Abstract
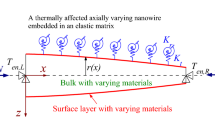
A theoretical framework, accounting for high-order surface stress, is implemented in a continuum mechanics model based on the Euler-Bernoulli theory of beams and columns to simulate the buckling and resonance behavior of nanowires (NWs). Closed-form expressions for the critical buckling load of uniaxial compression of NWs are derived for different types of end conditions. Size-dependent overall Young’s modulus is characterized versus the diameter of the NWs and is compared with the experimental data. The resonance frequency of NWs is also studied and compared with the simulation results based on nonlinear, finite deformation kinematics. We demonstrate that the present prediction considering both surface moment and surface stress agrees well with the experimental data, while the pure surface stress model may not be able to capture the general trend when the NW’s diameter is less than a certain size. We conclude that the present continuum mechanics approach, considering both high-order surface effects, could be served as one of the feasible tools to analyze the mechanical behavior of nanostructures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finn R.: Equilibrium Capillary Surfaces. Springer, New York (1986)
Gibbs J.W.: The Collected Works of J. W. Gibbs, vol. 1. Longman, New York (1928)
Gurtin M.E., Murdoch A.I.: A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 57, 291–323 (1975)
Gurtin M.E., Murdoch A.I.: Surface stress in solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 14, 431–440 (1978)
Chen T., Chiu M.S., Weng C.N.: Derivation of the generalized Young-Laplace equation of curved interfaces in nanoscaled solids. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 074308 (2006)
Ru C.Q.: Simple geometrical explanation of Gurtin-Murdoch model of surface elasticity with clarification of its related versions. Sci. China Phys. 53, 536–544 (2010)
Cammarata R.C., Sieradzki K., Spaepen F.: Simple model for interface stresses with application to misfit dislocation generation in epitaxial thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 1227 (2000)
Cammarata R.C., Trimble T.M., Srolovitz D.J.: Surface stress model for intrinsic stresses in thin films. J. Mater. Res. 15, 2468–2474 (2000)
Freund L.B., Suresh S.: Thin Film Materials: Stress, Defect Formation and Surface Evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Miller R.E., Shenoy V.B.: Size-dependent elastic properties of nanosized structural elements. Nanotechnology 11, 139–147 (2000)
Sharma P., Ganti S., Bhate N.: Effect of surfaces on the size-dependent elastic state of nano-inhomogeneities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 535–537 (2003)
Zhang Y., Ren Q., Zhao Y.: Modelling analysis of surface stress on a rectangular cantilever beam. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 37, 2140–2145 (2004)
Duan H.L., Wang J., Huang Z.P., Karihaloo B.L.: Eshelby formalism for nano-inhomogeneities. Proc. R. Soc. A. 461, 3335–3353 (2005)
Yan Z., Jiang L.: Surface effects on the electromechanical coupling and bending behaviours of piezoelectric nanowires. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 44, 075404 (2011)
Wang G.F., Wang T.J.: Deformation around a nanosized elliptical hole with surface effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 161901 (2006)
Wang G.F., Feng X.Q.: Surface effects on buckling of nanowires under uniaxial compression. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 141913 (2009)
Wang G.F., Feng X.Q.: Timoshenko beam model for buckling and vibration of nanowires with surface effects. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42, 155411 (2009)
Yang F.Q.: Size-dependent effective modulus of elastic composite materials: spherical nanocavities at dilute concentrations. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 3516–3520 (2004)
Li B., Huang S.Q., Feng X.Q.: Buckling and postbuckling of a compressed thin film bonded on a soft elastic layer: a three-dimensional analysis. Arch. Appl. Mech. 80, 175–188 (2010)
Yan Z., Jiang L.Y.: The vibrational and buckling behaviors of piezoelectric nanobeams with surface effects. Nanotechnology 22, 245703 (2011)
Wang G.F., Feng X.Q.: Effects of surface elasticity and residual surface tension on the natural frequency of microbeams. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 231904 (2007)
He J., Lilley C.M.: Surface stress effect on bending resonance of nanowires with different boundary conditions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 263108 (2008)
Chen H.A., Liu X., Hu G.K.: Overall plasticity of micropolar composites with interface effect. Mech. Mater. 40, 721–728 (2008)
