Abstract
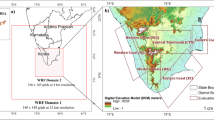
This study identifies the characteristics of summertime extreme rainfall events (ERE) according to the weather patterns in South Korea and compares the extreme rainfall model simulation skills depending on the use of cumulus parameterization. The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model simulations with and without the Kain–Fritsch cumulus scheme (CU_ON and CU_OFF experiment, respectively) are conducted over a 3 km high-resolution domain. The ERE-occurring days are clustered into four representative weather patterns (northern cyclonic circulation, frontal pattern between low and high, southwestern extratropical cyclone, and dominant positive geopotential height patterns) in terms of the 850 hPa geopotential height anomaly. As the occurrence dates of observed Clusters 1 and 2 overlap with a significant portion of the Changma period, their rainfall is characterized by continuous low-intensity rainfall. In contrast, relatively high-intensity, short-duration rainfall occurs mainly in Clusters 3 and 4. The WRF experiments generally describe the clustered weather patterns well. For CU_ON, the spatial distribution of the daily rainfall anomaly composite in Clusters 1 and 2 is well depicted, but the overall rainfall intensity is underestimated. CU_ON better reproduces the Clusters 1 and 2 type rainfall characterized by long-duration rainfall than CU_OFF. The observed rainfall events exceeding 20 mm h−1 intensity with a short-duration are reproduced better in CU_OFF than in CU_ON, showing reasonable performance for sub-daily time-scale rainfall in Clusters 3 and 4. Hence, the CU_ON well depicts the continuous low-intensity ERE type, while CU_OFF captures the ERE type where high-intensity rainfall with a short duration occurs relatively frequently.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The ASOS station data are available at https://www.data.go.kr/en/data/15043648/fileData.do. The ERA5 data can be downloaded at https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu. The typhoon data are available at https://www.weather.go.kr/w/typhoon/typ-history.do. The Changma period data are available at https://data.kma.go.kr/climate/rainySeason/selectRainySeasonList.do.
Code availability
Data analysis and graphics are conducted using Python 3 (https://www.python.org/) and NCAR command language (NCL; https://www.ncl.ucar.edu/). The codes used in this study are available at https://github.com/seogoing/WeatherClust.
References
Abadi AM, Rowe CM, Andrade M (2020) Climate regionalization in Bolivia: a combination of non-hierarchical and consensus clustering analyses based on precipitation and temperature. Int J Climatol 40:4408–4421. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6464
Afrizal T, Surussavadee C (2018) High-resolution climate simulations in the tropics with complex terrain employing the CESM/WRF model. Adv Meteorol 2018:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5707819
Bae D-H, Jung I-W, Chang H (2008) Long-term trend of precipitation and runoff in Korean river basins. Hydrol Process 22:2644–2656. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6861
Bae H, Ji H, Lim Y-J, Ryu Y, Kim M-H, Kim B-J (2019) Characteristics of drought propagation in South Korea: relationship between meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological droughts. Nat Hazards 99:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03676-3
Ban N, Schmidli J, Schär C (2014) Evaluation of the convection-resolving regional climate modeling approach in decade-long simulations. J Geophys Res: Atmos 119:7889–7907. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021478
Betts AK, Miller MJ (1986) A new convective adjustment scheme. Part II: single column tests using GATE wave, BOMEX, ATEX and arctic air-mass data sets. Q J R Meteorol Soc 112:693–709. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49711247308
Chattopadhyay A, Hassanzadeh P, Pasha S (2020) Predicting clustered weather patterns: a test case for applications of convolutional neural networks to spatio-temporal climate data. Sci Rep 10:1317. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57897-9
Chen F, Dudhia J (2001) Coupling an advanced land surface–hydrology model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: model implementation and sensitivity. Mon Weather Rev 129:569–585. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129%3c0569:Caalsh%3e2.0.Co;2
Ciarlo JM, Coppola E, Fantini A, Giorgi F, Gao X, Tong Y et al (2021) A new spatially distributed added value index for regional climate models: the EURO-CORDEX and the CORDEX-CORE highest resolution ensembles. Clim Dyn 57:1403–1424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05400-5
Collins WD, Hackney JK, Edwards DP (2002) An updated parameterization for infrared emission and absorption by water vapor in the National Center for Atmospheric Research Community Atmosphere Model. J Geophys Res 107:D22. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001jd001365
Deng A, Stauffer DR (2006) On improving 4-km mesoscale model simulations. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 45:361–381. https://doi.org/10.1175/jam2341.1
Diro GT, Tompkins AM, Bi X (2012) Dynamical downscaling of ECMWF Ensemble seasonal forecasts over East Africa with RegCM3. J Geophys Res: Atmos 117:D16103. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011jd016997
