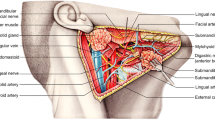
Abstract
Hypersalivation describes a relatively excessive salivary flow, which wets the patient himself and his surroundings. It may result because of insufficient oro-motor function, dysphagia, decreased central control and coordination. This update presents recent changes and innovation in the treatment of hypersalivation. Multidisciplinary diagnostic and treatment evaluation is recommended already at early stage and focus on dysphagia, saliva aspiration, and oro-motor deficiencies. Clinical screening tools and diagnostics such as fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing generate important data on therapy selection and control. Many cases profit from swallowing therapy programmes to activate compensation mechanisms as long compliances are given. In children with hypotonic oral muscles, oral stimulation plates can induce a relevant symptom release because of the improved lip closure. The pharmacologic treatment improved for pediatric cases as glycopyrrolate fluid solution (Sialanar®) is now indicated for hypersalivation within the EU. The injection of botulinum toxin into the salivary glands has shown safe and effective results with long-lasting saliva reduction. Here, a phase III trial is completed for incobotulinum toxin A and, in the US, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic hypersalivation. Surgical treatment should be reserved for isolated cases. External radiation is judged as a safe and effective therapy when using modern 3D techniques to minimize tissue damage. Therapy effects and symptom severity have to be followed, especially in cases with underlying neurodegenerative disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeleira MT, Pazos E, Ramos I, Outumuro M, Limeres J, Seoane-Romero J, Diniz M, Diz P (2014) Orthodontic treatment for disabled children: a survey of parents’ attitudes and overall satisfaction. BMC Oral Health 14:98
Alberty J, Oelrich M, Ludwig K, Hartmann S, Stoll W (2000) Efficacy of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction. Laryngoscope 110:1151–1156
American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Development Medicine (2017) Care pathways: sialorrhea in cerebral palsy. http://www.aacpdm.org/publications/care-pathways/sialorrhea. Accessed 13 June 2018
Andersen PM, Grönberg H, Franzen L, Funegård U (2001) External radiation of the parotid glands significantly reduces drooling in patients with motor neurone disease with bulbar paresis. J Neurol Sci 191:111–114
Assouline A, Levy A, Abdelnour-Mallet M, Gonzalez-Bermejo J, Lenglet T, Le Forestier N, Salachas F, Bruneteau G, Meininger V, Delanian S, Pradat PF (2014) Radiation therapy for hypersalivation: a prospective study in 50 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88:589–595
Bachrach SJ, Walter RS, Trzcinski K (1998) Use of glycopyrrolate and other anticholinergic medications for sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 37:485–490
Bader C, Niemann G (2010) Dysphagie bei Kindern mit Infantiler Zerebralparese—Fiberoptisch—endoskopische Befunde. Laryngorhinootologie 89:90–94
Banfi P, Ticozzi N, Lax A, Guidugli GA, Nicolini A, Silani V (2015) A review of options for treating sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Respir Care 60:446–454
Bartolome G (2014a) Aspirationsschnelltests und Klinische Schluckuntersuchung. In: Bartolome G, Schröter-Morasch H (eds) Schluckstörungen—Diagnostik und Rehabilitation, 5th edn. Elsevier, München, pp 151–171
Bartolome G (2014b) Grundlagen der funktionellen Dysphagietherapie (FDT). In: Bartolome G, Schröter-Morasch H (eds) Schluckstörungen – Diagnostik und Rehabilitation, 5th edn. Elsevier, München, pp 261–403
