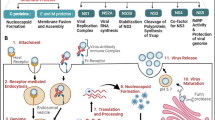
Abstract
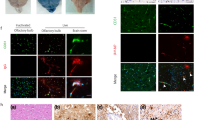
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection can cause brain tissue lesions characterized by neuronal death, and apoptosis is involved in JEV-induced neuronopathy. In the present study, mouse microglia were infected with JEV, and pyknosis with dark-staining nuclei of infected cells was detected using Hoechst 33342 staining. TUNEL staining showed that JEV infection promoted the apoptosis of BV2 cells, and the apoptosis rate was significantly increased at 24-60 hours postinfection (hpi) (P < 0.01) and was the highest at 36 h (P < 0.0001). Western blot results showed that the expression of the Bcl-2 protein in JEV-infected cells was downregulated significantly at 60 hpi (P < 0.001), whereas that of the Bax protein was observably upregulated at 60 hpi (P < 0.001). At the same time, the level of cytochrome c (Cyt c) was significantly increased (P < 0.001), and the expression levels of two apoptosis-related proteins, namely, cleaved caspase-3 (P < 0.01) and caspase-9 (P < 0.001), were elevated significantly. Immunofluorescence staining showed that the amount of Cyt c increased with time after infection. After BV2 cells were infected with JEV, the expression of RIG-1 increased significantly from 24 hpi to 60 h (P < 0.001). The expression of MAVS increased significantly at 24 h (P < 0.001) and decreased gradually from 24 h to 60 hpi. The expression of TBK1 and NF-κB (p65) was not significantly changed. The expression of p-TBK1 and p-NF-κB (p-p65) increased significantly within 24 h (P < 0.001) and decreased from 24 to 60 hpi. The expression levels of IRF3 and p-IRF3 peaked at 24 hpi (P < 0.001) and decreased gradually from 24 to 60 hpi. However, the expression levels of JEV proteins showed no significant change at 24 and 36 hpi but were markedly elevated at 48 and 60 hpi. Interference with the expression of the RIG-1 protein in BV2 cells resulted in a dramatic increase in the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 (P < 0.05), whereas the pro-apoptotic protein Bax, cleaved caspase-9, and especially cleaved caspase-3 were downregulated (P < 0.05), and viral protein expression was notably reduced (P < 0.05). These results indicate that JEV induces apoptosis through mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis pathways, interfering with the expression of RIG-1 in BV2 cells can inhibit viral replication and inhibit apoptosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data were obtained from the experiments conducted by the authors.
References
Adams JM, Cory S (2007) The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 26(9):1324–1337. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210220
Bendall LJ, Green DR (2014) Autopsy of a cell. Leukemia 28(6):1341–1343. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.17
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(1):57–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2038
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ (2009) Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136(4):642–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.035
Chattopadhyay S, Marques JT, Yamashita M, Peters KL, Smith K, Desai A, Williams BR, Sen GC (2010) Viral apoptosis is induced by IRF-3-mediated activation of Bax. EMBO J 29(10):1762–1773. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2010.50
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, Adams JM (2014) Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(1):49–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3722
Ghosh D, Basu A (2009) Japanese encephalitis-a pathological and clinical perspective. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3(9):e437. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000437
Ghoshal A, Das S, Ghosh S, Mishra MK, Sharma V, Koli P, Sen E, Basu A (2007) Proinflammatory mediators released by activated microglia induces neuronal death in Japanese encephalitis. Glia 55(5):483–496. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20474
Guo F, Yu X, Xu A, Xu J, Wang Q, Guo Y, Wu X, Tang Y, Ding Z, Zhang Y, Gong T, Pan Z, Li S, Kong L (2018) Japanese encephalitis virus induces apoptosis by inhibiting Foxo signaling pathway. Vet Microbiol 220:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.05.008
Huang M, Xu A, Wu X, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Guo F, Pan Z, Kong L (2016) Japanese encephalitis virus induces apoptosis by the IRE1/JNK pathway of ER stress response in BHK-21 cells. Arch Virol 161(3):699–703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2715-5
