Abstract
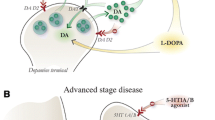
Dopamine (DA) replacement therapy with l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA) continues to be the gold-standard treatment for Parkinson’s disease (PD). Despite clear symptomatic benefit, long-term l-DOPA use often results in the development of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia (LID), significantly reducing quality of life and increasing costs for PD patients and their caregivers. Accumulated research has demonstrated that several pre- and post-synaptic mechanisms contribute to LID development and expression. In particular, raphe-striatal hyperinnervation and unregulated DA release from 5-HT terminals is postulated to play a central role in LID manifestation. As such, manipulation of the 5-HT system has garnered considerable attention. Both pre-clinical and clinical research has supported the potential of modulating the 5-HT system for LID prevention and treatment. This review discusses the rationale for continued investigation of several potential anti-dyskinetic strategies including 5-HT stimulation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors and blockade of 5-HT2A receptors and SERT. We present the latest findings from experimental and clinical investigations evaluating these 5-HT targets with the goal of identifying those with translational promise and the challenges associated with each.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansah TA, Ferguson MC, Nayyar T (2011) The 5-HT 2A receptor antagonist M100907 produces antiparkinsonian effects and decreases striatal glutamate. Front Sys Neurosci 5:1–6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2011.00048
Anttila SAK, Leinonen EVJ (2001) A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev 7(3):249–264
Ashby CR, Wang RY (1996) Pharmacological actions of the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine: a review. Synapse 394:349–394
Azkona G, Sagarduy A, Aristieta A, Vazquez N, Zubillaga V, Ruíz-Ortega JA, Sánchez-pernaute R (2013) Buspirone anti-dyskinetic effect is correlated with temporal normalization of dysregulated striatal DRD1 signalling in l-DOPA-treated rats. Neuropharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.024
Ba M, Kong M, Ma G, Yang H, Lu G, Chen S, Liu Z (2006) Cellular and behavioral effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT in a rat model of levodopa-induced motor complications. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.10.020
Ballanger B, Beaudoin-gobert XM, Neumane S, Epinat J, Metereau X, Duperrier S, Tremblay L (2016) Imaging dopamine and serotonin systems on MPTP monkeys: a longitudinal PET investigation of compensatory mechanisms. J Neurosci 36(5):1577–1589. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2010-15.2016
Bara-Jimenez W, Bibbiani F, Morris MJ, Dimitrova T, Sherzai A, Mouradian MM, Chase TN (2005) Effects of serotonin 5-HT1A agonist in advanced Parkinson’s Disease. Movement Disord 20(8):932–936. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20370
Barnes NM, Sharp T (1999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharm 38:1083–1152
Bartoszyk GD, Van Amsterdam C, Greiner HE, Rautenberg W, Russ H, Seyfried CA (2003) Sarizotan, a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor agonist and dopamine receptor ligand. Neurochemical profile. J Neural Transm. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0094-7
Basura GJ, Walker PD (2001) Serotonin 2A receptor regulation of striatal neuropeptide gene expression is selective for tachykinin, but not enkephalin neurons following dopamine depletion. Mol Brain Res 92:66–77
Bezard E, Tronci E, Pioli EY, Li Q, Porras G, Bjorklund A, Manola C (2013) Study of the antidyskinetic effect of eltoprazine in animal models of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Neurosci Res 28(8):1088–1096. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25366
Bézard E, Munoz A, Tronci E, Pioli EY, Li Q, Porras G, Carta M (2013) Anti-dyskinetic effect of anpirtoline in animal models of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Neurosci Res 77(4):242–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2013.10.002
Bibbiani F, Oh JD, Chase TN (2001) Serotonin 5-HT1A agonist improves motor complications in rodent and primate parkinsonian models. Neurology 57:1829–1834
Bishop C, Walker PD (2003) Combined intrastriatal dopamine D1 and serotonin 5-HT2 receptor stimulation reveals a mechanism for hyperlocomotion in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Neuroscience 121:649–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4522(03)00516-5
Bishop C, Daut GS, Walker PD (2005) Serotonin 5-HT 2A but not 5-HT 2C receptor antagonism reduces hyperlocomotor activity induced in dopamine-depleted rats by striatal administration of the D1 agonist SKF 82958. Neuropharm 49:350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.03.008
