Abstract
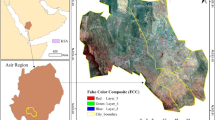
Urbanization is a complex phenomenon that has a profound impact on natural resources, economies, climate dynamics, and community structures. This study sets out to analyze the effects of urban sprawl on key urban regions in Bangladesh, covering urban, suburban, and rural landscapes. We used Landsat images from 1992 to 2022, processed and classified using the Google Earth Engine and Random Forest algorithm. Spatial metrics, Tupu method, ANOVA, and spatial regression models helped us quantify and explain land cover changes, their drivers, and consequences. Our findings show that the total built-up area in the five districts expanded from 1,200 km2 in 1992 to 2,800 km2 in 2022, with an overall yearly expansion rate of 3.5%. Meanwhile, vegetation cover declined from 2,500 km2 in 1992 to 1,500 km2 in 2022, with an average yearly loss rate of 2.5%. We identified population growth, economic development, and infrastructure expansion as the main drivers of urbanization, while land degradation, air and water pollution, and loss of biodiversity were the main consequences. Urbanization also had a significant impact on environmental functions, including carbon sequestration, water flow control, and urban heat mitigation, with varying effects across different urban areas and land use types. For instance, we found that carbon storage capacity decreased by 20% in urban areas, while it increased by 10% in rural areas. Our research highlights the crucial role of preserving and enhancing green spaces, including vegetation cover and water bodies, to mitigate urban heat and promote urban resilience. The findings underscore the need for sustainable urbanization, balancing economic growth with environmental protection and climate resilience, using geospatial and remote sensing techniques.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not Applicable.
Code Availability
Not Applicable.
References
(BBS) (2013) Statistics and Informatics Division (Sid) Ministry of Planning. Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS)
Abdullah HM, Islam I, Miah MdG, Ahmed Z (2019) Quantifying the spatiotemporal patterns of forest degradation in a fragmented, rapidly urbanizing landscape: A case study of Gazipur, Bangladesh. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 13:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2019.01.002
Ahmed, R, Roy, C (2015) An Integrated Approach to Environmental Management in Bangladesh. In Global Sustainability (pp. 185–201). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16477-9_10
Ali AMS (2007) Population pressure, agricultural intensification and changes in rural systems in Bangladesh. Geoforum 38(4):720–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOFORUM.2006.11.028
Anand, V, Oinam, B (2019) Future land use land cover prediction with special emphasis on urbanization and wetlands. 11(3), 225–234https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2019.1704304
Arifeen HM, Phoungthong K, Mostafaeipour A, Yuangyai N, Yuangyai C, Techato K, Jutidamrongphan W (2021) Determine the Land-Use Land-Cover Changes, Urban Expansion and Their Driving Factors for Sustainable Development in Gazipur Bangladesh. Atmosphere 12(10):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101353
Asabere SB, Acheampong RA, Ashiagbor G, Beckers SC, Keck M, Erasmi S, Schanze J, Sauer D (2020) Urbanization, land use transformation and spatio-environmental impacts: Analyses of trends and implications in major metropolitan regions of Ghana. Land Use Policy 96:104707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104707
Ayele, GT, Tebeje, AK, Demissie, SS, Belete, MA, Jemberrie, MA, Teshome, WM, Mengistu, DT, Teshale, EZ (2018) Time series land cover mapping and change detection analysis using geographic information system and remote sensing, Northern Ethiopia. Air, Soil and Water Research, 11. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622117751603/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/10.1177_1178622117751603-FIG12.JPEG
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (2011a) Population & Housing Census 2011, Statistics and Informatics Division (SID). Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (2011b) Report on Agriculture and Rural Statistics, Statistics and Informatics Division (SID). Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Berhe AA, Barnes RT, Six J, Marín-Spiotta E (2018) Role of Soil Erosion in Biogeochemical Cycling of Essential Elements: Carbon. Nitrogen, and Phosphorus 46:521–548. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV-EARTH-082517-010018
