Abstract
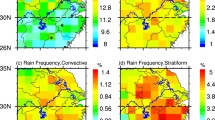
In this paper, the spatial and temporal characteristics of convective precipitation (CP) and large-scale precipitation (LSP) in southern China during 1980–2020 are analyzed using monthly mean precipitation data from MERRA-2. In addition, the possible effects of relative humidity on CP and LSP are explored. The results indicate the following. (1) The LSP dominates the proportion of total precipitation (TP). Both LSP and CP are more prevalent in the south and less prevalent in the north, but there is a difference in the regions of their maximum centers. (2) Significant interannual and seasonal variations are observed in precipitation. TP and LSP tended to be higher than average after the 1990s, while for the CP, a significant negative trend has dominated the past ten years. There are significant increasing trends for TP and LSP, with area-averaged linear trends of 78.1 mm/decade and 85.9 mm/decade, respectively, while that of CP is − 17.1 mm/decade. The increasing trends of LSP are mainly contributed by the precipitation of summer and autumn. (3) The variations of LSP are affected by relative humidity in the troposphere, while CP is only influenced by the changes in relative humidity due to air temperature or specific humidity. The trend of relative humidity is − 0.33%/decade, mainly due to rising temperature in the troposphere. (4) Changes in relative humidity caused by temperature or specific humidity alone act on large-scale precipitation through both interannual and interdecadal processes, causing large-scale precipitation to increase, and the convective precipitation is mainly affected by the interdecadal processes.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The MERRA2 Reanalysis datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The observed daily precipitation data for 2,374 stations that are available from the National Weather Information Center of the China Meteorological Administration.
Code availability
The code analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Allan RP, Soden BJ (2008) Atmospheric warming and the amplification of precipitation extremes. Science 321:1481–1484. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1160787
Allen MR, Ingram WJ (2002) Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 419:228–232
Arakawa A (2004) The cumulus parameterization problem: past, present, and future. J Clim 17:2493–2525. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017%3c2493:RATCPP%3e2.0.CO;2
Berg P, Moseley C, Haerter JO (2013) Strong increase in convective precipitation in response to higher temperatures. Nat Geosci 6:181–185. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1731
Bin Z, JianYin L, AiLan L, ChunHui L, DeJun G (2006) Frontal Rain and Summer Monsoon Rain During Prerainy Season in South China. Part I: Determination of the Division Dates J. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese) 30(6): 1207-1216. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2006.06.15
Chen J, Wu R, Wen Z (2012) Contribution of south China Sea tropical cyclones to an increase in southern China summer rainfall around 1993. Adv Atmos Sci 29:585–598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-1181-6
Chen S, Gan TY, Tan X, Shao D, Zhu J (2019) Assessment of CFSR, ERA-Interim, JRA-55, MERRA-2, NCEP-2 reanalysis data for drought analysis over China. Clim Dyn 53:737–757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-04611-1
Dai A (2006) Precipitation characteristics in eighteen coupled climate models. J Clim 19:4605–4630. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3884.1
Ding Y, Sun Y, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Song Y (2009) Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon Part II: Possible causes. Int J Climatol 29:1926–1944. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1759
Dongdong C, Yongjiu D (2009) Characteristics of Northwest China rainfall intensity in recent 50 years. Chinese J Atmos Sci (in Chinese) 33:923–935
Douville H, K Raghavan, J Renwick et al (2021) Water Cycle Changes. In: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, pp 34–37 In Press
Fu L, Li W, Zhang P, Zhang Q, Gao G (2011) Inter-Decadal Change of Hail Events over China and Causation Analysis in Northern China in Recent 50 Years. Meteorological Monthly (in Chinese) 37(6):669-676
Fu Y, Chen F, Liu G, Yang Y, Yuan R, Li R, Liu Q, Wang Y, Zhong L, Sun L (2016) Recent trends of summer convective and stratiform precipitation in mid-eastern China. Sci Rep 6:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33044
Gelaro R, McCarty W, Suárez MJ, Todling R, Molod A et al (2017) The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J Clim 30:5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1
Han X, Xue H, Zhao C, Lu D (2016) The roles of convective and stratiform precipitation in the observed precipitation trends in Northwest China during 1961–2000. Atmos Res 169:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.10.001
Hartmann DL, Klein Tank et al (2013) Observations: atmosphere and surface, in: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, 159–254. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.008