Bishop C, Taylor JL, Kuhn DM, Eskow KL, Park JY, Walker PD (2006) MDMA and fenfluramine reduce l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia via indirect 5-HT1A receptor stimulation. Eur J Neurosci 23(January):2669–2676. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04790.x
Bishop C, Krolewski DM, Eskow KL, Barnum CJ, Dupre KB, Deak T, Walker PD (2009) Contribution of the striatum to the effects of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation in l-DOPA-treated hemiparkinsonian rats. J Neurosci Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21978
Bishop C, George JA, Buchta W, Goldenberg AA, Mohamed M, Dickinson SO, Jaunarajs KLE (2012) Serotonin transporter inhibition attenuates l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia without compromising l-DOPA efficacy in hemi-parkinsonian rats. Eur J Neurosci 36:2839–2848. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08202.x
Bonifati V, Fabrizio E, Cipriani R, Vanacore N, Meco G (1994) Buspirone in levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Clin Neuropharmacol 17(1):73–82
Boyer EW, Shannon M (2005) The serotonin syndrome. N Engl J Med 35(11):1112
Campbell BM, Walker PD (2001) MK-801 prevents dopamine D1 but not serotonin 2A stimulation of striatal preprotachykinin mRNA expression. NeuroReport 12(5):953–955
Carta M, Carlsson T, Kirik D, Bjorklund A (2007) Dopamine released from 5-HT terminals is the cause of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats. Brain 130:1819–1833. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm082
Castro ME, Pascual J, Romon T, Berciano J, Figols J, Pazos A (1998) 5-HT 1B receptor binding in degenerative movement disorders. Brain Res 790:323–328
Chang A, Fox SH (2016) Psychosis in Parkinson’s disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Drugs 76:1093–1118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0600-5
Charnay Y, Leger L (2010) Brain serotonergic circuits. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 12(4):471–487
Chen Y, Huang W, Lin Y, Cheng C, Liu R, Wang S-J, Ma KH (2012) Characterization of 4-[18 F]-ADAM as an imaging agent for SERT in non-human primate brain using PET: a dynamic study. Nucl Med Biol 39(2):279–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2011.08.002
Chung KA, Carlson NE, Nutt JG (2005) paroxetine treatment does not alter the motor response to levodopa in PD. Neurology 64:1797–1798
Chung YC, Kim SR, Jin BK, Alerts E (2010) Paroxetine prevents loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting brain inflammation and oxidative stress in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. J Immunol 185:1230–1237. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1000208
Conti MM, Ostock CY, Lindenbach D, Goldenberg AA, Kampton E, Dell’isola R, Bishop C (2014) Effects of prolonged selective serotonin reuptake inhibition on the development and expression of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemi- parkinsonian rats. Neuropharm 77:1–8
Conti MM, Meadows SM, Melikhov-sosin M, Lindenbach D, Hallmark J, Werner DF, Bishop C (2016) Monoamine transporter contributions to l-DOPA effects in hemi—parkinsonian rats. Neuropharm 110:125–134
Cotzias GC, Van Woert MH, Schiffer LM (1967) Aromatic amino acids and modification of parkinsonism. N Engl J Med 276(7):374–379
Cotzias GC, Papavasiliou PS, Gellene R (1969) Modification of Parkinsonism—chronic treatment with l-dopa. N Engl J Med 280(7):337–345
Cummings J, Isaacson S, Mills R, Williams H, Chi-burris K, Corbett A, Ballard C (2014) Pimavanserin for patients with Parkinson’ s disease psychosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 383:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62106-6
Dekundy A, Lundblad M, Danysz W, Cenci MA (2007) Modulation of l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements by clinically tested compounds: further validation of the rat dyskinesia model. Behav Brain Rese 179:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.01.013
Devane CL, Nemeroff CB (2001) Clinical pharmacokinetics of quetiapine. Clin Pharmacokinetics 40(7):509–522
Ding S, Li L, Zhou FM (2015) Robust presynaptic serotonin 5-HT 1B receptor inhibition of the striatonigral output and its sensitization by chronic fluoxetine treatment. J Neurophys 113(9):3397–3409
Donnelly K (2008) Cardiac valvular pathology: comparative pathology and animal models of acquired cardiac valvular diseases. Toxicol Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623307312707
Dupre KB, Eskow KL, Negron G, Bishop C (2007) The differential effects of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation on dopamine receptor-mediated abnormal involuntary movements and rotations in the primed hemiparkinsonian rat. Brain Res 1158(1):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.05.005