Bose A, Chowdhury IR (2020) Monitoring and modeling of spatio-temporal urban expansion and land-use/land-cover change using markov chain model: a case study in Siliguri Metropolitan area, West Bengal India. Model Earth Syst Environ 6(4):2235–2249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00842-6
Breiman L (2001) Random Forest. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Bulleri F, Chapman MG (2010) The introduction of coastal infrastructure as a driver of change in marine environments. J Appl Ecol 47(1):26–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2009.01751.x
Chowdhury M, Hasan ME, Abdullah-Al-Mamun MM (2020) Land use/land cover change assessment of Halda watershed using remote sensing and GIS. The Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 23(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJRS.2018.11.003
De Carvalho RM, Szlafsztein CF (2019) Urban vegetation loss and ecosystem services: The influence on climate regulation and noise and air pollution. Environ Pollut 245:844–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2018.10.114
de Mello K, Taniwaki RH, de Paula FR, Valente RA, Randhir TO, Macedo DR, Leal CG, Rodrigues CB, Hughes RM (2020) Multiscale land use impacts on water quality: Assessment, planning, and future perspectives in Brazil. J Environ Manage 270:110879. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2020.110879
Faulkner S (2004) Urbanization impacts on the structure and function of forested wetlands. Urban Ecosystems 7(2):89–106. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UECO.0000036269.56249.66
Foody GM (2020) Explaining the unsuitability of the kappa coefficient in the assessment and comparison of the accuracy of thematic maps obtained by image classification. Remote Sens Environ 239:111630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111630
Gautam L, Rai R (2022) Land Use and Land Cover Change Analysis Using Google Earth Engine in Manamati Watershed of Kathmandu District Nepal. Third Pole: J Geograph Educ 22:49–60. https://doi.org/10.3126/TTP.V22I01.52560
Gelman, A (2005) Analysis of variance—why it is more important than ever. The Annals of Statistics, 33(1). https://doi.org/10.1214/009053604000001048
Groffman PM, Cavender-Bares J, Bettez ND, Grove JM, Hall SJ, Heffernan JB, Hobbie SE, Larson KL, Morse JL, Neill C, Nelson K, O’Neil-Dunne J, Ogden L, Pataki DE, Polsky C, Chowdhury RR, Steele MK (2014) Ecological homogenization of urban USA. Front Ecol Environ 12(1):74–81. https://doi.org/10.1890/120374
Hailu A, Mammo S, Kidane M (2020) Dynamics of land use, land cover change trend and its drivers in Jimma Geneti District. Western Ethiopia Land Use Policy 99:105011. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LANDUSEPOL.2020.105011
Hao Y, Liu Y-M (2016) The influential factors of urban PM2.5 concentrations in China: a spatial econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 112:1443–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.005
Haque MI, Basak R (2017) Land cover change detection using GIS and remote sensing techniques: A spatio-temporal study on Tanguar Haor, Sunamganj, Bangladesh. The Egyptian J Remote Sens Space Sci 20(2):251–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJRS.2016.12.003
Hasan S, Shi W, Zhu X, Abbas S (2019) Monitoring of Land Use/Land Cover and Socioeconomic Changes in South China over the Last Three Decades Using Landsat and Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing 11(14):1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS11141658
Hassan MM (2017) Monitoring land use/land cover change, urban growth dynamics and landscape pattern analysis in five fastest urbanized cities in Bangladesh. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 7:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSASE.2017.07.001
Hassan MM, Nazem MNI (2016) Examination of land use/land cover changes, urban growth dynamics, and environmental sustainability in Chittagong city, Bangladesh. Environ Dev Sustain 18(3):697–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10668-015-9672-8/TABLES/3
Hassan M, Southworth J (2017) Analyzing Land Cover Change and Urban Growth Trajectories of the Mega-Urban Region of Dhaka Using Remotely Sensed Data and an Ensemble Classifier. Sustainability 10(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010010
Hassan, MM, Nazem, MNI (2016b) Examination of land use/land cover changes, urban growth dynamics, and environmental sustainability in Chittagong city, Bangladesh. Environ, Dev Sustain, 18(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-015-9672-8