Fantini A, Raffaele F, Torma C, Bacer S, Coppola E, Giorgi F et al (2018) Assessment of multiple daily precipitation statistics in ERA-Interim driven Med-CORDEX and EURO-CORDEX experiments against high resolution observations. Clim Dyn 51:877–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3453-4
Fosser G, Khodayar S, Berg P (2015) Benefit of convection permitting climate model simulations in the representation of convective precipitation. Clim Dyn 44:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2242-1
Fragoso M, Tildes Gomes P (2008) Classification of daily abundant rainfall patterns and associated large-scale atmospheric circulation types in Southern Portugal. Int J Climatol 28:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1564
Frei C, Christensen JH, Déqué M, Jacob D, Jones RG, Vidale PL (2003) Daily precipitation statistics in regional climate models: evaluation and intercomparison for the European Alps. J Geophys Res: Atmos 108(1–4):73–86. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002287
Gao X, Shi Y, Song R, Giorgi F, Wang Y, Zhang D (2008) Reduction of future monsoon precipitation over China: comparison between a high resolution RCM simulation and the driving GCM. Meteorol Atmos Phys 100:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-008-0296-5
Geetha B, Balachandran S (2016) Diabatic heating and convective asymmetries during rapid intensity changes of tropical cyclones over North Indian Ocean. Trop Cyclone Res Rev 5:32–46. https://doi.org/10.6057/2016TCRRh1.04
Giorgi F, Mearns LO (1991) Approaches to the simulation of regional climate change: a review. Rev Geophys 29:191–216. https://doi.org/10.1029/90RG02636
Giorgi F, Shields C (1999) Tests of precipitation parameterizations available in latest version of NCAR regional climate model (RegCM) over continental United States. J Geophys Res: Atmos 104:6353–6375. https://doi.org/10.1029/98JD01164
Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P, Hirahara S, Horányi A, Muñoz-Sabater J et al (2020) The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 146:1999–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803
Hohenegger C, Brockhaus P, Schär C (2008) Towards climate simulations at cloud-resolving scales. Meteorol Z 17:383–394. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2008/0303
Hong J-Y, Ahn J-B (2015) Changes of early summer precipitation in the Korean Peninsula and nearby regions based on RCP simulations. J Clim 28:3557–3578. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-14-00504.1
Hong S-Y, Dudhia J, Chen S-H (2004) A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation. Mon Weather Rev 132:103–120. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132%3c0103:Aratim%3e2.0.Co;2
Hong S-Y, Noh Y, Dudhia J (2006) A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon Weather Rev 134:2318–2341. https://doi.org/10.1175/mwr3199.1
Im E-S, Ha S, Qiu L, Hur J, Jo S, Shim K-M (2021) An evaluation of temperature-based agricultural indices over Korea from the high-resolution WRF simulation. Frontiers in Earth Science 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.656787
Ishida K, Tanaka K, Hama T (2019) Sensitivity analysis of convective parameterizations of a regional climate model in higher-resolution domains for long-term precipitation reconstruction. J Water Clim Chang 11:1467–1480. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2019.069
Janjić ZI (1994) The step-mountain eta coordinate model: further developments of the convection, viscous sublayer, and turbulence closure schemes. Mon Weather Rev 122:927–945. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1994)122%3c0927:Tsmecm%3e2.0.Co;2
Jo E, Park C, Son S-W, Roh J-W, Lee G-W, Lee Y-H (2019) Classification of localized heavy rainfall events in South Korea. Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 56:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-019-00128-7
Jung H-S, Lim G-H, Oh J-H (2001) Interpretation of the transient variations in the time series of precipitation amounts in Seoul, Korea. Part I: diurnal variation. J Clim 14:2989–3004. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014%3c2989:Iottvi%3e2.0.Co;2
Jung I-W, Bae D-H, Kim G (2011) Recent trends of mean and extreme precipitation in Korea. Int J Climatol 31:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2068
Kain JS (2004) The Kain-Fritsch convective parameterization: an update. J Appl Meteorol 43:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2004)043%3c0170:Tkcpau%3e2.0.Co;2
Karmacharya J, Jones R, Moufouma-Okia W, New M (2017) Evaluation of the added value of a high-resolution regional climate model simulation of the South Asian summer monsoon climatology. Int J Climatol 37:3630–3643. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4944
Kim W, Jhun J-G, Ha K-J, Kimoto M (2011) Decadal changes in climatological intraseasonal fluctuation of subseasonal evolution of summer precipitation over the Korean Peninsula in the mid-1990s. Adv Atmos Sci 28:591–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-010-0037-9
Kim H-K, Moon B-K, Kim M-K, Park J-Y, Hyun Y-K (2021) Three distinct atmospheric circulation patterns associated with high temperature extremes in South Korea. Sci Rep 11:12911. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92368-9