Dupre KB, Ostock CY, Jaunarajs KLE, Button T, Savage LM, Wolf W, Bishop C (2011) Local modulation of striatal glutamate efflux by serotonin 1A receptor stimulation in dyskinetic, hemiparkinsonian rats. Exp Neurol 229(2):288–299
Durif F, Vidailhet M, Bonnet AM, Blin J, Agid Y (1995) Levodopa-induced dyskinesias are improved by fluoxetine. Neurology 45:1855–1858
Durif F, Debilly B, Galitzky M, Morand D, Viallet F, Borg M, Rascol O (2004) Clozapine improves dyskinesias in Parkinson disease A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology 62:381–388
Ener RA, Meglathery SB, Van Decker WA, Gallagher RM (2003) Serotonin syndrome and other serotonergic disorders. Am Acad Pain Med 4(1):63–74
Eskow Jaunarajs KL, Dupre KB, Steiniger A, Klioueva A, Moore A, Kelly C, Bishop C (2009) Serotonin 1B receptor stimulation reduces D1 receptor agonist-induced dyskinesia. NeuroReport 00(00):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283300fd7
Eskow KL, Dupre KB, Barnum CJ, Dickinson SO, Park JY, Bishop C (2009) The role of the dorsal raphe nucleus in the development, expression, and treatment of l-dopa-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian rats. Synapse 63:610–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20630
Eskow KL, Gupta V, Alam S, Park JY, Bishop C (2007) The partial 5-HT 1A agonist buspirone reduces the expression and development of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in rats and improves L-DOPA efficacy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 87(3):306–314
Ferguson MC, Nayyar T, Deutch AY, Ansah TA (2010) 5-HT2A receptor antagonists improve motor impairments in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharm 59(1–2):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.03.013.5-HT
Ferguson MC, Nayyar T, Ansah TA (2014) Reverse microdialysis of a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist alters extracellular glutamate levels in the striatum of the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 615:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2014.03.016.Reverse
Fernandez HH, Trieschmann ME, Friedman JH (2004) Aripiprazole for drug-induced psychosis in Parkinson disease: preliminary experience. Clin Neuropharmacol 27(1):4–5
Fidalgo C, Ko WKD, Tronci E, Li Q, Stancampiano R, Chuan Q, Carta M (2015) Effect of serotonin transporter blockade on l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in animal models of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroscience 298:389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.04.027
Frechilla D, Cobreros A, Saldise L, Moratalla R, Insausti R, Luquin M-R, Joaquin DR (2001) Serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor expression is selectively enhanced in the striosomal compartment of chronic. Synapse 296(February 2000):288–296
Friedman JH, Berman RM, Goetz CG, Factor SA, Ondo WG, Wojcieszek J, Marcus RN (2006) Open-label flexible-dose pilot study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of aripiprazole in patients with psychosis associated with Parkinson’ s Disease. Movement Disord 21(12):2078–2081. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21091
Gagnon D, Gregoire L, Paolo T Di, Parent M (2015) Serotonin hyperinnervation of the striatum with high synaptic incidence in parkinsonian monkeys. Brain Struct Funct 221(7):3675–3691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1125-5
Gefvert O, Bergstrom M, Langstrom B, Lundberg T, Lindstrom L, Yates R (1998) Time course of central nervous dopamine-D 2 and 5-HT2 receptor blockade and plasma drug concentrations after discontinuation of quetiapine (Seroquel®) in patients with schizophrenia. Psychopharm 135:119–126
Ghiglieri V, Mineo D, Vannelli A, Cacace F, Mancini M, Pendolino V, Picconi B (2016) Neurobiology of disease modulation of serotonergic transmission by eltoprazine in l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: behavioral, molecular, and synaptic mechanisms. Neurobiol Dis 86:140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.11.022
Goetz CG, Damier P, Hicking C, Laska E, Muller T, Olanow CW, Russ H (2007) Sarizotan as a treatment for dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Movement Disord 22(2):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21226
Goetz CG, Laska E, Hicking C, Stat D, Damier P, Müller T, Russ H (2009) Placebo influences on dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disord 23(5):700–707. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21897.Placebo
Grégoire L, Samadi P, Graham J, Bédard PJ, Bartoszyk GD, Di Paolo T (2009) Low doses of sarizotan reduce dyskinesias and maintain antiparkinsonian efficacy of l-Dopa in parkinsonian monkeys. Parkinson Relat D 15(6):445–452
