Abstract
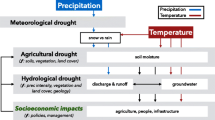
The temporal variations and spatial patterns of drought in Shandong Province of Eastern China were investigated by calculating the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) at 1-, 3-, 6-, 12-, and 24-month time scales. Monthly precipitation and air temperature time series during the period 1960–2012 were collected at 23 meteorological stations uniformly distributed over the region. The non-parametric Mann-Kendall test was used to explore the temporal trends of precipitation, air temperature, and the SPEI drought index. S-mode principal component analysis (PCA) was applied to identify the spatial patterns of drought. The results showed that an insignificant decreasing trend in annual total precipitation was detected at most stations, a significant increase of annual average air temperature occurred at all the 23 stations, and a significant decreasing trend in the SPEI was mainly detected at the coastal stations for all the time scales. The frequency of occurrence of extreme and severe drought at different time scales generally increased with decades; higher frequency and larger affected area of extreme and severe droughts occurred as the time scale increased, especially for the northwest of Shandong Province and Jiaodong peninsular. The spatial pattern of drought for SPEI-1 contains three regions: eastern Jiaodong Peninsular and northwestern and southern Shandong. As the time scale increased to 3, 6, and 12 months, the order of the three regions was transformed into another as northwestern Shandong, eastern Jiaodong Peninsular, and southern Shandong. For SPEI-24, the location identified by REOF1 was slightly shifted from northwestern Shandong to western Shandong, and REOF2 and REOF3 identified another two weak patterns in the south edge and north edge of Jiaodong Peninsular, respectively. The potential causes of drought and the impact of drought on agriculture in the study area have also been discussed. The temporal variations and spatial patterns of drought obtained in this study provide valuable information for water resources planning and drought disaster prevention and mitigation in Eastern China.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgomeo E, Pflug G, Hall JW, Hochrainer-Stigler S (2015) Assessing water resource system vulnerability to unprecedented hydrological drought using copulas to characterize drought duration and deficit. Water Resour Res 51(11):8927–8948. doi:10.1002/2015WR017324
Capra A, Scicolone B (2012) Spatiotemporal variability of drought on a short-medium time scale in the Calabria Region (Southern Italy). Theor Appl Climatol 110(3):471–488. doi:10.1007/s00704-012-0720-0
Dai AG (2011) Drought under global warming: a review. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Climate Change 2(1):45–65. doi:10.1002/wcc.81
Das PK, Dutta D, Sharma JR, Dadhwal VK (2016) Trends and behaviour of meteorological drought (1901–2008) over Indian region using standardized precipitation-evapotranspiration index. Int J Climatol 36(2):909–916. doi:10.1002/joc.4392
Di Lena B, Vergni L, Antenucci F, Todisco F, Mannocchi F (2014) Analysis of drought in the region of Abruzzo (Central Italy) by the standardized precipitation index. Theor Appl Climatol 115(1–2):41–52. doi:10.1007/s00704-013-0876-2
Du J, Fang J, Xu W, Shi P (2013a) Analysis of dry/wet conditions using the standardized precipitation index and its potential usefulness for drought/flood monitoring in Hunan Province, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 27(2):377–387. doi:10.1007/s00477-012-0589-6
Du L, Tian Q, Yu T, Meng Q, Jancso T, Udvardy P, Huang Y (2013b) A comprehensive drought monitoring method integrating MODIS and TRMM data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 23:245–253. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2012.09.010
Ehsanzadeh E, Ouarda T, Saley HM (2011) A simultaneous analysis of gradual and abrupt changes in Canadian low streamflows. Hydrol Process 25(5):727–739
Feng L, Li T, Yu W (2014) Cause of severe droughts in Southwest China during 1951-2010. Clim Dyn 43(7–8):2033–2042. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-2026-z
Ganguli P, Reddy MJ (2014) Ensemble prediction of regional droughts using climate inputs and the SVM-copula approach. Hydrol Process 28(19):4989–5009. doi:10.1002/hyp.9966
Gao Z, Gao W, Chang N (2011) Integrating temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI) and regional water stress index (RWSI) for drought assessment with the aid of LANDSAT TM/ETM plus images. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 13(3):495–503. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2010.10.005