Bath PM, Scutt P, Love J, Clavé P, Cohen D, Dziewas R, Iversen HK, Ledl C, Ragab S, Soda H, Warusevitane A, Woisard V, Hamdy S, Swallowing Treatment Using Pharyngeal Electrical Stimulation (STEPS) trial investigators (2016) Pharyngeal electrical stimulation for treatment of dysphagia in subacute stroke. Stroke 47:1562–1570
Becker A, Shapira J, Chaushu S (2000) Orthodontic treatment for disabled children: motivation, expectation and satisfaction. Eur J Orthod 22:151–158
Becmeur F, Schneider A, Flaum V, Klipfel C, Pierrel C, Lacreuse I (2013) Which surgery for drooling in patients with cerebral palsy ? J Pediatr Surg 48:2171–2174
Blasco PA (2002) Management of drooling: 10 years after the consortium on Drooling, 1990. Dev Med Child Neurol 44:778–781
Blasco PA, Allaire JH (1992) Drooling in the developmentally disabled: management practices and recommendations. Consortium on Drooling. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:849–862
Blasco PA, Stansbury JC (1996) Glycopyrrolate treatment of chronic drooling. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 150:932–935
Blissit KT, Tillery E, Latham C, Pacheco-Perez J (2014) Glycopyrrolate for treatment of clozapine-induced sialorrhea in adults. Am J Health Syst Pharm 71:1282–1287
Borg M, Hirst F (1998) The role of radiation therapy in the management of sialorrhea. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 41:1113–1119
Burkhead LM, Sapienza CM, Rosenbek JC (2007) Strength-training exercise in dysphagia rehabilitation: principles, procedures, and directions for future research. Dysphagia 22:251–265
Camp-Bruno JA, Winsberg BG, Green-Parsons AR, Abrams JP (1989) Efficacy of benztropine therapy for drooling. Dev Med Child Neurol 31:309–319
Carnaby G, Hankey GJ, Pizzi J (2006) Behavioural intervention for dysphagia in acute stroke: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 5:31–37
Checklin M, Etty-Leal M, Iseli TA, Potter N, Fisher S, Chapman L (2015) Saliva management options for difficult-to-wean people with tracheostomy following severe acquired brain injury (ABI): a review of the literature. Brain Inj 29:1–10
Christiansen H, Wolff HA, Knauth J, Hille A, Vorwerk H, Engelke C, Rödel R, Laskawi R (2009) Radiatio: therapieoption bei therapierefraktärer Speichelfistel. HNO 57:1325–1358
Crysdale WS, White A (1989) Submandibular duct relocation for drooling: a 10-year experience with 194 patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 101:87–92
Crysdale WS, McCann C, Roske L, Joseph M, Semenuk D, Chait P (2006) Saliva control issues in the neurologically challenged. A 30 year experience in team management. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70:519–527
De Simone GG, Eisenchlas JH, Junin M, Pereyra F, Brizuela R (2006) Atropine drops for drooling: a randomized controlled trial. Palliat Med 20:665–671
Del Tredici K, Jost WH (2012) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Nervenarzt 83:1282–1291
Diesener P (1999) Schluckstörungen bei Kindern: Bildgebende Diagnostik mittels transnasaler Videoendoskopie. Prakt Pädiatrie 5:36–42
Doeltgen SH, Huckabee M-L (2012) Swallowing neurorehabilitation: from the research laboratory to routine clinical application. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 93:207–213
Ellies M, Rohrbach-Volland S, Arglebe C, Wilken B, Laskawi R, Hanefeld F (2002a) Successful management of drooling with botulinum toxin A in neurologically disabled children. Neuropediatrics 33:327–330
Ellies M, Laskawi R, Rohrbach-Volland S, Arglebe C, Beuche W (2002b) Botulinum toxin to reduce saliva flow: selected indications for ultrasound-guided toxin application into salivary glands. Laryngoscope 112:82–86
Feussner H, Schröter-Morasch H (2014) Chirurgische Interventionen bei Schluckstörungen. In: Bartolome G, Schröter-Morasch H (eds) Schluckstörungen—Diagnostik und Rehabilitation, 5th edn. Elsevier, München, pp 493–517