Gresch PJ, Walker PD (1999a) Synergistic interaction between serotonin-2 receptor and dopamine D1 receptor stimulation on striatal preprotachykinin mRNA expression in the 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rat. Mol Brain Res 70:125–134
Gresch P, Walker P (1999b) Serotonin-2 receptor stimulation normalizes striatal preprotachykinin messenger RNA in an animal model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroscience 93(3):831–841
Grunder G, Kungel M, Ebrecht M, Gorocs T, Modell S (2006) Aripiprazole: pharmacodynamics of a dopamine partial agonist for the treatment of schizophrenia. Pharmacopsychiatry 39:S21–S25. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-931485
Haberzettl R, Bert B, Fink H, Fox MA (2013) Animal models of the serotonin syndrome: a systematic review. Behav Brain Res 256:328–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.08.045
Hagino Y, Takamatsu Y, Yamamoto H, Iwamura T, Murphy DL, Uhl GR, Ikeda K (2011) Effects of MDMA on extracellular dopamine and serotonin levels in mice lacking dopamine and/or serotonin transporters. Curr Neuropharmacol 9(1):91–95
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Veyres N, Frouni I, Kwan C, Sid-Otmane L, Huot P (2017) The effect of mirtazapine on dopaminergic psychosis and dyskinesia in the parkinsonian marmoset. Psychopharmacol 234(6):905–911
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018) The effect of mianserin on the severity of psychosis and dyskinesia in the parkinsonian marmoset. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 81:367–371
Hammerstad JP, Carter J, Nutt JG, Casten GC, Shrotriya RC, Alms DR, Temple D (1986) Buspirone in Parkinson’s Disease.pdf. Clinl Neuropharmacol 9(6):556–560
Henderson J, Yiannikas C, Graham JS (1992) Effect of ritanserin, a highly selective 5-HT2 receptor antagonist, on Parkinson’s disease. Clinl Exper Neurol 29:277–282
Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, Hartig PR, Martin GR, Mylecharane EJ, Humphrey PPA (1994) Union of pharmacology for 5-hydroxytryptamine classification (serotonin). Pharmacol Rev 46(2):157–203
Hummeli T, Hummel C, Friedeli I, Pauli E, Kobal G (1994) A comparison of the antinociceptive effects of imipramine, tramadol and anpirtoline. Brit J Pharmacol 37:325–333
Huot P, Johnston TH, Lewis KD, Koprich JB, Reyes MG, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2011a) Characterization of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) enantiomers in vitro and in the MPTP-lesioned primate: R-MDMA reduces severity of dyskinesia, whereas S-MDMA extends duration of ON-time. J Neurosci 31(19):7190–7198. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1171-11.2011
Huot P, Fox SH, Newman-Tancredi A, Brotchie JM (2011b) Anatomically selective serotonergic type 1A and serotonergic type 2A therapies for Parkinson’s disease: an approach to reducing dyskinesia without exacerbating parkinsonism? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 339(1):2–8
Huot P, Johnston TH, Gandy MN, Reyes MG, Fox SH, Piggott MJ, Brotchie JM (2012a) The monoamine re-uptake inhibitor UWA-101 improves motor fluctuations in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset. PLoS ONE 7(9):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045587
Huot P, Johnston TH, Koprich JB, Winkelmolen L, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2012b) Regulation of cortical and striatal 5-HT 1A receptors in the MPTP-lesioned macaque. Neurobiol Aging 33:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.09.011
Huot P, Johnston TH, Winkelmolen L, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2012c) 5-HT 2A receptor levels increase in MPTP-lesioned macaques treated chronically with l-DOPA. Neurobiol Aging 33(1):194.e5–194.e15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.04.035
Huot P, Johnston TH, Koprich JB, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2013) The pharmacology of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’ s Disease. Pharmacol Rev 65:171–222
Huot P, Johnston TH, Lewis KD, Koprich JB, Reyes MG, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2014) UWA-121, a mixed dopamine and serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, enhances l-DOPA anti-parkinsonian action without worsening dyskinesia or psychosis-like behaviours in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset. Neuropharm 82:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.012
Huot P, Johnston TH, Fox SH, Newman-tancredi A, Brotchie JM (2015) Neuropharmacology The highly-selective 5-HT 1A agonist F15599 reduces l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia without compromising anti-parkinsonian benefits in the MPTP-lesioned macaque. Neuropharm 97:306–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.05.033
