Abstract
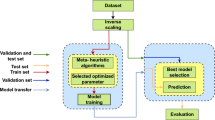
Prediction of Indian summer monsoon uses a number of climatic variables that are historically known to provide a high skill. However, relationships between predictors and predictand could be complex and also change with time. The present work attempts to use a machine learning technique to identify new predictors for forecasting the Indian monsoon. A neural network-based non-linear dimensionality reduction technique, namely, the sparse autoencoder is used for this purpose. It extracts a number of new predictors that have prediction skills higher than the existing ones. Two non-linear ensemble prediction models of regression tree and bagged decision tree are designed with identified monsoon predictors and are shown to be superior in terms of prediction accuracy. Proposed model shows mean absolute error of 4.5 % in predicting the Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Lastly, geographical distribution of the new monsoon predictors and their characteristics are discussed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldi P (2012) Autoencoders, unsupervised learning, and deep architectures. ICML Unsupervised Transf Learn 27:37–50
Blanford HF (1884) On the connexion of the Himalaya snowfall with dry winds and seasons of drought in India. Proc R Soc Lond 37(232–234):3–22
Boriah S, Simon G, Naorem M, Steinbach M, Kumar V, Klooster S, Potter C (2004) Predicting land temperature using ocean data. In: Proceedings of the knowledge discovery in databases KDD, Citeseer
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24(2):123–140
Cherchi A, Navarra A (2013) Influence of ENSO and of the Indian ocean dipole on the Indian summer monsoon variability. Clim Dyn 41(1):81–103
Compo G, Whitaker J, Sardeshmukh P, Matsui N, Allan R, Yin X, Gleason B, Vose R, Rutledge G, Bessemoulin P, Bronnimann S, Brunet M, Crouthamel R, Grant A, Groisman P, Jones P, Kruk M, Kruger A, Marshall G, Maugeri M, Mok H, Nordli O, Ross T, Trigo R, Wang X, Woodruff S, Worley S (2011) The twentieth century reanalysis project. Q J R Meteor Soc 137(654):1–28
DelSole T, Shukla J (2002) Linear prediction of Indian monsoon rainfall. J Clim 15:3645–3658
DelSole T, Shukla J (2012) Climate models produce skillful predictions of Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 39(9):L09–703
Gadgil S, Vinayachandran P, Francis P, Gadgil S (2004) Extremes of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall, ENSO and equatorial Indian ocean oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 31(12):L12213
Gadgil S, Rajeevan M, Nanjundiah R (2005) Monsoon prediction-Why yet another failure? Curr Sci 88(9):1389–1400
Goswami BN, Ajayamohan R (2001) Intraseasonal oscillations and interannual variability of the Indian summer monsoon. J Clim 14(6):1180–1198
Gowariker V, Thapliyal V, Kulshrestha SM, Mandal GS, Sen Roy N, Sikka DR (1991) A power regression model for long range forecast of southwest monsoon rainfall over India. Mausam 42(2):125–130
Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR (2006) Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313(5786):504–507
Hong YT, Hong B, Lin QH, Zhu YX, Shibata Y, Hirota M, Uchida M, Leng XT, Jiang HB, Xu H (2003) Correlation between Indian ocean summer monsoon and North Atlantic climate during the Holocene. Earth Planet Sci Lett 211(3):371–380
Krishnamurti TN, Bhalme H (1976) Oscillations of a monsoon system. Part I. Observational aspects. J Atmos Sci 33(10):1937–1954
Kucharski F, Bracco A, Yoo JH, Molteni F (2008) Atlantic forced component of the Indian monsoon interannual variability. Geophys Res Lett 35(4):L04706
Kumar N, Nasser M, Sarker SC (2011) A new singular value decomposition based robust graphical clustering technique and its application in climatic data. J Geogr Geol 3(1):227–238
Li S, Lu J, Huang G, Hu K (2008) Tropical Indian Ocean basin warming and East Asian summer monsoon: a multiple AGCM study. J Clim 21(22):6080–6088
Li Y, Yang R (2013) A hybrid algorithm combining auto-encoder network with sparse Bayesian regression optimized by artificial bee colony for short-term wind power forecasting. Przeglkad Elektrotechniczny 89(2a):223–228
Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) Classification and regression by random forest. R News 2(3):18–22
Liu JNK, Hu Y, He Y, Chan PW, Lai L (2015) Deep neural network modeling for big data weather forecasting. In: Information granularity, big data, and computational intelligence, Springer, pp 389–408
Loh WY (2008) Classification and regression tree methods. Encyclo of statistics in quality and reliability, pp 315–323
MATLAB (2012) Statistics and machine learning toolbox. MATLAB version 2012b, The MathWorks Inc., Natick, Massachusetts, US
Nanjundiah RS, Francis P, Ved M, Gadgil S (2013) Predicting the extremes of Indian summer monsoon rainfall with coupled ocean-atmosphere models. Curr Sci 104(10):1380–1393
Rajeevan M, Pai DS, Dikshit SK, Kelkar RR (2004) IMD’s new operational models for long-range forecast of southwest monsoon rainfall over India and their verification for 2003. Curr Sci 86(3):422–431
Rajeevan M, Pai DS, Kumar RA, Lal B (2007) New statistical models for long-range forecasting of southwest monsoon rainfall over India. Clim Dyn 28(7–8):813–828
Sap MNM, Awan AM (2005) Finding spatio-temporal patterns in climate data using clustering. In: Proceedings of the 2005 international conference cyberworlds, IEEE, pp 8–15
Schott FA, Xie SP, McCreary JP (2009) Indian Ocean circulation and climate variability. Rev Geophys 47(1):RG1002
Smith TM, Reynolds R, Peterson T, Lawrimore J (2008) Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged land-ocean surface temperature analysis (1880-2006). J Clim 21(10):2283–2296
Song C, Liu F, Huang Y, Wang L, Tan T (2013) Auto-encoder based data clustering. In: Progress in pattern recognition, image analysis, computer vision and applied, Springer, pp 117–124
Steinbach M, Tan PN, Kumar V, Klooster S, Potter C (2003) Discovery of climate indices using clustering. Proceedings of ACM, ACM SIGKDD, pp 446–455
Thapliyal V, Kulshrestha S (1992) Recent models for long range forecasting of south-west monsoon rainfall in India. Mausam 43(3):239–248
Walker G (1924) Correlation in seasonal variations of weather-IV, a further study of world weather. Mem India Meteorol Dept 24:275–332
Wang B, Xiang B, Li J, Webster PJ, Rajeevan MN, Liu J, Ha KJ (2015) Rethinking Indian monsoon rainfall prediction in the context of recent global warming. Nature 6:7154
Xue Y, Smith T, Reynolds R (2003) Interdecadal changes of 30-yr SST normals during 1871–2000. J Climate 16:1601–1612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: J. T. Fasullo.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, M., Mitra, P. & Nanjundiah, R.S. Autoencoder-based identification of predictors of Indian monsoon. Meteorol Atmos Phys 128, 613–628 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0431-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0431-7