Abstract
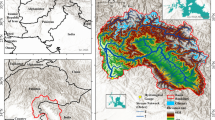
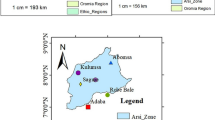
Afforestation is an important human activity that changes land use, and would affect regional climate. However, the impact of afforestation on the regional climate in arid and semi-arid regions remains a subject of controversy. By ensemble sensitivity simulations using Advanced Research Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model, this study investigates the influence of vegetation category change within a 100 km width along the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River (YR) on regional climate. Results suggest that afforestation would reduce summer surface temperature by -0.05 ~ -0.8℃ and increase summer convective precipitation by 3 ~ 45 mm in the afforestation regions, instead, summer non-convective precipitation would increase (3 ~ 35 mm) in the upper reaches of the YR. The increased non-convective precipitation in the upper reaches of the YR could be attributed to the increased integral water vapor convergence, cloud hydrometeor, and decreased cloud top temperature. In the afforested region, the increased convective precipitation could be related to the enhanced thermodynamic and water vapor conditions. These findings emphasize that even on regional scale in semi-arid and arid regions, greening can lead to evident regional climate impacts, these also provide insight for policymakers in formulating sustainable afforestation strategies.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The CRU dataset can be downloaded from https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/hrg/cru_ts_4.07/cruts.2304141047.v4.07/, the FNL data can be obtained from https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds083-2/.
Code availability
The code generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arkin PA, Ardanuy PE (1989) Estimating climatic-scale precipitation from space: a review. J Clim 2:1229–1238. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1989)002%3c1229:ECSPFS%3e2.0.CO;2
Arora VK, Montenegro A (2011) Small temperature benefits provided by realistic afforestation efforts. Nat Geosci 4:514–518. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1182
Barrett EC (1970) The estimation of monthly rainfall from satellite data. Mon Weather Rev 98:322–327. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1970)098%3c0322:TEOMRF%3e2.3.CO;2
Bonan GB (2008) Forests and climate change: forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 320:1444–1449. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1155121
Bright RM, Davin E, O’Halloran T, Pongratz J, Zhao K, Cescatti A (2017) Local temperature response to land cover and management change driven by non-radiative processes. Nat Clim Change 7:296–302. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3250
Bryan BA, Gao L, Ye Y, Sun X, Connor JD, Crossman ND, Stafford-Smith M, Wu J, He C, Yu D, Liu Z, Li A, Huang Q, Ren H, Deng X, Zheng H, Niu J, Han G, Hou X (2018) China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 559:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0280-2
Burakowski E, Tawfik A, Ouimette A, Lepine L, Novick K, Ollinger S, Zarzycki C, Bonan G (2018) The role of surface roughness, albedo, and Bowen ratio on ecosystem energy balance in the Eastern United States. Agric For Meteorol 249:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.030
Cao Q, Wu J, Yu D, Wang W (2019) The biophysical effects of the vegetation restoration program on regional climate metrics in the Loess Plateau, China. Agric For Meteorol 268:169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.01.022
Charney JG (1975) Dynamics of deserts and drought in the Sahel. Q J R Meteorol Soc 101:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49710142802
Chen L, Dirmeyer PA (2016) Adapting observationally based metrics of biogeophysical feedbacks from land cover/land use change to climate modeling. Environ Res Lett 11:034002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/3/034002
Chen F, Dudhia J (2001) Coupling an advanced land surface-hydrology model with the penn state–NCAR MM5 modeling system. part i: model implementation and sensitivity. Mon Weather Rev 129:569–585. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129%3c0569:CAALSH%3e2.0.CO;2
Chen L, Ma Z, Mahmood R, Zhao T, Li Z, Li Y (2017a) Recent land cover changes and sensitivity of the model simulations to various land cover datasets for China. Meteorol Atmospheric Phys 129:395–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0478-5
Chen L, Ma Z, Zhao T (2017b) Modeling and analysis of the potential impacts on regional climate due to vegetation degradation over arid and semi-arid regions of China. Clim Change 144:461–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-016-1847-2