Fischbacher L, Schröter-Morasch H (2003) Medikamentöse Speichelreduktion bei Neurogener Dysphagie. In: Gross M, Kruse E (eds) Aktuelle phoniatrische-pädaudiologische Aspekte 2003/2004, Band 11. Medicombooks.de im Verlag videel, Niebüll
Formeister EJ, Dahl JP, Rose AS (2014) Surgical management of chronic sialorrhea in pediatric patients: 10-year experience from one tertiary care institution. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 78:1387–1392
Groß M (2017) Sekretretention. In: Keller S (ed) Außerklinische Intensivpflege. Elsevier, München, p p365
Guidubaldi A, Fasano A, Ialongo T, Piano C, Pompili M, Mascianà R, Siciliani L, Sabatelli M, Bentivoglio AR (2011) Botulinum toxin A versus B in sialorrhea: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, crossover pilot study in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26:313–319
Hawkey NM, Zaorsky NG, Galloway TJ (2016) The role of radiation therapy in the management of sialorrhea: a systematic review. Laryngoscope 126:80–85
Hinchey JA, Shephard T, Furie K, Smith D, Wang D, Tonn S, Stroke practice improvement network investigators (2005) Formal dysphagia screening protocols prevent pneumonia. Stroke 36:1972–1976
Holzapfel K (2014) Radiologische Diagnostik von Schluckstörungen. In: Bartolome G, Schröter-Morasch H (eds) Schluckstörungen—Diagnostik und Rehabilitation, 5th edn. Elsevier, München, pp 123–151
Hussein I, Kershaw AE, Tahmassebi JF, Fayle SA (1998) The management of drooling in children and patients with mental and physical disabilities: a literature review. Int J Paediatr Dent 8:3–11
Hyson HC, Johnson AM, Jog MS (2002) Sublingual atropine for sialorrhea secondary to parkinsonism: a pilot study. Mov Disord 17:1318–1320
Jost WH (2016) The option of sonographic guidance in botulinum toxin injection for drooling in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 123:51–55
Jost WH, Friedman A, Michel O, Flatau-Baqué, Csikós J, Blitzer A (2019) SIAXI: Placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study of incobotulinumtoxinA for sialorrhea. Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000007368 (Epub ahead of print)
Kahl KG, Hagenah J, Zapf S, Trillenberg P, Klein C, Lencer R (2004) Botulinum toxin as an effective treatment of clozapine-induced hypersalivation. Psychopharmacology 173:229–230
Kahl KG, Trillenberg P, Kordon A, Lencer R, Klein C, Hagenah J (2005) Pharmacological strategies for clozapine-induced hypersalivation: treatment with botulinum toxin B in one patient and review of the literature. Nervenarzt 76:205–208
Katona G, Csákányi Z, Lorincz A, Gerlinger I (2008) Bilateral submandibular duct relocation by high-frequency radiosurgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265:1103–1108
Kok SE, van der Burg JJ, van Hulst K, Erasmus CE, van den Hoogen FJ (2016) The impact of submandibular duct relocation on drooling and the well-being of children with neurodevelopmental disabilities. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 88:173–178
Lagalla G, Millevolte M, Capecci M, Provinciali L, Ceravolo MG (2009) Long-lasting benefits of botulinum toxin type B in Parkinson‘s disease-related drooling. Ceravolo MG. J Neurol 256:563–667
Lakraj AA, Moghimi N, Jabbari B (2013) Sialorrhea: anatomy, pathophysiology and treatment with emphasis on the role of botulinum toxins. Toxins (Basel) 5:1010–1031
Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olsen N (1988) Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: a new procedure. Dysphagia 2:216–219
Laskawi R, Winterhoff J, Köhler S, Kottwitz L, Matthias C (2013) Botulinum toxin treatment of salivary fistulas following parotidectomy: follow-up results. Oral Maxillofac Surg 17:281–285