Heagerty PJ, Lumley T, Pepe MS (2000) Time-Dependent ROC Curves for Censored Survival Data and a Diagnostic Marker. Biometrics 56(2):337–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00337.x
Hossain Bhuiyan MM, Islam K, Islam KN, Jashimuddin M (2018) Monitoring dynamic land-use change in rural–urban transition: a case study from Hathazari Upazila. Bangladesh 3(4):247–257. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2018.1556034
Hossain F, Moniruzzaman (2021) Environmental change detection through remote sensing technique: A study of Rohingya refugee camp area (Ukhia and Teknaf sub-district), Cox’s Bazar. Bangladesh Environmental Challenges 2:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100024
Huang Y, Li P, An Q, Mao F, Zhai W, Yu K, He Y (2021) Long-term land use/cover changes reduce soil erosion in an ionic rare-earth mineral area of southern China. Land Degrad Dev 32(14):4042–4055. https://doi.org/10.1002/LDR.3890
Immitzer M, Atzberger C, Koukal T (2012) Tree Species Classification with Random Forest Using Very High Spatial Resolution 8-Band WorldView-2 Satellite Data. Remote Sensing 4(9):2661–2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs4092661
Imran HM, Hossain A, Shammas MI, Das MK, Islam MdR, Rahman K, Almazroui M (2022) Land surface temperature and human thermal comfort responses to land use dynamics in Chittagong city of Bangladesh. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 13(1):2283–2312. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2022.2114384
Islam, MN, Tamanna, S, van Amstel, A, Noman, M, Ali, MSS, Aparajita, DM, Roy, P, Tanha, SR, Sarkar, N, Ashiquzzaman, M, Ghosh, SK, Hasnat, SR, Bhuiyan, MF, Sayef, M, Saha, P, Hasan, GR, Ghosh, A (2021) Climate Change Impact and Comprehensive Disaster Management Approach in Bangladesh: A Review. Springer Climate, 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71950-0_1/COVER
Islam, S, Ma, M, Hossain, MN, Ganguli, S, Sarker, MNI (2021) Temporal Evaluation of Climate Change on Land Use and Land Cover Changes in the Southeastern Region of Bangladesh from 2001 to 2016. Climate Change Management, 509–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77259-8_26/COVER
Janssen LLF, van der Wel FJM (1994) Accuracy assessment of satellite derived land cover data: a review. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 60:419–426
Kafy AA, Rahman MS, Faisal AA, Hasan MM, Islam M (2020) Modelling future land use land cover changes and their impacts on land surface temperatures in Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 18:100314. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSASE.2020.100314
Kafy AA, Dey NN, Al Rakib A, Rahaman ZA, Nasher NMR, Bhatt A (2021) Modeling the relationship between land use/land cover and land surface temperature in Dhaka. Bangladesh Using CA-ANN Algorithm Environmental Challenges 4:100190. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVC.2021.100190
Karim Islam K, Bani M-S, Muhtazaruddin (2019) Renewable Energy for Sustainable Growth and Development: An Evaluation of Law and Policy of Bangladesh. Sustainability 11(20):5774. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205774
Khaleda S (2013) The poultry value chain and sustainable development of poultry microenterprises that utilize homestead lands: A case study in Gazipur. Bangladesh Land Use Policy 30(1):642–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.05.010
Khan MMH, Bryceson I, Kolivras KN, Faruque F, Rahman MM, Haque U (2015) Natural disasters and land-use/land-cover change in the southwest coastal areas of Bangladesh. Reg Environ Change 15(2):241–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10113-014-0642-8/METRICS
Lin X, Xu M, Cao C, Singh RP, Chen W, Ju H (2018) Land-Use/Land-Cover Changes and Their Influence on the Ecosystem in Chengdu City, China during the Period of 1992–2018. Sustainability 10(10):3580. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU10103580
Lu L, Kuenzer C, Guo H, Li Q, Long T, Li X (2014) A Novel Land Cover Classification Map Based on a MODIS Time-Series in Xinjiang China. Remote Sensing 6(4):3387–3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS6043387
Mahto R, Sahu AML, Soni PK (2022) Change Detection of Vegetative Covers in Kalara Nala Watershed of Damoh District Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Int J Environ Climate Change 12(12):1680–1689. https://doi.org/10.9734/IJECC/2022/V12I121611
