Hane K.: Analysis of the resonance characteristics of a cantilever vibrated photothermally in a liquid. J. Appl. Phys. 73, 2654–2658 (1993)
Sorokin S.V., Chapman C.J.: Asymptotic analysis of nonlinear vibration of an elastic plate under heavy fluid loading. J. Sound Vib. 284, 1131–1144 (2005)
Sorokin S.V., Kadyrov S.G.: modeling of nonlinear oscillations of elastic structures in heavy fluid loading conditions. J. Sound Vib. 222, 425–451 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabani, R., Sharafkhani, N., Tariverdilo, S. et al. Dynamic analysis of an electrostatically actuated circular micro-plate interacting with compressible fluid. Acta Mech 224, 2025–2035 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-0877-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-0877-3