Lawson G, Remacle M (2006) Endoscopic cricopharyngeal myotomy: indications and technique. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 14:437–441
Lee ZI, Yu KJ, Lee DH, Hong SK, Woo SB, Kim JM, Park D (2017) The effect of nebulized glycopyrrolate on posterior Drooling in patients with brain injury: two cases of different brain lesions. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 96:e155–e158
Leung JG, Schak KM (2017) Potential problems surrounding the use of sublingually administered ophthalmic atropine for sialorrhea. Schizophr Res 185:202–203
Lim M, Mace A, Nouraei SA, Sandhu G (2006) Botulinum toxin in the management of sialorrhoea: a systematic review. Clin Otolaryngol 31:267–272
Limbrock J, Mundmotorik (2017) Empfehlungen für Babys und Kleinkinder mit Störungen der oralen Funktion. Osteopat Medizin 18:38–41
Limbrock GJ, Hoyer H, Scheying H (1990) Drooling, chewing and swallowing dysfunctions in children with cerebral palsy: treatment according to Castillo-Morales. ASDC J Dent Child 57:445–451
Logemann JA (1997) Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. Pro-Ed, Austin
Man WH, Colen-de Koning JC, Schulte PF, Cahn W, van Haelst IM, Doodeman HJ, Egberts TC, Heerdink ER, Wilting I (2017) The effect of glycopyrrolate on nocturnal sialorrhea in patients using clozapine: a randomized, crossover, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 37:155–161
Mankarious LA, Bottrill ID, Huchzermeyer PM, Bailey CM (1999) Long-term follow-up of submandibular duct rerouting for the treatment of sialorrhea in the pediatric population. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:303–307
Marinone S, Gaynor W, Johnston J, Mahadevan M (2017) Castillo morales appliance therapy in the treatment of drooling children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 103:129–132
Martin TJ, Conley SF (2007) Long-term efficacy of intra-oral surgery for sialorrhea. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:54–58
Matos Santana TE, Capurso NA, Ranganathan M, Yoon G (2017) Sublingual atropine in the treatment of clozapine-induced sialorrhea. Schizophr Res 182:144–145
Mier RJ, Bachrach SJ, Lakin RC, Barker T, Childs J, Moran M (2000) Treatment of sialorrhea with glycopyrrolate: a double-blind, dose-ranging study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 154:1214–1218
Mikami DLY, Furia CLB, Welker AF (2017) Addition of Kinesio Taping of the orbicularis oris muscles to speech therapy rapidly improves drooling in children with neurological disorders. Dev Neurorehabil 21:1–6
Murray J, Langmore SE, Ginsberg S, Dostie A (1996) The significance of accumulated oropharyngeal secretions and swallowing frequency in predicting aspiration. Dysphagia 11:99–103
Neppelberg E, Haugen DF, Thorsen L, Tysnes OB (2007) Radiotherapy reduces sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 14:1373–1377
Neubauer PD, Rademaker AW, Leder SB (2015) The yale pharyngeal residue severity rating scale: an anatomically defined and image-based tool. Dysphagia 30:521–528
Noonan K, Prunty S, Ha JF, Vijayasekaran S (2014) Surgical management of chronic salivary aspiration. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 78:2079–2082
Olthoff A, Carstens PO, Zhang S, von Fintel E, Friede T, Lotz J, Frahm J, Schmidt J (2016a) Evaluation of dysphagia by novel real-time MRI. Neurology 87:2132–2138
Olthoff A, Joseph AA, Weidenmüller M, Riley B, Frahm J (2016b) Real-time MRI of swallowing: intraoral pressure reduction supports larynx elevation. NMR Biomed 29:1618–1623
Ondo WG, Hunter C, Moore W (2004) A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of botulinum toxin B for sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 62:37–40
Parr JR, Weldon E, Pennington L, Steen N, Williams J, Fairhurst C, O’Hare A, Lodh R, Colver A (2014) The drooling reduction intervention trial (DRI): a single blind trial comparing the efficacy of glycopyrronium and hyoscine on drooling in children with neurodisability. Trials 15:60