Davin EL, de Noblet-Ducoudré N (2010) Climatic impact of global-scale deforestation: radiative versus nonradiative processes. J Clim 23:97–112. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI3102.1
Devaraju N, Bala G, Modak A (2015) Effects of large-scale deforestation on precipitation in the monsoon regions: Remote versus local effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:3257–3262. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1423439112
Fan X, Ma Z, Yang Q, Han Y, Mahmood R, Zheng Z (2015) Land use/land cover changes and regional climate over the Loess Plateau during 2001–2009. Part i: Observational Evidence. Clim Change 129:427–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-014-1069-4
Feddema J, Oleson K, Bonan G, Mearns L, Buja L, Meehl G, Washington W (2006) The importance of land-cover change in simulating future climates. Science 310:1674–1678. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1118160
Feng X, Fu B, Lu N, Zeng Y, Wu B (2013) How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: an analysis of carbon sequestration in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci Rep 3:2846. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02846
Foley JA, DeFries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Monfreda C, Patz JA, Prentice IC, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 309:570–574. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1111772
Fu B, Wang S, Liu Y, Liu J, Liang W, Miao C (2017) Hydrogeomorphic ecosystem responses to natural and anthropogenic changes in the loess plateau of China. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 45:223–243. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-063016-020552
He G, ZHAO Y, WANG J, WANG Q, ZHU Y (2018) Impact of large-scale vegetation restoration project on summer land surface temperature on the Loess Plateau, China. J Arid Land 10:892–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-018-0105-z
Hong, SY, Lim J (2006) The WRF single-moment 6-class microphysics scheme (WSM6). J Korean Meteor Soc 42:129–151
Huang L, Zhai J, Sun CY, Liu JY, Ning J, Zhao GS (2018) Biogeophysical forcing of land-use changes on local temperatures across different climate regimes in China. J Clim 31:7053–7068. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0116.1
Iacono MJ, Delamere JS, Mlawer EJ, Shephard MW, Clough SA, Collins WD (2008) Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J Geophys Res Atmospheres 113. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD009944
Jiang Y, Wang G, Liu W, Erfanian A, Peng Q, Fu R (2021) Modeled response of south american climate to three decades of deforestation. J Clim 34:2189–2203. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0380.1
Jiménez PA, Dudhia J, González-Rouco JF, Navarro J, Montávez JP, García-Bustamante E (2012) A revised scheme for the WRF surface layer formulation. Mon Weather Rev 140:898–918. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-11-00056.1
Kain JS (2004) The kain-fritsch convective parameterization: an update. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 43:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2004)043%3c0170:TKCPAU%3e2.0.CO;2
Laguë MM, Swann ALS (2016) Progressive midlatitude afforestation: impacts on clouds, global energy transport, and precipitation. J Clim 29:5561–5573. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0748.1
Laguë MM, Swann ALS, Boos WR (2021) Radiative feedbacks on land surface change and associated tropical precipitation shifts. J Clim 34:6651–6672. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0883.1
Lee X, Goulden ML, Hollinger DY, Barr A, Black TA, Bohrer G, Bracho R, Drake B, Goldstein A, Gu L, Katul G, Kolb T, Law BE, Margolis H, Meyers T, Monson R, Munger W, Oren R, Paw UKT, Richardson AD, Schmid HP, Staebler R, Wofsy S, Zhao L (2011) Observed increase in local cooling effect of deforestation at higher latitudes. Nature 479:384–387. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10588
Lejeune Q, Davin EL, Guillod BP, Seneviratne SI (2015) Influence of Amazonian deforestation on the future evolution of regional surface fluxes, circulation, surface temperature and precipitation. Clim Dyn 44:2769–2786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2203-8
Lejeune Q, Seneviratne SI, Davin EL (2017) Historical land-cover change impacts on climate: comparative assessment of LUCID and CMIP5 multimodel experiments. J Clim 30:1439–1459. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0213.1
Li J, Li Z, Lü Z (2016) Analysis of spatiotemporal variations in land use on the Loess Plateau of China during 1986–2010. Environ Earth Sci 75:997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5807-y