Houze R (1997) Stratiform precipitation in regions of convection: A meteorological paradox? [J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc 78(10): 2179–2195. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1997)0782.0.CO;2
Hu L, Li YD, Song Y, Deng DF (2011) Seasonal variability in tropical and subtropical convective and stratiform precipitation of the East Asian monsoon. Sci China Earth Sci (in Chinese) 54:1595–1603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-011-4225-y
Huang R, Chen J, Wang L, Lin Z (2012) Characteristics, processes, and causes of the spatio-temporal variabilities of the East Asian monsoon system. Adv Atmos Sci 29:910–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-2015-x
Jing YANG, Sicheng HE, Qing BAO (2021) Convective/large-scale rainfall partitions of tropical heavy precipitation in CMIP6 atmospheric models. Adv Atmos Sci 38:1020–1027
Kendall MG (1955) Rank correlation methods, 2nd edn. Charles Griffin, London, p 196
Kharin VV, Zwiers FW, Zhang X, Wehner M (2013) Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in the CMIP5 ensemble. Clim Change 119:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-013-0705-8
Kyselý J, Rulfová Z, Farda A, Hanel M (2015) Convective and stratiform precipitation characteristics in an ensemble of regional climate model simulations. Clim Dyn 46:227–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2580-7
Leary CA, Houze RA Jr (1979) The structure and evolution of convection in a tropical cloud cluster. J Atmos Sci 36:437–457
Lin W, Juan F (2011) Two major modes of the wintertime precipitation over China. Chinese J Atmos Sci (in Chinese) 35:1105–1116
Lin Fu, Weijing Li, Peiqun Z, Qiang Z, Ge G (2011) Inter-decadal Change of Hail Events over China and Causation Analysis in Northern China in Recent 50 Years. Meteorological Monthly (in Chinese) 37:669–676
Liu H, Zhi-gang W, Hong W, Zheng-chao L, Chao W (2012) Characterstics of tropopause height over china in recent 51 years. PLATEAU Meteorol (in Chinese) 31:351–358
Liu P, Li CY, Wang Y, Fu YF (2013) Climatic characteristics of convective and stratiform precipitation over the Tropical and Subtropical areas as derived from TRMM PR. Sci China Earth Sci 56:375–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-012-4474-4
Liu P, Fu Y (2010) Climatic Characteristics of Summer Convective and Stratiform Precipitation in Southern China Based on Measurements by TRMM Precipitation Radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese) 34(4):802-814. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2010.04.12
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13:245–259
Peng LIU, Yu FU (2010) Climatic characteristics of summer convective and stratiform precipitation in southern China based on measurements by TRMM precipitation radar. Chinese J Atmos Sci (in Chinese) 34:802–814
Qian C, Zhang X, Li Z (2019) Linear trends in temperature extremes in China, with an emphasis on non-Gaussian and serially dependent characteristics. Clim Dyn 53(1):533–550
Reichle RH, Draper CS, Liu Q, Girotto M, Mahanama SPP, Koster RD, De Lannoy GJM (2017) Assessment of MERRA-2 land surface hydrology estimates. J Clim 30:2937–2960. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0720.1
Reichle RH, Liu Q, Koster RD, Draper CS, Mahanama SPP, Partyka GS (2017) Land surface precipitation in MERRA-2. J Clim 30:1643–1664. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0570.1
Rugui S, Quanzhen T, Yingying L (1983) The circulation change in lower and upper troposphere in lower latitudes and the rainfall during the pre-typhoon rain-season. Proc Symp Summer Monsoon South East Asia. People’s Press Yunnan Prov (in Chinese) 10–19
Ruiting Z, Qingcun Z, Ming Z (2004) A numerical simulation of monsoon and the correlation between monsoon and westerlies. CHINESE J Atmos Sci (in Chinese) 28:7–22
Ruiz-Leo AM, Hernández E, Queralt S, Maqueda G (2013) Convective and stratiform precipitation trends in the Spanish Mediterranean coast. Atmos Res 119:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.07.019
Rulfová Z, Kyselý J (2013) Disaggregating convective and stratiform precipitation from station weather data. Atmos Res 134:100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.07.015
Rulfová Z, Beranová R, Kyselý J (2017) Climate change scenarios of convective and large-scale precipitation in the Czech Republic based on EURO-CORDEX data. Int J Climatol 37:2451–2465. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4857
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389
Seneviratne S, Nicholls N, Easterling D et al (2012). Changes in climate extremes and their impacts on the natural physical environment. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139177245.006
Shen Q, Zhang SX, Zhao JH, Wang X (2013) Contribution of typhoon over coastal waters to summer rainfall in eastern China. Acta Phys Sin (in Chinese) 62(18): 189201. https://doi.org/10.7498/aps.62.189201
Si D, Hu ZZ, Kumar A, Jha B, Peng P, Wang W, Han R (2016) Is the interdecadal variation of the summer rainfall over eastern China associated with SST? Clim Dyn 46:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2574-5
Sui CH, Tsay CT, Li X (2007) Convective-stratiform rainfall separation by cloud content. J Geophys Res Atmos 112:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD008082