Postma AG, Heesters M, van Laar T (2007) Radiotherapy to the salivary glands as treatment of sialorrhea in patients with parkinsonism. Mov Disord 22:2430–2435
Praharaj SK, Munoli RN, Sharma PS (2014) Low-dose glycopyrrolate for clozapine-associated sialorrhea. J Clin Psychopharmacol 34:392
Prosiegel M, Buchholz D (2014) Mit Schluckstörungen assoziierte neurologische Erkrankungen. In: Bartolome G, Schröter-Morasch H (eds) Schluckstörungen—Diagnostik und Rehabilitation, 5th edn. Elsevier, München, pp 61–89
Prosiegel M, Bartolome G, Biniek R, Fheodoroff K, Schlaegel W, Schröter-Morasch H, Steube D, Witte U. Saltuari U (2008) Rehabilitation neurogener Dysphagien. In: Diener HC (ed) Leitlinien für Diagnostik und Therapie in der Neurologie. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 908–919
Qurashi I, Chu S, Husain N, Drake RJ, Chaudhry I, Deakin JF (2016) Glycopyrrolate in comparison to hyoscine hydrobromide and placebo in the treatment of hypersalivation induced by clozapine (GOTHIC1): study protocol for a randomised controlled feasibility study. Trials 17:553
Reed J, Mans CK, Brietzke SE (2009) Surgical management of drooling: a meta-analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:924–931
Reynolds J, Carroll S, Sturdivant C (2016) Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing: a multidisciplinary alternative for assessment of infants with dysphagia in the neonatal intensive care unit. Adv Neonatal Care 16:37–43
Rohrbach S, Gross M (2014) Die transnasale fiberoptisch-endoskopische Schluckuntersuchung (FEES) bei Kindern—Standardisiertes diagnostisches Vorgehen. Monatsschrift Kinderheilkunde 162:329–333
Rohrbach S, Laskawi R (2004) Praktische Anwendung von Botulinum-Toxin im Kopf—Hals-Bereich. HNO 52:635–641
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB (1996) A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11:93–98
S3 Leitlinie Palliativmedizin (2015) https://www.leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/index.php?id=80&type=0. Accesed 31 July 2018
Schroeder AS, Kling T, Huss K, Borggraefe I, Koerte IK, Blaschek A, Jahn K, Heinen F, Berweck S (2012) Botulinum toxin type A and B for the reduction of hypersalivation in children with neurological disorders: a focus on effectiveness and therapy adherence. Neuropediatrics 43:27–36
Schröter-Morasch H, Graf S (2014) Dysphagiediagnostik durch den HNO-Arzt. HNO 62:324–334
Seegenschmiedt MH, Makoski HB, Trott KR, Brady LW (2008) Sialorrhea/Hypersalivation. In: Seegenschmiedt MH, Makoski HB, Trott KR, Brady LW (eds) Radiotherapy for non-malignant disorders. Springer, Berlin, pp 573–579
Sittironnarit G, Ames D, Bush AI, Faux N, Flicker L, Foster J, Hilmer S, Lautenschlager NT, Maruff P, Masters CL, Martins RN, Rowe C, Szoeke C, Ellis KA, AIBL research group (2011) Effects of anticholinergic drugs on cognitive function in older Australians: results from the AIBL study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 31:173–178
Squires N, Humberstone M, Wills A, Arthur A (2014) The use of botulinum toxin injections to manage drooling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neurone disease: a systematic review. Dysphagia 29:500–508
Steffen A, Ortfeld S, Schönweiler R (2011a) Drooling bei neuropädiatrischen Patienten—ein Update. Klin Padiatr 223:5–9
Steffen A, Wollenberg B, Schönweiler R, Brüggemann N, Meyners T (2011b) Drooling nach Strahlentherapie—Botulinumtoxin als erfolgreiches Therapieverfahren. HNO 59:115–117
Steffen A, Beutner D, Hakim S, Jost W, Kahl KG, Laskawi R, Lencer R, Mall V, Mehrhoff FW, Meyners T, Schönweiler R, Schröder S, Schröter-Morasch H, Schuster M, Steinlechner S, Winterhoff J, Zenk J, Lichius O, AWMF (2013) Hypersalivation—inauguration of the S2k guideline (AWMF) in short form. Laryngorhinootologie 92:515–522