Huot P, Sgambato-Faure V, Fox SH, McCreary AC (2017) Serotonergic approaches in Parkinson’ s Disease: translational perspectives, an update. ACS Chem Neurosci 8:973–986. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00440
Iderberg H, Mccreary AC, Varney MA, Cenci MA, Newman-Tancredi A (2015) Neuropharmacology activity of serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor “biased agonists” in rat models of Parkinson’s disease and l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Neuropharm 93:52–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.01.012
Iravani MM, Jackson MJ, Kuoppamamaki M, Smith LA, Jenner P (2003) 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamohetamine (ecstasy) inhibits dyskinesia expression and normalizes motor activity in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated primates. J Neurosci 23(27):9107–9115
Iravani MM, Tayarani-binazir K, Chu WB, Jackson MJ, Jenner P (2006) Primates, the selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1a agonist (R)-(+)-8-OHDPAT inhibits levodopa-induced dyskinesia but only with increased motor disability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319(3):1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.110429.glutamate
Johnson SW, Mercuri NB, North RA (1992) 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1B receptors block the GABA, synaptic potential in rat dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 12(5):2000–2006
Johnston TH, Millar Z, Huot P, Wagg K, Thiele S, Salomonczyk D, Brotchie JM (2012) A novel MDMA analog, UWA-101, that lacks psychoactivity and cytotoxicity, enhances l-DOPA benefit in parkinsonian primates. FASEB 26(5):2154–2163. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-195016
Kalant H (2001) The pharmacology and toxicology of “ecstasy” (MDMA) and related drugs. CMAJ Can Med Assoc J 165(7):917–928
Kannari K, Kurahashi K, Tomiyama M, Maeda T, Arai A, Baba M, Matsunaga M (2002) Tandospirone citrate, a selective 5-HT1A agonist, alleviates L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. No to shinkei 54(2):133–137
Kannari K, Shen H, Arai A, Tomiyama M, Baba M (2006) Reuptake of l-DOPA-derived extracellular dopamine in the striatum with dopaminergic denervation via serotonin transporters. Neurosci Lett 402:62–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2006.03.059
Katzenschlager R, Manson AJ, Evans A, Watt H, Lees AJ (2004) Low dose quetiapine for drug induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease: a double blind cross over study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:295–297
Ko WKD, Li Q, Cheng LY, Morelli M, Carta M, Bezard E (2017) A preclinical study on the combined effects of repeated eltoprazine and preladenant treatment for alleviating L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease. Eur J Pharmacol 813:10–16
Kuan W, Zhao J, Barker RA (2008) The role of anxiety in the development of levodopa-induced dyskinesias in an animal model of Parkinson’ s disease, and the effect of chronic treatment with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram. Psychopharm 197:279–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1030-6
Larsen MB, Sonders MS, Mortensen OV, Larson GA, Zahniser NR, Amara SG (2011) Dopamine transport by the serotonin transporter: mechanistically distinct mode of substrate translocation. J Neurosci 31(17):6605–6615. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0576-11.2011.Dopamine
Lebsanft HB, Kohles T, Kovar K-A, Schmidt WJ (2005) 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine counteracts akinesia enantioselectively in rat rotational behavior and catalepsy. Synapse 55:148–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20102
Lee J, Seongho S, Lee JS, Kim H, Kim YK, Beom SJ (2015) Putaminal serotonergic innervation Monitoring dyskinesia risk in Parkinson disease. Neurology 85(10):853–860
Lejeune F, Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Millan MJ (1997) Interactions of (+)- and -8- and 7-hydroxy-2- (di-n-propylamino) tetralin at human (h)D3, hD2 and h serotonin 1A receptors and their modulation of the activity of serotoninergic and dopaminergic neurones in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280(3):1241–1249
Ligeois J, Bruhwyler J, Damas J, Rogister F, Masereel B, Geczy J, Delarge J (1995) Modulation of clozapine structure increases its selectivity for the dopamine D4 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 273:R1–R3
Linazasoro G (2000) Worsening of Parkinson’ s disease by citalopram. Parkinsonism Relat D 6(111–113):111–113
Lindenbach D, Palumbo N, Ostock CY, Vilceus N, Conti MM, Bishop C (2015) Side effect profile of 5-HT treatments for Parkinson’s disease and l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in rats. Brit J Pharmacol 172(1):119–130