Tianbao Z, Fu C, Jian K, Guo W (2010) Research status and progress of global atmospheric reanalysis data. Adv Earth Sci 25:242–254
Tremblay A (2005) The stratiform and convective components of surface precipitation. J Atmos Sci 62:1513–1528. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS3411.1
Trenberth KE, Dai A, Rasmussen RM, Parsons DB (2003) The changing character of precipitation. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 84:1205–1218. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-84-9-1205
Trenberth K, Jones P, Ambenje P et al (2007) Observations: surface and atmospheric climate change. Chapter 3, in: Climate Change. 235–336
Wan RJ, Wu GX (2006) Study on the climatic mechanism of Spring rain in Jiangnan. Science China Earth Sciences (in Chinese) 10:936–950. https://doi.org/10.1360/zd2006-36-10-936
Wan H, Zhang X, Zwiers FW, Shiogama H (2013) Effect of data coverage on the estimation of mean and variability of precipitation at global and regional scales. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:534–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50118
Wang X, Zhou W, Li C, Wang D (2012) Effects of the East Asian summer monsoon on tropical cyclone genesis over the South China Sea on an interdecadal time scale. Adv Atmos Sci 29:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-1080-x
Wang G, Wang D, Trenberth KE, Erfanian A, Yu M, Bosilovich MG, Parr DT (2017) The peak structure and future changes of the relationships between extreme precipitation and temperature. Nat Clim Chang 7:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3239
Weijing L, Jinging Z, Yanling S, Jingpeng L, Yu L, Yuyang S, Jingxin L (2015) Changes in spatio-temporal distribution of drought/flood disaster in southern china under global climate warming. Meteorol Mon (in Chinese) 41:261–271
Weijing L, Ruonan Z, Chenghu S, Hongchang R, Jingpeng L, Jinqing Z, Xiang L (2016) Recent research advances on the interannual variations of drought/flood in south China and associated causes. J Appl Meteorol Sci (in Chinese) 27:577–591
Westra S, Alexander LV, Zwiers FW (2013) Global increasing trends in annual maximum daily precipitation. J Clim 26:3904–3918. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00502.1
Wu J, Zhang L, Zhao D, Tang J (2015) Impacts of warming and water vapor content on the decrease in light rain days during the warm season over eastern China. Clim Dyn 45:1841–1857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2438-4
Xiaoxia Z, Yihui D, Panxing W (2008) Moisture transpotr in Asian summer monsoon region and its relationship with summer precipitation in China. Acta Meteorol Sin (in Chinese) 66:59–70
Yali L, Hui W, Renhe Z, Weimiao Q, Zhengzhao L (2013) Comparison of rainfall characteristics and convective properties of monsoon precipitation systems over South China and the Yangtze and Huai River basin. J Clim 26:110–132. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00100.1
Zelinka MD, Klein SA, Taylor KE, Andrews T, Webb MJ, Gregory JM, Forster PM (2013) Contributions of different cloud types to feedbacks and rapid adjustments in CMIP5. J Climate 26:5007–5027. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00555.1
Zhang RH (2015) Natural and human-induced changes in summer climate over the East Asian monsoon region in the last half century: a review. Adv Clim Chang Res 6:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accre.2015.09.009
Zhang W, Zhou T (2019) Significant increases in extreme precipitation and the associations with global warming over the global land monsoon regions. J Clim 32:8465–8488. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-18-0662.1
Zhou J, Zhi R, Li Y, Zhao J, Xiang B, Wu Y, Feng G (2020) Possible causes of the significant decrease in the number of summer days with light rain in the east of southwestern China. Atmos Res 236:104804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104804
Zipser EJ (1977) Mesoscale and convective-scale downdrafts as distinct components of squall-line circulation. Mon Wea Rev 105:1568–1589
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Zhao Junhu for the helpful comments on the original manuscript. The daily precipitation data were obtained from the CMA at http://data.cma.cn/. The relative humidity, specific humidity, and temperature data were obtained from https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets?keywords=merra2&page=1.
Funding
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) [grant number 42130610, 42075017, 41875096, 41875093 and]; the National Key Research and Development Program of China [grant numbers 2017YFC1502303 and 2018YFA0606301].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization: Han Zhang, Junhu Zhao, Guolin Feng; methodology: Han Zhang, Junhu Zhao, Bicheng Huang, Naihui Zang; formal analysis and investigation: Han Zhang, Junhu Zhao, Jie Yang; writing: Han Zhang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhao, J., Huang, B. et al. The variabilities of convective precipitation and large-scale precipitation in southern China for the period 1980–2020. Theor Appl Climatol 148, 1529–1543 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04017-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04017-4