Konduru RT, Takahashi HG (2020) Effects of convection representation and model resolution on diurnal precipitation cycle over the Indian monsoon region: toward a convection-permitting regional climate simulation. J Geophys Res: Atmos 125:e2019JD032150. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD032150
Kotroni V, Lagouvardos K (2004) Evaluation of MM5 high-resolution real-time forecasts over the urban area of Athens, Greece. J Appl Meteorol 43:1666–1678. https://doi.org/10.1175/jam2170.1
Lee D-K, Park J-G, Kim J-W (2008) Heavy rainfall events lasting 18 days from July 31 to August 17, 1998, over Korea. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan. Ser II 86:313–333. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.86.313
Lee S-W, Lee D-K, Chang D-E (2011) Impact of horizontal resolution and cumulus parameterization scheme on the simulation of heavy rainfall events over the Korean Peninsula. Adv Atmos Sci 28:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-010-9217-x
Lee J-Y, Kwon M, Yun K-S, Min S-K, Park I-H, Ham Y-G et al (2017) The long-term variability of Changma in the East Asian summer monsoon system: a review and revisit. Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 53:257–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-017-0032-5
Lee M-H, Bae D-H, Im E-S (2019) Effect of the horizontal resolution of climate simulations on the hydrological representation of extreme low and high flows. Water Resour Manage 33:4653–4666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02359-9
Liu J, Bray M, Han D (2012) Sensitivity of the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model to downscaling ratios and storm types in rainfall simulation. Hydrol Process 26:3012–3031. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8247
Lucas-Picher P, Argüeso D, Brisson E, Tramblay Y, Berg P, Lemonsu A et al (2021) Convection-permitting modeling with regional climate models: latest developments and next steps. WIREs Clim Chang 12:e731. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.731
MacQueen J (1967) Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability, Oakland, CA, USA, 281–297.
Mayor YG, Mesquita MDS (2015) Numerical simulations of the 1 May 2012 deep convection event over Cuba: sensitivity to cumulus and microphysical schemes in a high-resolution model. Adv Meteorol 2015:973151. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/973151
Meredith EP, Maraun D, Semenov VA, Park W (2015) Evidence for added value of convection-permitting models for studying changes in extreme precipitation. J Geophys Res: Atmos 120:12500–12513. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024238
Miyasaka T, Kawase H, Nakaegawa T, Imada Y, Takayabu I (2020) Future projections of heavy precipitation in Kanto and associated weather patterns using large ensemble high-resolution simulations. Sola 16:125–131. https://doi.org/10.2151/sola.2020-022
Nguyen-Le D, Yamada TJ (2019) Using weather pattern recognition to classify and predict summertime heavy rainfall occurrence over the Upper Nan River Basin, northwestern Thailand. Weather Forecast 34:345–360. https://doi.org/10.1175/waf-d-18-0122.1
NIMS (2014) Improvement of prediction skills in very short, short and mid-term for severe weather. National Institute of Meteorological Research, South Korea. https://doi.org/10.23000/TRKO201500014009
Park C, Min S-K, Lee D, Cha D-H, Suh M-S, Kang H-S et al (2016) Evaluation of multiple regional climate models for summer climate extremes over East Asia. Clim Dyn 46:2469–2486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2713-z
Park C, Son S-W, Kim J-H (2021a) Role of baroclinic trough in triggering vertical motion during summertime heavy rainfall events in Korea. J Atmos Sci 78:1687–1702. https://doi.org/10.1175/jas-d-20-0216.1
Park C, Son S-W, Kim J, Chang E-C, Kim J-H, Jo E et al (2021b) Diverse synoptic weather patterns of warm-season heavy rainfall events in South Korea. Mon Weather Rev 149:3875–3893. https://doi.org/10.1175/mwr-d-20-0388.1
Park C, Shin S-W, Cha D-H, Suh M-S, Hong S-Y, Ahn J-B et al (2022a) Future projections of precipitation using bias–corrected high–resolution regional climate models for sub–regions with homogeneous characteristics in South Korea. Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 58:715–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-022-00292-3
Park H, Kim G, Cha D-H, Chang E-C, Kim J, Park S-H et al (2022b) Effect of a scale-aware convective parameterization scheme on the simulation of convective cells-related heavy rainfall in South Korea. J Adv Model Earth Syst 14:e2021MS002696. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021MS002696
Pennelly C, Reuter G, Flesch T (2014) Verification of the WRF model for simulating heavy precipitation in Alberta. Atmos Res 135–136:172–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.09.004
Prein AF, Gobiet A, Suklitsch M, Truhetz H, Awan NK, Keuler K et al (2013) Added value of convection permitting seasonal simulations. Clim Dyn 41:2655–2677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1744-6
Prein AF, Langhans W, Fosser G, Ferrone A, Ban N, Goergen K et al (2015) A review on regional convection-permitting climate modeling: demonstrations, prospects, and challenges. Rev Geophys 53:323–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014RG000475