Lindgren HS, Andersson DR, Lagerkvist S, Nissbrandt H, Cenci MA (2010) l-Dopa-induced dopamine efflux in the striatum and the substantia nigra in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease: temporal and quantitative relationship to the expression of dyskinesia. J Neurochem 112:1465–1476. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06556.x
Llado-Pelfort L, Assié M-B, Newman-Tancredi A, Artigas F, Celada P (2010) Preferential in vivo action of F15599, a novel 5-HT 1A receptor agonist, at postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Brit J Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00738.x
Ludwig CL, Weinberger DR, Bruno G, Gillespie M, Bakker K, LeWitt PA, Chase TN (1986) Buspirone, Parkinson’s Disease, and the locus ceruleus.pdf. Clin Neuroph 9(4):373–378
Lundblad M, Andersson M, Winkler C, Kirik D, Wierup N, Cenci MA (2002) Pharmacological validation of behavioural measures of akinesia and dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson’ s disease. Eur J Neurosci 15:120–132
Marin C, Aguilar E, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Bartoszyk GD, Obeso JA (2009) Local administration of sarizotan into the subthalamic nucleus attenuates levodopa-induced dyskinesias in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Psychopharmacol 204(2):241–250
Martel J-C, Assié M, Buritova J, Lauressergues E, Cosi C, Heusler P, Cussac D (2009) Signal transduction and functional selectivity of F15599, a preferential post-synaptic 5-HT 1A receptor agonist. Brit J Pharmacol 156:338–353. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00001.x
Mazzucchi S, Frosini D, Ripoli A, Nicoletti V, Linsalata G, Bonuccelli U, Ceravolo R (2015) Serotonergic antidepressant drugs and l-dopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scandinavica 6:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12314
Mccreary AC, Varney MA, Newman-Tancredi A (2016) Neuropharmacology the novel 5-HT 1A receptor agonist, NLX-112 reduces l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements in rat: a chronic administration study with microdialysis measurements. Neuropharmacology 105:651–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.01.013
Meadows SM, Chambers NE, Conti MM, Bossert SC, Tasber C, Sheena E, Bishop C (2017) Characterizing the differential roles of striatal 5-HT 1A auto- and hetero-receptors in the reduction of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Exp Neurology 292:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.03.013
Meco G, Marini S, Lestingi L, Linfante I (1988) Controlled single-blind crossover study of ritanserin and placebo in l-dopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Ther Res 43(2):262–270
Meco G, Fabrizio E, Rezze S Di, Alessandri A, Pratesi L (2003) Mirtazapine in l-Dopa-induced dyskinesias. Clin Neuropharm 26(4):179–181
Meco G, Stirpe P, Edito F, Purcaro C, Valente M, Bernardi S, Vanacore N (2009) Aripiprazole in l-dopa-induced dyskinesias : a one-year open-label pilot study. J Neur Tranns 116:881–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0231-z
Miguelez C, Navailles S, Delaville C, Marquis L, Lagière M, Benazzouz A, De Deurwaerdère P (2016) l-DOPA elicits non-vesicular releases of serotonin and dopamine in hemiparkinsonian rats in vivo. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 26(8):1297–1309
Mills R, Revell S, Bahr D, Williams H, Johnson A, Friedman JH (2008) A double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation trial of pimavanserin in Parkinson’s disease and psychosis. Mov Disord 23:S221–S222
Morgante L, Epifanio A, Spina E, Zappia M, Di Rosa AE, Marconi R, Quattrone A (2004) Quetiapine and clozapine in parkinsonian patients with dopaminergic psychosis. Clin Neuropharmacol 27(4):153–156
Morin N, Morissette M, Gregoire L, Rajput A, Di Paolo T (2015) Contribution of brain serotonin subtype 1B receptors in levodopa- induced motor complications. Neuropharmacology 99:356–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.002
Müller T, Olanow CW, Nutt J, Hicking C, Laska E, Russ H (2006) The Paddy-2 study: the evaluation of sarizotan for treatment-associated for dyskinesia in PD patients. Mov Disord 21(Suppl 15):S591
Ng KY, Chase TN, Colburn RW, Kopin IJ (1970) l-Dopa-induced release of cerebral monoamines. Science 170(3953):76–77
Oh JD, Bibbiani F, Chase TN (2002) Quetiapine attenuates levodopa-induced motor complications in rodent and primate parkinsonian models. Exp Neurol 177:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.2002.8009
Olanow CW, Damier P, Goetz CG, Mueller T, Nutt J, Rascol O, Russ H (2004) Disease patients with levodopa-induced dyskinesias (the SPLENDID study. Clin Neuropharm 27(2):58–62
Ostock CY, Dupre KB, Eskow Jaunarajs KL, Walters H, George J, Krolewski D, Bishop C (2011) Role of the primary motor cortex in l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and its modulation by 5-HT1A receptor stimulation. Neuropharmacology 61:753–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.05.021
