Summary
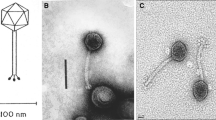
N-terminal amino acid sequences of major capsid proteins (Mcps) of three vibriophages (KVP20, KVP40 and nt-1), two aeromonad phages (Aeh 1 and 65) and coliphage T4 were compared. All these phages are morphologically similar, belonging to family Myoviridae and the vernacular genus name “T4-like phages”. A dendrogram constructed from homology data indicated that (i) the three vibriophages were closely related, (ii) the two aeromonad phages were also fairly related and (iii) these five phages were all distantly, but definitely, related to coliphage T4. These results suggest that Mcps of morphologically similar phages are highly conserved and may serve as a measure to assess the phylogenetic relationships among different phages of similar morphology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received January 14, 1999 Accepted March 14, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuzaki, S., Kuroda, M., Kimura, S. et al. Major capsid proteins of certain Vibrio and Aeromonas phages are homologous to the equivalent protein, gp23*, of coliphage T4. Arch. Virol. 144, 1647–1651 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050618
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050618