Qiu L, Im E-S, Hur J, Shim K-M (2020) Added value of very high resolution climate simulations over South Korea using WRF modeling system. Clim Dyn 54:173–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04992-x
Rauscher SA, Coppola E, Piani C, Giorgi F (2010) Resolution effects on regional climate model simulations of seasonal precipitation over Europe. Clim Dyn 35:685–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-009-0607-7
Rousseeuw PJ (1987) Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J Comput Appl Math 20:53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-0427(87)90125-7
Seo GY, Ahn JB (2020) Sensitivity analysis of cumulus parameterization in WRF model for simulating summer heavy rainfall in South Korea. J Clim Res 15:243–256. https://doi.org/10.14383/cri.2020.15.4.243
Seo KH, Son JH, Lee JY, Park HS (2015) Northern East Asian monsoon precipitation revealed by airmass variability and its prediction. J Clim 28:6221–6233. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-14-00526.1
Skamarock C, Klemp B, Dudhia J, Gill O, Liu Z, Berner J et al. (2019) A description of the advanced research WRF model version 4. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.7369994.v4
Song H-J, Sohn B-J (2015) Two heavy rainfall types over the Korean Peninsula in the humid East Asian summer environment: a satellite observation study. Mon Weather Rev 143:363–382. https://doi.org/10.1175/mwr-d-14-00184.1
Syakur MA, Khotimah BK, Rochman EMS, Satoto BD (2018) Integration K-means clustering method and elbow method for identification of the best customer profile cluster. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 336:012017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/336/1/012017
Tao W-K, Simpson J, McCumber M (1989) An ice-water saturation adjustment. Mon Weather Rev 117:231–235. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1989)117%3c0231:Aiwsa%3e2.0.Co;2
Tao Y, Cao J, Lan G, Su Q (2016) The zonal movement of the Indian-East Asian summer monsoon interface in relation to the land–sea thermal contrast anomaly over East Asia. Clim Dyn 46:2759–2771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2729-4
Torma C, Giorgi F, Coppola E (2015) Added value of regional climate modeling over areas characterized by complex terrain-precipitation over the Alps. J Geophys Res: Atmos 120:3957–3972. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD022781
Wang S, Yu E, Wang H (2012) A simulation study of a heavy rainfall process over the Yangtze River valley using the two-way nesting approach. Adv Atmos Sci 29:731–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-1176-y
Warner TT, Hsu H-M (2000) Nested-model simulation of moist convection: the impact of coarse-grid parameterized convection on fine-grid resolved convection. Mon Weather Rev 128:2211–2231. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2000)128%3c2211:NMSOMC%3e2.0.CO;2
Weusthoff T, Ament F, Arpagaus M, Rotach MW (2010) Assessing the benefits of convection-permitting models by neighborhood verification: examples from MAP D-PHASE. Mon Weather Rev 138:3418–3433. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010mwr3380.1
Wootten A, Bowden JH, Boyles R, Terando A (2016) The sensitivity of WRF downscaled precipitation in Puerto Rico to cumulus parameterization and interior grid nudging. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 55:2263–2281. https://doi.org/10.1175/jamc-d-16-0121.1
Xu Z, Han Y, Yang Z (2019) Dynamical downscaling of regional climate: a review of methods and limitations. Sci China Earth Sci 62:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-018-9261-5
Yu X, Lee T-Y (2011) Role of convective parameterization in simulations of heavy precipitation systems at grey-zone resolutions — case studies. Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 47:99–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-011-0001-3
Zhao S, Deng Y, Black RX (2017) A dynamical and statistical characterization of U.S. extreme precipitation events and their associated large-scale meteorological patterns. J Clim 30:1307–1326. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0910.1
Zhao Y, Zhou T, Li P, Furtado K, Zou L (2021) Added value of a convection permitting model in simulating atmospheric water cycle over the Asian Water Tower. J Geophys Res: Atmos 126:e2021JD034788. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JD034788
Zhao Y, Deng L, Li Z, Wang Y (2022) Quantitative attribution of vertical motion responsible for summer heavy rainfall over North China. J Geophys Res: Atmos 127:e2021JD035765. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JD035765
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of Rural Development Administration Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development under Grant Project No. PJ01475503, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ga-Yeong Seo performed model run, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. Joong-Bae Ahn conceptualized the research and revised the manuscript writing. All authors contributed to the manuscript review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, GY., Ahn, JB. Comparative study on the characteristics of rainfall simulation over South Korea by summertime weather patterns according to the use of cumulus parameterization. Theor Appl Climatol 154, 907–924 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04603-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04603-0