Duan H.L., Wang J., Huang Z.P., Karihaloo B.L.: Size-dependent effective elastic constants of solids containing nano-inhomogeneities with interface stress. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53, 1574–1596 (2005)
Benveniste Y., Miloh T.: Soft neutral elastic inhomogeneities with membrane-type interface conditions. J. Elast. 88, 87–111 (2007)
Chen T., Dvorak G.J., Yu C.C.: Size-dependent elastic properties of unidirectional nano-composites with interface stresses. Acta. Mech. 188, 39–54 (2007)
Quang H.L., He Q.C.: Estimation of the effective thermoelastic moduli of fibrous nanocomposites with cylindrically anisotropic phases. Arch. Appl. Mech. 79, 225–248 (2009)
Chen T., Chiu M.S.: Effects of higher-order interface stresses on the elastic states of two-dimensional composites. Mech. Mater. 43, 212–221 (2011)
Jing G.Y., Duan H.L., Sun X.M., Zhang Z.S., Xu J., Li Y.D., Wang X.J., Yu D.P.: Surface effects on elastic properties of silver nanowires: contact atomic-force microscopy. Phys. Rev. B. 73, 235409 (2006)
Zhu Y., Xu F., Qin Q., Fung W.Y., Lu W.: Mechanical properties of vapor-liquid-solid synthesized silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 9, 3934–3939 (2009)
Timoshenko S.P., Gere J.M.: Theory of Elastic Stability. McGraw-Hill, New York (1961)
Weaver W., Timoshenko S.P., Young D.H.: Vibration Problems in Engineering. Wiley, New York (1990)
Cuenot S., Fretigny C., Demoustier-Champagne S., Nysten B.: Surface tension effect on the mechanical properties of nanomaterials measured by atomic force microscopy. Phys. Rev. B. 69, 165410 (2004)
Song J., Wang X., Riedo E., Wang Z.L.: Elastic property of vertically aligned nanowires. Nano Lett. 5, 1954–1958 (2005)
Chen C.Q., Shi Y., Zhang Y.S., Zhu J., Yan Y.J.: Size dependence of Young’s modulus in ZnO nanowires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 075505 (2006)
Ni H., Li X.: Young’s modulus of ZnO nanobelts measured using atomic force microscopy and nanoindentation techniques. Nanotechnology 17, 3591–3597 (2006)
Riaz M., Nur O., Willander M., Klason P.: Buckling of ZnO nanowires under uniaxial compression. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 103118 (2008)
Jing Y., Meng Q., Gao Y.: Molecular dynamics simulation on the buckling behavior of silicon nanowires under uniaxial compression. Comput. Mater. Sci. 45, 321–326 (2009)
Cho J., Joshi M.S., Sun C.T.: Effect of inclusion size on mechanical properties of polymeric composites with micro and nano particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 1941–1952 (2006)
Ji L.W., Young S.J., Fang T.H., Liu C.H.: Buckling characterization of vertical ZnO nanowires using nanoindentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 033109 (2007)
Young S.J., Ji L.W., Chang S.J., Fang T.H., Hsueh T.J., Meen T.H., Chen I.C.: Nanoscale mechanical characteristics of vertical ZnO nanowires grown on ZnO: Ga/glass templates. Nanotechnology 18, 225603 (2007)
Chiu M.S., Chen T.: Effects of high-order surface stress on static bending behavior of nanowires. Physica E 44, 714–718 (2011)
Chiu, M.S., Chen, T.: Higher-order surface stress effects on buckling of nanowires under uniaxial compression. Procedia Engineering 10, 397–402 (2011) (11th International Conference on the Mechanical Behavior of Materials, ICM11)
He J., Lilley C.M.: Surface effect on the elastic behavior of static bending nanowires. Nano Lett. 8, 1798–1802 (2008)
Shenoy V.B.: Atomistic calculations of elastic properties of metallic fcc crystal surfaces. Phys. Rev. B. 71, 094104 (2005)
Song F., Huang G.L., Park H.S., Liu X.N.: A continuum model for the mechanical behavior of nanowires including surface and surface-induced initial stresses. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48, 2154–2163 (2011)
Park H.S.: Surface stress effects on the resonant properties of silicon nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 123504 (2008)
Park H.S.: Surface stress effects on the critical buckling strains of silicon nanowires. Comput. Mater. Sci. 51, 396–401 (2012)
Park H.S., Klein P.A.: Surface stress effects on the resonant properties of metal nanowires: the importance of finite deformation kinematics and the impact of the residual surface stress. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 3144–3166 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, MS., Chen, T. Effects of high-order surface stress on buckling and resonance behavior of nanowires. Acta Mech 223, 1473–1484 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-012-0673-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-012-0673-5