Jiang R, Ye J, Zhu B, Song Y, Chen H, Cao S (2014) Roles of TLR3 and RIG-I in mediating the inflammatory response in mouse microglia following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J Immunol Res 2014:787023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/787023
Kirshner JR, Karpova AY, Kops M, Howley PM (2005) Identification of TRAIL as an interferon regulatory factor 3 transcriptional target. J Virol 79(14):9320–9324. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.14.9320-9324.2005
Kumar S (2007) Caspase function in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 14(1):32–43. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402060
Lee SH, Choi BY, Lee SH, Kho AR, Jeong JH, Hong DK, Suh SW (2017) Administration of protocatechuic acid reduces traumatic brain injury-induced neuronal death. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122510
Li Y, Hou L, Ye J, Liu X, Dan H, Jin M, Chen H, Cao S (2010) Development of a convenient immunochromatographic strip for the diagnosis of infection with Japanese encephalitis virus in swine. J Virol Methods 168(1–2):51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.04.015
Mokarram P, Albokashy M, Zarghooni M, Moosavi MA, Sepehri Z, Chen QM, Hudecki A, Sargazi A, Alizadeh J, Moghadam AR, Hashemi M, Movassagh H, Klonisch T, Owji AA, Los MJ, Ghavami S (2017) New frontiers in the treatment of colorectal cancer: Autophagy and the unfolded protein response as promising targets. Autophagy 13(5):781–819. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2017.1290751
Rodrigues A, Costa R, Silva S, Dias I, Dias RB, Bezerra DP (2021) Cell signaling pathways as molecular targets to eliminate AML stem cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 160:103277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103277
Satchidanandam V (2020) Japanese encephalitis vaccines. Curr Treat Opt Infect Dis 12(4):375–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40506-020-00242-5
Shao L (2013) Preparation and characterization of Japanese encephalitis virus NS5 and E protein mab.dissertation, Huazhong Agricultural University
Wang Q, Xin X, Wang T, Wan J, Ou Y, Yang Z, Yu Q, Zhu L, Guo Y, Wu Y, Ding Z, Zhang Y, Pan Z, Tang Y, Li S, Kong L (2019) Japanese encephalitis virus induces apoptosis and encephalitis by activating the PERK pathway. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00887-19
Ye J, Zhang H, He W, Zhu B, Zhou D, Chen Z, Ashraf U, Wei Y, Liu Z, Fu ZF, Chen H, Cao S (2016) Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis identifies the critical role of JNK1 in neuroinflammation induced by Japanese encephalitis virus. Sci Signal 9(448):a98. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaf5132
Ye J, Chen Z, Li Y, Zhao Z, He W, Zohaib A, Song Y, Deng C, Zhang B, Chen H, Cao S (2017) Japanese encephalitis virus NS5 inhibits type I interferon (IFN) production by blocking the nuclear translocation of IFN regulatory factor 3 and NF-kappaB. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00039-17
Yu CY, Hsu YW, Liao CL, Lin YL (2006) Flavivirus infection activates the XBP1 pathway of the unfolded protein response to cope with endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Virol 80(23):11868–11880. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00879-06
Zhang Y, Jing J, Li X, Wang J, Feng X, Cao R, Chen P (2015) Integration analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in swine testis cells infected with Japanese encephalitis virus. Infect Genet Evol 32:342–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2015.03.037
Zhang J, Gao M, Liu Z, Gu C (2021) Effects of autophagy regulators on apoptosis in the brain of mice infected with Japanese encephalitis virus. Acta Vet Zootech Sin 52(02):506–514
Zhu B, Ye J, Nie Y, Ashraf U, Zohaib A, Duan X, Fu ZF, Song Y, Chen H, Cao S (2015) MicroRNA-15b modulates japanese encephalitis virus-mediated inflammation via targeting RNF125. J Immunol 195(5):2251–2262. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1500370
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (SQ2022YFD1800105) and the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (32030107) to CG and SC. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Animal welfare statement
The authors confirm that the ethical policies of the journal, as noted on the journal's author guidelines page, have been adhered to. No ethical approval was required, as no animal trials were conducted in this research article.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Tim Skern .
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Liu, Z., Guo, X. et al. Japanese encephalitis virus induces apoptosis by activating the RIG-1 signaling pathway. Arch Virol 168, 169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-023-05780-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-023-05780-z