Owens MJ, Morgan WN, Plott SJ, Nemeroff CB (1997) Neurotransmitter receptor and transporter binding profile of antidepressants and their metabolites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283(3):1305–1322
Owens MJ, Knight DL, Nemeroff CB (2001) Second-generation SSRIs: human Monoamine transporter binding profile of Escitalopram and R-Fluoxetine. Biol Psychiat 50:345–350
Pagano G, Niccolini F, Fusar-Poli P, Politis M (2017) Serotonin transporter in Parkinson’s Disease: a meta-analysis of positron emission tomography studies. Annals of Neurol 81:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24859
Paolone G, Brugnoli A, Arcuri L, Mercatelli D, Morari M (2015) Eltoprazine prevents levodopa-induced dyskinesias by reducing striatal glutamate and direct pathway activity. Movement Disord 30(13):1728–1738. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26326
Parkinson Study Group (1999) Low-dose clozapine for the treatment of drug-induced psychosis in Parkinson’s Disease. N Engl J Med 340(10):757–763
Parrott AC (2002) Recreational ecstasy/MDMA, the serotonin syndrome, and serotonergic neurotoxicity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71(4):837–844
Pinna A, Ko WKD, Costa G, Tronci E, Fidalgo C, Simola N, Morelli M (2016) Antidyskinetic effect of A2A and 5HT1A/1B receptor ligands in two animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 31(4):501–511
Politis M, Wu K, Loane C, Kiferle L, Molloy S, Brooks DJ, Piccini P (2010) Staging of serotonergic dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease : an in vivo PET study C-DASB. Neurobiol Dis 40(1):216–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.05.028
Politis M, Wu K, Loane C, Brooks DJ, Kiferle L, Turkheimer FE, Piccini P (2014) Serotonergic mechanisms responsible for levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease patients. J Clin Invest 124(3):1340–1349
Pompeiano M, Palacious JM, Mengod G (1992) Distribution and cellular localization of mRNA coding for5HT1A receptor in the rat brain: correlation with receptor binding. J Neurosci 12(2):1992
Pompeiano M, Palacious JM, Mengod G (1994) Distribution of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptor family mRNAs, comparison between 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. Mol Brain Res 23:163–178
Rampello L, Chiechio S, Raffaele R, Vecchio I, Nicoletti F (2002) The SSRI, citalopram, improves bradykinesia in patients with Parkinson’s Disease treated with l-Dopa. Clin Neuropharmacol 25(1):21–24
Rascol O, Damier P, Goetz CG et al (2006) A large phase III study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of sarizotan in the treatment of l-dopa-induced-dyskinesia associated with PD: the Paddy-1 study. Mov Disord 21(Suppl 15):S492–S493
Reddy S, Factor SA, Molho ES, Feustel PJ (2002) The effect of quetiapine on psychosis and motor function in parkinsonian patients with and without dementia. Mov Disord 17(4):676–681
Riahi G, Morissette M, Samadi P, Parent M, Di Paolo T (2013) Basal ganglia serotonin 1B receptors in parkinsonian monkeys with l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Biochem Pharmacol 86:970–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.08.005
Roberts C (2006) ACP-103, a 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonist. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7:653–660
Roth BL (2011) 5-HT2A Serotonin Receptor Biology Interacting proteins, kinases, and paradoxical regulation. Neuropharmacology 61(3):348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.012.5-HT
Rothman RB, Clark RD, Partilla JS, Baumann MH (2003) (+)-Fenfluramine and Its major metabolite, (+)-norfenfluramine, are potent substrates for norepinephrine transporters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305(3):1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.103.049684.and
Roussakis AA, Politis M, Towey D, Piccini P (2016) Serotonin-to-dopamine transporter ratios in Parkinson disease relevance for dyskinesias. Neurology 86(12):1152–1158
Rudnick G (2006) Structure/function relationships in serotonin transporter: new insights from the structure of a bacterial transporter. In: Sitte HH, Freissmuth M (eds) Neurotransmitter transporters. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, vol 175. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 59–73
Rylander D, Parent M, Sullivan SSO, Dovero S, Lees AJ, Bezard E, Cenci MA (2010) Maladaptive plasticity of serotonin axon terminals in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22097
Sari Y, Miquel M, Brisorgueil M, Ruiz G, Doucet E, Hamon M, Verge D (1999) Cellular and subcellular localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B receptors in the rat central nervous system: immunocytochemical, autoradiographic and lesion studies. Neuroscience 88(3):899–915