Steffen A, Hasselbacher K, Heinrichs S, Wollenberg B (2014) Botulinum toxin for salivary disorders in the treatment of head and neck cancer. Anticancer Res 34:6627–6632
Steffen A, Hasselbacher K, Brüggemann N, Heinrichs S, Schönweiler R, Wollenberg B (2015) Botulinumtoxin bei funktioneller hypersalivation—alles eine Frage der Dosis? Laryngorhinootologie 94:378–382
Steinlechner S, Klein C, Moser A, Lencer R, Hagenah J (2010) Botulinum toxin B as an effective and safe treatment for neuroleptic-induced sialorrhea. Psychopharmacology 207:593–597
Stone CA, N O‘Leary (2009) Systematic review of the effectiveness of botulinum toxin or radiotherapy for sialorrhea in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Pain Symptom Manag 37:246–258
Suntrup S, Marian T, Schröder JB, Suttrup I, Muhle P, Oelenberg S, Hamacher C, Minnerup J, Warnecke T, Dziewas R (2015) Electrical pharyngeal stimulation for dysphagia treatment in tracheotomized stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med 41:1629–1637
Thomas-Stonell N, Greenberg J (1988) Three treatment approaches and clinical factors in the reduction of drooling. Dysphagia 3:73–78
Uppal HS, De R, D’Souza AR, Pearman K, Proops DW (2003) Bilateral submandibular duct relocation for drooling: an evaluation of results for the Birmingham Children’s Hospital. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 260:48–51
van Hulst K, van den Engel-Hoek L, Geurts ACH, Jongerius PH, van der Burg JJW, Feuth T, van den Hoogen FJA, Erasmus CE (2018) Development of the drooling infants and preschoolers scale (DRIPS) and reference charts for monitoring saliva control in children aged 0–4 years. Infant Behav Dev 50:247–256
Vashishta R, Nguyen SA, White DR, Gillespie MB (2013) Botulinum toxin for the treatment of sialorrhea: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148:191–196
Verma R, Anand KS (2017) Botulinum toxin: a novel therapy for clozapine-induced sialorrhoea. Psychopharmacology 235:369–371
Weikamp JG, Schinagl DA, Verstappen CC, Schelhaas HJ, de Swart BJ, Kalf JG (2016) Botuninum toxin-A injections vs. radiotherapy for drooling in ALS. Acta Neurol Scand 134:224–231
Wildiers H, Dhaenekint C, Demeulenaere P, Clement PM, Desmet M, Van Nuffelen R, Gielen J, Van Droogenbroeck E, Geurs F, Lobelle JP, Menten J, Flemish Federation of Palliative Care (2009) Atropine, hyoscine butylbromide, or scopolamine are equally effective for the treatment of death rattle in terminal care. J Pain Symptom Manage 38:124–133
Wilken B, Aslami B, Backes H (2008) Successful treatment of drooling in children with neurological disorders with botulinum toxin A or B. Neuropediatrics 39:200–204
Wu KP, Ke JY, Chen CY, Chen CL, Chou MY, Pei YC (2011) Botulinum toxin type A on oral health in treating sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Child Neurol 26:838–843
Zeller RS, Davidson J, Lee HM, Cavanaugh PF (2012a) Safety and efficacy of glycopyrrolate oral solution for management of pathologic drooling in pediatric patients with cerebral palsy and other neurologic conditions. Ther Clin Risk Manag 8:25–32
Zeller RS, Lee HM, Cavanaugh PF, Davidson J (2012b) Randomized phase III evaluation of the efficacy and safety of a novel glycopyrrolate oral solution for the management of chronic severe drooling in children with cerebral palsy or other neurologic conditions. Ther Clin Risk Manag 8:15–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steffen, A., Jost, W., Bäumer, T. et al. Hypersalivation: update of the German S2k guideline (AWMF) in short form. J Neural Transm 126, 853–862 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02000-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02000-4