Abstract
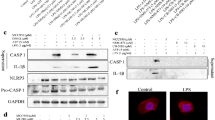
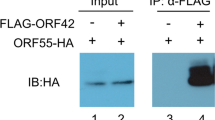
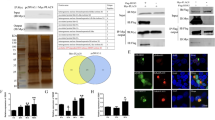
Avian reovirus (ARV) causes viral arthritis, chronic respiratory diseases, retarded growth and malabsorption syndrome. The ARV p10 protein, a viroporin responsible for the induction of cell syncytium formation and apoptosis, is rapidly degraded in host cells. However, the mechanism of p10 degradation and its relevance are still unclear. We report here the identification of cellular lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP-1) as an interaction partner of p10 by yeast two-hybrid screening, immunoprecipitation and confocal microscopy assays. We found that rapid degradation of p10 was associated with ubiquitination. Importantly, ARV p10 degradation in host cells could be completely abolished by knockdown of LAMP-1 by siRNA, indicating that LAMP-1 is required for ARV p10 degradation in host cells. In contrast, overexpression of LAMP-1 facilitated p10 degradation. Furthermore, knockdown of LAMP-1 allowed p10 accumulation, enhancing p10-induced apoptosis and viral release. Thus, LAMP-1 plays a critical role in ARV p10 degradation associated with inhibition of apoptosis and viral release.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARV:
-
Avian reovirus
- LAMP-1:
-
Lysosome-associated membrane protein 1
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
References
Barry C, Duncan R (2009) Multifaceted sequence-dependent and -independent roles for reovirus FAST protein cytoplasmic tails in fusion pore formation and syncytiogenesis. J Virol 83:12185–12195
Barry C, Key T, Haddad R, Duncan R (2010) Features of a spatially constrained cystine loop in the p10 FAST protein ectodomain define a new class of viral fusion peptides. J Biol Chem 285:16424–16433
Beal RE, Toscano-Cantaffa D, Young P, Rechsteiner M, Pickart CM (1998) The hydrophobic effect contributes to polyubiquitin chain recognition. Biochemistry 37:2925–2934
Benavente J, Martinez-Costas J (2007) Avian reovirus: structure and biology. Virus Res 123:105–119
Bodelon G, Labrada L, Martinez-Costas J, Benavente J (2001) The avian reovirus genome segment S1 is a functionally tricistronic gene that expresses one structural and two nonstructural proteins in infected cells. Virology 290:181–191
Boehme KW, Hammer K, Tollefson WC, Konopka-Anstadt JL, Kobayashi T, Dermody TS (2013) Nonstructural protein sigma1s mediates reovirus-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J Virol 87:12967–12979
Bohley P (1996) Surface hydrophobicity and intracellular degradation of proteins. Biol Chem 377:425–435
Chen JW, Madamanchi N, Madamanchi NR, Trier TT, Keherly MJ (2001) Lamp-1 is upregulated in human glioblastoma cell lines induced to undergo apoptosis. J Biomed Sci 8:365–374
Chulu JL, Lee LH, Lee YC, Liao SH, Lin FL, Shih WL, Liu HJ (2007) Apoptosis induction by avian reovirus through p53 and mitochondria-mediated pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356:529–535
Clancy EK, Duncan R (2009) Reovirus FAST protein transmembrane domains function in a modular, primary sequence-independent manner to mediate cell–cell membrane fusion. J Virol 83:2941–2950
Clarke P, Tyler KL (2003) Reovirus-induced apoptosis: a minireview. Apoptosis 8:141–150
Coffey CM, Sheh A, Kim IS, Chandran K, Nibert ML, Parker JS (2006) Reovirus outer capsid protein micro1 induces apoptosis and associates with lipid droplets, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria. J Virol 80:8422–8438
Cohnen A, Chiang SC, Stojanovic A, Schmidt H, Claus M, Saftig P, Janssen O, Cerwenka A, Bryceson YT, Watzl C (2013) Surface CD107a/LAMP-1 protects natural killer cells from degranulation-associated damage. Blood 122:1411–1418
Connolly JL, Rodgers SE, Clarke P, Ballard DW, Kerr LD, Tyler KL, Dermody TS (2000) Reovirus-induced apoptosis requires activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB. J Virol 74:2981–2989
Corcoran JA, Duncan R (2004) Reptilian reovirus utilizes a small type III protein with an external myristylated amino terminus to mediate cell–cell fusion. J Virol 78:4342–4351
Eskelinen EL (2006) Roles of LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy. Mol Aspects Med 27:495–502
Geng H, Zhang Y, Liu-Partanen Y, Vanhanseng Guo D, Wang Y, Liu M, Tong G (2009) Apoptosis induced by duck reovirus p10.8 protein in primary duck embryonated fibroblast and Vero E6 cells. Avian Dis 53:434–440
Gouvea VS, Schnitzer TJ (1982) Polymorphism of the migration of double-stranded RNA genome segments of avian reoviruses. J Virol 43:465–471
Gouvea VS, Schnitzer TJ (1982) Polymorphism of the genomic RNAs among the avian reoviruses. J Gen Virol 61(Pt 1):87–91