Miah MT, Fariha JN, Kafy A-A, Islam R, Biswas N, Duti BM, Fattah MdA, Alsulamy S, Khedher KM, Salem MA (2024) Exploring the nexus between land cover change dynamics and spatial heterogeneity of demographic trajectories in rapidly growing ecosystems of south Asian cities. Ecol Ind 158:111299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111299
Miah, MD, Hasan, R, Uddin, H (2020) Agricultural development and the rural economy: The case of Bangladesh. Bangladesh’s Economic and Social Progress: From a Basket Case to a Development Model, 237–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1683-2_8/COVER
Nahrin K (2019) Environmental area conservation through urban planning: case study in Dhaka. J Property, Planning Environ Law 12(1):55–71. https://doi.org/10.1108/JPPEL-11-2018-0033
Naibbi AI, Baily B, Healey RG, Collier P (2014) Changing Vegetation Patterns in Yobe State Nigeria: An Analysis of the Rates of Change, Potential Causes and the Implications for Sustainable Resource Management. Int J Geosci 05(01):50–62. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2014.51007
Naikoo MW, Rihan M, Ishtiaque M, Shahfahad (2020) Analyses of land use land cover (LULC) change and built-up expansion in the suburb of a metropolitan city: Spatio-temporal analysis of Delhi NCR using landsat datasets. J Urban Manag 9(3):347–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JUM.2020.05.004
Niu X, Liao F, Liu Z, Wu G (2022) Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Land-Use Transition from the Perspective of Urban-Rural Transformation Development: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Delta. Land 11(5):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050631
Noman AHMd, Mia MA, Banna H, Rana MdS, Alam ASAF, Gee CS, Isa CR, Er AC (2016) City profile: Narayanganj, Bangladesh. Cities 59:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2016.05.020
Patwary, MM, Ashraf, S, Shuvo, FK (2020) Land use changes and their effects on urban ecosystem services value: A study of khulna city, bangladesh. 2020 IEEE India Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, InGARSS 2020 - Proceedings, 62–65. https://doi.org/10.1109/INGARSS48198.2020.9358927
Qian, Y, Zeng, G, Pan, Y, Liu, Y, Zhang, L, Li, K (2021) A Prediction Model for High Risk of Positive RT-PCR Test Results in COVID-19 Patients Discharged From Wuhan Leishenshan Hospital, China. Front Publ Health, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.778539
Rahman HMT, Hickey GM (2019) Assessing Institutional Responses to Climate Change Impacts in the North-Eastern Floodplains of Bangladesh. Environ Manage 63(5):596–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-019-01155-w
Rahman MTU, Tabassum F, Rasheduzzaman M, Saba H, Sarkar L, Ferdous J, Uddin SZ, Zahedul Islam AZM (2017) Temporal dynamics of land use/land cover change and its prediction using CA-ANN model for southwestern coastal Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 189(11):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-017-6272-0/METRICS
Rai R, Zhang Y, Paudel B, Li S, Khanal N (2017) A Synthesis of Studies on Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics during 1930–2015 in Bangladesh. Sustainability 9(10):1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9101866
Rashid N, Alam JAMM, Chowdhury MdA, Islam SLU (2022) Impact of landuse change and urbanization on urban heat island effect in Narayanganj city, Bangladesh: A remote sensing-based estimation. Environmental Challenges 8:100571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2022.100571
Reid H, Shafiqul Alam S (2017) Ecosystem-based approaches to adaptation: evidence from two sites in Bangladesh. Climate Dev 9(6):518–536. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2016.1167663
Rodriguez-Galiano VF, Chica-Olmo M, Abarca-Hernandez F, Atkinson PM, Jeganathan C (2012) Random Forest classification of Mediterranean land cover using multi-seasonal imagery and multi-seasonal texture. Remote Sens Environ 121:93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.12.003
Roy B (2021) A machine learning approach to monitoring and forecasting spatio-temporal dynamics of land cover in Cox’s Bazar district, Bangladesh from 2001 to 2019. Environmental Challenges 5:100237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100237
Santhosh LG, Shilpa DN (2023) Assessment of LULC change dynamics and its relationship with LST and spectral indices in a rural area of Bengaluru district, Karnataka India. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 29:100886. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSASE.2022.100886