Giles BD, Flocas AA (1984) Air temperature variations in Greece. Part 1. Persistence, trend, and fluctuations. J Climatol 4(5):531–539
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2013) Analysis of precipitation and drought data in Serbia over the period 1980–2010. J Hydrol 494:32–42. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.04.044
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2014) Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought in Serbia. J Hydrol 510:110–123. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.12.030
Gunda T, Hornberger GM, Gilligan JM (2016) Spatiotemporal patterns of agricultural drought in Sri Lanka: 1881–2010. Int J Climatol 36(2):563–575. doi:10.1002/joc.4365
Guttman NB (1998) Comparing the Palmer drought index and the standardized precipitation index. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34(1):113–121
Han L, Zhang Q, Ma P, Jia J, Wang J (2016) The spatial distribution characteristics of a comprehensive drought risk index in southwestern China and underlying causes. Theor Appl Climatol 124(3–4):517–528. doi:10.1007/s00704-015-1432-z
Hirsch RM, Slack JR, Smith RA (1982) Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resour Res 18(1):107–121
Jhajharia D, Shrivastava SK, Sarkar D, Sarkar S (2009) Temporal characteristics of pan evaporation trends under the humid conditions of northeast India. Agric For Meteorol 149(5):763–770. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2008.10.024
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation measures. Charles Griffin, London, p. 202
Kumar S, Merwade V, Kam J, Thurner K (2009) Streamflow trends in Indiana: effects of long term persistence, precipitation and subsurface drains. J Hydrol 374(1–2):171–183
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13(3):245–259
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales, Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology. American Meteorological Society, Anaheim, CA, pp. 179–184
Mirabbasi R, Fakheri-Fard A, Dinpashoh Y (2012) Bivariate drought frequency analysis using the copula method. Theor Appl Climatol 108(1–2):191–206. doi:10.1007/s00704-011-0524-7
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 391(1–2):204–216. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.07.012
Modarres R, Da Silva V (2007) Rainfall trends in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran. J Arid Environ 70(2):344–355. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2006.12.024
Moeletsi ME, Walker S (2012) Assessment of agricultural drought using a simple water balance model in the Free State Province of South Africa. Theor Appl Climatol 108(3–4):425–450. doi:10.1007/s00704-011-0540-7
Myronidis D, Stathis D, Ioannou K, Fotakis D (2012) An integration of statistics temporal methods to track the effect of drought in a shallow Mediterranean Lake. Water Resour Manag 26(15):4587–4605. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0169-z
Naddeo V, Scannapieco D, Zarra T, Belgiorno V (2013) River water quality assessment: implementation of non-parametric tests for sampling frequency optimization. Land Use Policy 30(1):197–205. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.03.013
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological drought. US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau, Washington, DC
Potop V, Boroneant C, Mozny M, Stepanek P, Skalak P (2014) Observed spatiotemporal characteristics of drought on various time scales over the Czech Republic. Theor Appl Climatol 115(3–4):563–581. doi:10.1007/s00704-013-0908-y
Qian C, Zhou T (2014) Multidecadal variability of North China aridity and its relationship to PDO during 1900–2010. J Clim 27(3):1210–1222. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00235.1
Raziei T, Bordi I, Pereira LS (2013) Regional drought modes in Iran using the SPI: the effect of time scale and spatial resolution. Water Resour Manag 27(6SI):1661–1674. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0120-3
Santos JF, Pulido-Calvo I, Portela MM (2010) Spatial and temporal variability of droughts in Portugal. Water Resour Res 46:W03503. doi:10.1029/2009WR008071
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63(324):1379–1389
Shamshirband S, Gocic M, Petkovic D, Javidnia H, Ab Hamid SH, Mansor Z, Qasem SN (2015) Clustering project management for drought regions determination: a case study in Serbia. Agric For Meteorol 200:57–65. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.09.020
Sheffield J, Wood EF, Roderick ML (2012) Little change in global drought over the past 60 years. Nature 491(7424):435–440. doi:10.1038/nature11575
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr Rev 38(1):55–94. doi:10.2307/210739