Hsu CJ, Wang CY, Lee LH, Shih WL, Chang CI, Cheng HL, Chulu JL, Ji WT, Liu HJ (2006) Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against avian reovirus sigma C protein and their application in detection of avian reovirus isolates. Avian Pathol 35:320–326
Hsu HW, Su HY, Huang PH, Lee BL, Liu HJ (2005) Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of P10- and P17-encoding genes of avian reovirus. Avian Dis 49:36–42
Key T, Duncan R (2014) A compact, multifunctional fusion module directs cholesterol-dependent homomultimerization and syncytiogenic efficiency of reovirus p10 FAST proteins. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004023
Krzewski K, Gil-Krzewska A, Nguyen V, Peruzzi G, Coligan JE (2013) LAMP1/CD107a is required for efficient perforin delivery to lytic granules and NK-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 121:4672–4683
Labrada L, Bodelon G, Vinuela J, Benavente J (2002) Avian reoviruses cause apoptosis in cultured cells: viral uncoating, but not viral gene expression, is required for apoptosis induction. J Virol 76:7932–7941
Lin HY, Chuang ST, Chen YT, Shih WL, Chang CD, Liu HJ (2007) Avian reovirus-induced apoptosis related to tissue injury. Avian Pathol 36:155–159
Lin PY, Lee JW, Liao MH, Hsu HY, Chiu SJ, Liu HJ, Shih WL (2009) Modulation of p53 by mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and protein kinase C delta during avian reovirus S1133-induced apoptosis. Virology 385:323–334
Lin PY, Liu HJ, Liao MH, Chang CD, Chang CI, Cheng HL, Lee JW, Shih WL (2010) Activation of PI 3-kinase/Akt/NF-kappaB and Stat3 signaling by avian reovirus S1133 in the early stages of infection results in an inflammatory response and delayed apoptosis. Virology 400:104–114
Lin PY, Liu HJ, Chang CD, Chang CI, Hsu JL, Liao MH, Lee JW, Shih WL (2011) Avian reovirus S1133-induced DNA damage signaling and subsequent apoptosis in cultured cells and in chickens. Arch Virol 156:1917–1929
Liu HJ, Lin PY, Lee JW, Hsu HY, Shih WL (2005) Retardation of cell growth by avian reovirus p17 through the activation of p53 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:709–715
Reed LJ, Muench H (1938) A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am J Epidemiol 27:493–497
Rodriguez-Grille J, Busch LK, Martinez-Costas J, Benavente J (2014) Avian reovirus-triggered apoptosis enhances both virus spread and the processing of the viral nonstructural muNS protein. Virology 462–463:49–59
Salsman J, Top D, Boutilier J, Duncan R (2005) Extensive syncytium formation mediated by the reovirus FAST proteins triggers apoptosis-induced membrane instability. J Virol 79:8090–8100
Schnitzer TJ, Ramos T, Gouvea V (1982) Avian reovirus polypeptides: analysis of intracellular virus-specified products, virions, top component, and cores. J Virol 43:1006–1014
Shih WL, Hsu HW, Liao MH, Lee LH, Liu HJ (2004) Avian reovirus sigmaC protein induces apoptosis in cultured cells. Virology 321:65–74
Shmulevitz M, Yameen Z, Dawe S, Shou J, O’Hara D, Holmes I, Duncan R (2002) Sequential partially overlapping gene arrangement in the tricistronic S1 genome segments of avian reovirus and Nelson Bay reovirus: implications for translation initiation. J Virol 76:609–618
Shmulevitz M, Salsman J, Duncan R (2003) Palmitoylation, membrane-proximal basic residues, and transmembrane glycine residues in the reovirus p10 protein are essential for syncytium formation. J Virol 77:9769–9779
Shmulevitz M, Corcoran J, Salsman J, Duncan R (2004) Cell–cell fusion induced by the avian reovirus membrane fusion protein is regulated by protein degradation. J Virol 78:5996–6004
Top D, Barry C, Racine T, Ellis CL, Duncan R (2009) Enhanced fusion pore expansion mediated by the trans-acting Endodomain of the reovirus FAST proteins. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000331
Varela R, Benavente J (1994) Protein coding assignment of avian reovirus strain S1133. J Virol 68:6775–6777
Varela R, Martinez-Costas J, Mallo M, Benavente J (1996) Intracellular posttranslational modifications of S1133 avian reovirus proteins. J Virol 70:2974–2981
Zhang Z, Lin W, Li X, Cao H, Wang Y, Zheng SJ (2015) Critical role of eukaryotic elongation factor 1 alpha 1 (EEF1A1) in avian reovirus sigma-C-induced apoptosis and inhibition of viral growth. Arch Virol 160:1449–1461
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jingliang Su for his kind assistance. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (#31272543 and #31430085) and Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-Industry Technology Research System (#NYCYTX-41).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., He, Z., Tang, J. et al. A critical role of LAMP-1 in avian reovirus P10 degradation associated with inhibition of apoptosis and virus release. Arch Virol 161, 899–911 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2731-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2731-5