Li Y, Li Z, Zhihui L, Geng X, Deng X (2013) Numerical simulation of the effects of grassland degradation on the surface climate in overgrazing area of Northwest China. Adv Meteorol 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/270192
Li Y, Piao S, Li LZX, Chen A, Wang X, Ciais P, Huang L, Lian X, Peng S, Zeng Z, Wang K, Zhou L (2018) Divergent hydrological response to large-scale afforestation and vegetation greening in China. Sci Adv 4:eaar4182. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar4182
Liang W, Bai D, Jin Z, You Y, Li J, Yang Y (2015) A Study on the streamflow change and its relationship with climate change and ecological restoration measures in a sediment concentrated region in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour Manag 29:4045–4060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1044-5
Liu J, Li S, Ouyang Z, Tam C, Chen X (2008) Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:9477–9482. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0706436105
Liu Y, Ge J, Guo W, Cao Y, Chen C, Luo X, Yang L, Wang S (2023) Revisiting Biophysical Impacts of Greening on Precipitation Over the Loess Plateau of China Using WRF With Water Vapor Tracers. Geophys Res Lett 50:e2023GL102809. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GL102809
Nakanishi M, Niino H (2006) An lmproved Mellor-Yamada level-3 Model: its numerical stability and application to a regional prediction of advection fog. Bound-Layer Meteorol 119:397–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-005-9030-8
Oleson KW, Bonan GB, Levis S, Vertenstein M (2004) Effects of land use change on North American climate: impact of surface datasets and model biogeophysics. Clim Dyn 23:117–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-004-0426-9
Perugini L, Caporaso L, Marconi S, Cescatti A, Quesada B, de Noblet-Ducoudré N, House JI, Arneth A (2017) Biophysical effects on temperature and precipitation due to land cover change. Environ Res Lett 12:053002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa6b3f
Pielke RA, Niyogi D (2009) The Role of Landscape Processes within the Climate System. In: Otto J-C, Dikau R (eds) Landform - Structure, Evolution, Process Control. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 67–85
Pitman AJ, Avila FB, Abramowitz G, Wang YP, Phipps SJ, de Noblet-Ducoudré N (2011) Importance of background climate in determining impact of land-cover change on regional climate. Nat Clim Change 1:472–475. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1294
Portmann R, Beyerle U, Davin E, Fischer EM, De Hertog S, Schemm S (2022) Global forestation and deforestation affect remote climate via adjusted atmosphere and ocean circulation. Nat Commun 13:5569. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33279-9
Reynolds JF, Smith DMS, Lambin EF, Turner BL, Mortimore M, Batterbury SPJ, Downing TE, Dowlatabadi H, Fernández RJ, Herrick JE, Huber-Sannwald E, Jiang H, Leemans R, Lynam T, Maestre FT, Ayarza M, Walker B (2007) Global desertification: building a science for dryland development. Science 316:847–851. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1131634
Shao R, Zhang B, Su T, Long B, Cheng L, Xue Y, Yang W (2019) Estimating the increase in regional evaporative water consumption as a result of vegetation restoration over the Loess Plateau, China. J Geophys Res Atmospheres 124:11783–11802. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031295
Shukla J, Nobre C, Sellers P (1990) Amazon Deforestation and Climate Change. Science 247:1322–1325. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.247.4948.1322
Swann ALS, Fung IY, Chiang JCH (2012) Mid-latitude afforestation shifts general circulation and tropical precipitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:712–716. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116706108
Swann ALS, Fung IY, Liu Y, Chiang JCH (2014) Remote vegetation feedbacks and the mid-holocene Green Sahara. J Clim 27:4857–4870. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00690.1
Swann ALS, Longo M, Knox RG, Lee E, Moorcroft PR (2015) Future deforestation in the Amazon and consequences for South American climate. Agric for Meteorol 214–215:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.07.006
Tian L, Zhang B, Chen S, Wang X, Ma X, Pan B (2022) Large-scale afforestation enhances precipitation by intensifying the atmospheric water cycle over the Chinese Loess Plateau. J Geophys Res Atmospheres 127:e2022JD036738. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022JD036738
Tian L, Zhang B, Wang X, Chen S, Pan B (2022) Large-Scale Afforestation Over the Loess Plateau in China Contributes to the Local Warming Trend. J Geophys Res Atmospheres 127:e2021JD035730. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JD035730
Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Lubchenco J, Melillo JM (1997) Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science 277:494–499. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5325.494
Wang C, Yang J, Yang K, Zhang F, Zhang S, Li K, Yang Y (2022) Changing precipitation characteristics in the Yellow River Basin in the last 60 years and tendency prediction for next 30 years. Arid Zone Res 39(3):708–722
Wang X, Guo W, Qiu B, Liu Y, Sun J, Ding A (2017) Quantifying the contribution of land use change to surface temperature in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Atmospheric Chem Phys 17:4989–4996. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-4989-2017
Wei H, Fu C (1998) Study of the sensitivity of a regional model in response to land cover change over northern China. Hydrol Process 12:2249–2265. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(19981030)12:13/14%3c2249::AID-HYP733%3e3.0.CO;2-Q
Wierik SA, Cammeraat ELH, Gupta J, Artzy-Randrup YA (2021) Reviewing the Impact of Land Use and Land-Use Change on Moisture Recycling and Precipitation Patterns. Water Resour Res 57:e2020WR029234. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020WR029234
Xue Y, Shukla J (1993) The Influence of Land Surface Properties on Sahel Climate. Part 1: Desertification. J Clim 6:2232–2245. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006%3c2232:TIOLSP%3e2.0.CO;2
Yang Y, Guan H, Batelaan O, McVicar TR, Long D, Piao S, Liang W, Liu B, Jin Z, Simmons CT (2016) Contrasting responses of water use efficiency to drought across global terrestrial ecosystems. Sci Rep 6:23284. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23284
Yang J, Yang K, Zhang F, Wang C (2023) Contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to historical changes in vegetation cover and its future projections in the Yellow River basin, China. Int J Climatol 43:6434–6449. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.8213
Yu L, Leng G (2022) Global effects of different types of land use and land cover changes on near-surface air temperature. Agric for Meteorol 327:109232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2022.109232
Yu E, Wang H, Sun J, Gao Y (2013) Climatic response to changes in vegetation in the Northwest Hetao Plain as simulated by the WRF model. Int J Climatol 33:1470–1481. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3527
Zeng Z, Wang D, Yang L, Wu J, Ziegler AD, Liu M, Ciais P, Searchinger TD, Yang Z-L, Chen D, Chen A, Li LZX, Piao S, Taylor D, Cai X, Pan M, Peng L, Lin P, Gower D, Feng Y, Zheng C, Guan K, Lian X, Wang T, Wang L, Jeong S-J, Wei Z, Sheffield J, Caylor K, Wood EF (2021) Deforestation-induced warming over tropical mountain regions regulated by elevation. Nat Geosci 14:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-020-00666-0
Zhang J (2005) Impact of land surface deg-radation in northern China and southern Mongolia on re-gional climate. Chin Sci Bull 50:75. https://doi.org/10.1360/04wd0054
Zhang B, Tian L, Zhao X, Wu P (2021) Feedbacks between vegetation restoration and local precipitation over the Loess Plateau in China. Sci China Earth Sci 64:920–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9751-8
Zhang F, Bi K, Wei S, Wang C (2024) The response of precipitation to initial soil moisture over the tibetan plateau: respective effects of boundary layer vertical heat and vapor diffusions. Mon Weather Rev 152(2):589–605
Zhao G, Mu X, Wen Z, Wang F, Gao P (2013) Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad Dev 24:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2246
Acknowledgements
The Supercomputing Center of the Lanzhou University provides computation support. National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42175064), the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (23YFFA0001), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.41471034).
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42175064), the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (23YFFA0001), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.41471034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dehua Gao: Data processing, Data analysis, Graphing, Writing-Original draft preparation. Feimin Zhang: Supervision, Validation, Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Chenghai Wang: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing- Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, D., Zhang, F. & Wang, C. Climatic effects of afforestation over the middle-upper reaches of the yellow river. Theor Appl Climatol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-024-05023-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-024-05023-4