Tosunoglu F, Can I (2016) Application of copulas for regional bivariate frequency analysis of meteorological droughts in Turkey. Nat Hazards 82(3):1457–1477. doi:10.1007/s11069-016-2253-9
Vicente-Serrano SM, Begueria S, Lopez-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23(7):1696–1718. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1
Wang X, Hou X, Li Z, Wang Y (2014) Spatial and temporal characteristics of meteorological drought in Shandong Province, China, from 1961 to 2008. Adv Meteorol 2014:873593. doi:10.1155/2014/873593
Wei K, Wang L (2013) Reexamination of the aridity conditions in arid northwestern China for the last decade. J Clim 26(23):9594–9602. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00605.1
Wilhite DA, Glantz MH (1985) Understanding: the drought phenomenon: the role of definitions. Water Int 10(3):111–120. doi:10.1080/02508068508686328
Wu H, Hayes MJ, Weiss A, Hu Q (2001) An evaluation of the standardized precipitation index, the China-Z index and the statistical Z-score. Int J Climatol 21(6):745–758. doi:10.1002/joc.658
Wu H, Hayes MJ, Wilhite DA, Svoboda MD (2005) The effect of the length of record on the standardized precipitation index calculation. Int J Climatol 25(4):505–520. doi:10.1002/joc.1142
Xiao M, Zhang Q, Singh VP, Liu L (2016) Transitional properties of droughts and related impacts of climate indices in the Pearl River basin, China. J Hydrol 534:397–406. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.01.012
Xu G, Liu X, Qin D, Chen T, Sun W, An W, Wang W, Wu G, Zeng X, Ren J (2014) Drought history inferred from tree ring delta C-13 and delta O-18 in the central Tianshan Mountains of China and linkage with the North Atlantic Oscillation. Theor Appl Climatol 116(3–4):385–401. doi:10.1007/s00704-013-0958-1
Xu K, Yang D, Yang H, Li Z, Qin Y, Shen Y (2015) Spatio-temporal variation of drought in China during 1961–2012: a climatic perspective. J Hydrol 526(SI):253–264. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.09.047
Zhai J, Su B, Krysanova V, Vetter T, Gao C, Jiang T (2010) Spatial variation and trends in PDSI and SPI indices and their relation to streamflow in 10 large regions of China. J Clim 23(3):649–663. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI2968.1
Zhang Q, Sun P, Li J, Singh VP, Liu J (2015b) Spatiotemporal properties of droughts and related impacts on agriculture in Xinjiang, China. Int J Climatol 35(7):1254–1266. doi:10.1002/joc.4052
Zhang Q, Sun P, Li J, Xiao M, Singh VP (2015a) Assessment of drought vulnerability of the Tarim River basin, Xinjiang, China. Theor Appl Climatol 121(1–2):337–347. doi:10.1007/s00704-014-1234-8
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Singh VP, Chen X (2013) Copula-based risk evaluation of droughts across the Pearl River basin, China. Theor Appl Climatol 111(1–2):119–131. doi:10.1007/s00704-012-0656-4
Zhang Q, Xu C, Zhang Z (2009) Observed changes of drought/wetness episodes in the Pearl River basin, China, using the standardized precipitation index and aridity index. Theor Appl Climatol 98(1–2):89–99. doi:10.1007/s00704-008-0095-4
Zou XK, Zhai PM, Zhang Q (2005) Variations in droughts over China: 1951–2003. Geophys Res Lett 32:L047074. doi:10.1029/2004GL021853
Zuo DP, Xu ZX, Wu W, Zhao J, Zhao FF (2014) Identification of streamflow response to climate change and human activities in the Wei River Basin, China. Water Resour Manag 28(3):833–851. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0519-0
Zuo DP, Xu ZX, Yang H, Liu XC (2012) Spatiotemporal variations and abrupt changes of potential evapotranspiration and its sensitivity to key meteorological variables in the Wei River basin, China. Hydrol Process 26(8):1149–1160. doi:10.1002/hyp.8206
Acknowledgments
This study is jointly supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2013BAC05B04); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51309010); Special Fund for Research on Public Interests (Grant No. 201401036); the Ministry of Water Resources, PR China; the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (Grant No. 2012DFG22140); the Ministry of Science and Technology, PR China; Water Ecological Civilization Pilot Key Technology Research and Development Program (Grant No. SSTWMZCJH-SD02); Department of Water Resources of Shandong Province; and Shandong Province Finance Bureau, PR China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, D., Cai, S., Xu, Z. et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of drought at various time scales in Shandong Province of Eastern China. Theor Appl Climatol 131, 271–284 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1969-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1969-5