Sharma R, Nehren U, Rahman SA, Meyer M, Rimal B, Seta GA, Baral H (2018) Modeling Land Use and Land Cover Changes and Their Effects on Biodiversity in Central Kalimantan Indonesia. Land 7(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/LAND7020057
Song X-P, Hansen MC, Stehman SV, Potapov PV, Tyukavina A, Vermote EF, Townshend JR (2018) Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 560(7720):639–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0411-9
Sultan MT, Sharmin F, Badulescu A, Stiubea E, Xue K (2020) Travelers’ Responsible Environmental Behavior towards Sustainable Coastal Tourism: An Empirical Investigation on Social Media User-Generated Content. Sustainability 13(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010056
Tassi A, Vizzari M (2020) Object-Oriented LULC Classification in Google Earth Engine Combining SNIC, GLCM, and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sensing 12(22):3776. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223776
Thomas A (2019) Detection of land use / cover changes of the KOSH region over a period of 14 years using the South African National Land Cover datasets for 2000 and 2014. South African J Geomatics 8(2):108–129. https://doi.org/10.4314/SAJG.V8I2.1
Tian J, Wang B, Zhang C, Li W, Wang S (2020) Mechanism of regional land use transition in underdeveloped areas of China: A case study of northeast China. Land Use Policy 94:104538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104538
Walter SD (2005) The partial area under the summary ROC curve. Stat Med 24(13):2025–2040. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.2103
Willard CA (2020) Statistical Methods. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429261039
Wu Y, Li S, Yu S (2016) Monitoring urban expansion and its effects on land use and land cover changes in Guangzhou city. China Environ Monitor Assess 188(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5069-2
Yang, Y, Feng, Z, Liu, D, Zhang, J (2006) The spatial-temporal change of grassland in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), 3082–3085. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2006.795
Zadbagher E, Becek K, Berberoglu S (2018) Modeling land use/land cover change using remote sensing and geographic information systems: case study of the Seyhan Basin. Turkey Environ Monitor Assess 190(8):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-018-6877-Y/METRICS
Zhao J, Feng X, Deng L, Yang Y, Zhao Z, Zhao P, Peng C, Fu B (2020) Quantifying the Effects of Vegetation Restorations on the Soil Erosion Export and Nutrient Loss on the Loess Plateau. Front Plant Sci 11:573126. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPLS.2020.573126/BIBTEX
Ziaul Hoque M, Islam I, Ahmed M, Shamim Hasan S, Ahmed Prodhan F (2022) Spatio-temporal changes of land use land cover and ecosystem service values in coastal Bangladesh. The Egyptian J Remote Sens Space Sci 25(1):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJRS.2022.01.008
Acknowledgements
The Authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through a large research group. Project group number RGP. 2/262/44.
Funding
This research work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University under grant number RGP. 2/262/44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jannatun Nahar Fariha Conceptualization, Project administration Data collection, Formal analysis, Data curation, Supervision, Resources, Software, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Validation, Writing – review & editing. Md Tanvir Miah Conceptualization, Data collection, Formal analysis, Data curation, Supervision, Resources, Software, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Validation, Writing – review & editing. Zamil Ahamed Limon Project administration, Resources, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. Saleh Alsulamy Project administration, Resources, Methodology, Investigation, Validation, Funding, Writing – review & editing. Abdulla Al Kafy Project administration, Formal analysis, Supervision, Resources, Software, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SK Nafiz Rahman Project administration, Resources, Methodology, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fariha, J.N., Miah, M.T., Limon, Z.A. et al. Quantifying spatial dynamics of urban sprawl for climate resilience sustainable natural resource management by utilizing geostatistical and remote sensing techniques. Theor Appl Climatol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-024-05000-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-024-05000-x