Schipper J, Tulp MTM, Sijbesma H (1990) Neurochemical profile of eltoprazine.pdf. Drug Metab Drug Interact 8(1–2):85–114
Schlicker E, Werner U, Nickel B, Hamon M, Gozlan H, Nickel B, Gothert M (1992) Anpirtoline, a novel, highly potent 5HT1B receptor agonist with antinociceptive/antidepressant-like actions in rodent. Brit J Pharmacol 105:732–738
Shi WX, Nathaniel P, Bunney BS (1995) Ritanserin, a 5-HT2A/2C antagonist, reverses direct dopamine agonist-induced inhibition of midbrain dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274(2):735–740
Stahl SM (1998) Mechanism of action of serotonin selective reuptake inhibitors Serotonin receptors and pathways mediate therapeutic effects and side effects. J Affect Disorders 51:215–235
Stahl SM (2016) Mechanism of action of pimavanserin in Parkinson’ s disease psychosis : targeting serotonin 5HT2A and 5HT2C receptors. CNS Spectr 21:271–275. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1092852916000407
Strecker K, Wegner F, Hesse S, Becker G-A, Patt M, Meyer P, Sabri O (2011) Preserved serotonin transporter binding in de novo Parkinson’ s disease: negative correlation with the dopamine transporter. J Neurol 258:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5666-5
Svenningsson P, Rosenblad C, Arvidsson KE, Wictorin K, Keywood C, Shankar B, Widner H (2015) Eltoprazine counteracts l-DOPA-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease: a dose-finding study. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu409
Tahar AH, Belanger N, Bangassoro E, Gregoire L, Bedard PJ (2000) Antidyskinetic effect of JL-18, a clozapine analog, in parkinsonian monkeys. Eur J Pharmacol 399:183–186
Tatsumi M, Groshan K, Blakely RD, Richelson E (1997) Pharmacological profile of antidepressants and related compounds at human monoamine transporters. Eur J Pharmacol 340:249–258
Taylor JL, Bishop C, Ullrich T, Rice KC, Walker PD (2006) Serotonin 2A receptor antagonist treatment reduces dopamine D1 receptor-mediated rotational behavior but not l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements in the unilateral dopamine-depleted rat. Neuropharmacology 50:761–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.12.004
Tronci E, Fidalgo C, Stancampiano R, Carta M (2015) Effect of selective and non-selective serotonin receptor activation on l-DOPA-induced therapeutic efficacy and dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats. Behav Brain Res 292:300–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.06.034
van de Vijver D, Roos R, Jansen P, Porsius A, de Boer A (2002) Start of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and increase of antiparkinsonian drug treatment in patients on levodopa. Brit J Clin Pharmacol 54:168–170
Vanover KE, Betz AJ, Weber SM, Bibbiani F, Kielaite A, Weiner DM, Salamone JD (2008) A 5-HT 2A receptor inverse agonist, ACP-103, reduces tremor in a rat model and levodopa-induced dyskinesias in a monkey model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90:540–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.04.010
Varnas K, Bonaventure P, Sedvall G (2001) Autoradiographic mapping of 5-HT 1B and 5-HT 1D receptors in the post mortem human brain using [3 H] GR 125743. Brain Res 915:47–57
Verrico CD, Miller GM, Madras BK (2007) MDMA (Ecstasy) and human dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin transporters: implications for MDMA-induced neurotoxicity and treatment. Psychopharmacology 189(4):489–503
Visanji NP, Gomez-ramirez J, Johnston TH, Pires D, Voon V, Brotchie JM, Fox SH (2006) Pharmacological characterization of psychosis-like behavior in the MPTP-lesioned nonhuman primate model of Parkinson’ s Disease. Movement Disord 21(11):1879–1891. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21073
Yahr MD, Duvoisin RC, Schear MJ, Barrett RE, Hoehn MM (1969) Treatment of Parkinsonism with levodopa. Arch Neurol (Chic) 21:343–354
Yamato H, Kannari K, Shen H, Suda T, Matsunaga M (2000) Fluoxetine reduces l-DOPA-derived extracellular DA in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat striatum. NeuroReport 12(68):1123–1126
Yoshida K, Sugita T, Higuchil H, Hishikawa Y (1998) Effect of tandospirone on tardive dyskinesia and parkinsonian symptoms. Eur Pschiatry 13(8):421–422
Zhang X, Andren PE, Greengard P, Svenningsson P (2007) Evidence for a role of the 5-HT1B receptor and its adaptor protein, p11, in l-DOPA treatment of an animal model of Parkinsonism. Proc Nat Acad Sci 105(6):2163–2168
Acknowledgements
Thank you to Carolyn Saito for her constructive feedback on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lanza, K., Bishop, C. Serotonergic targets for the treatment of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J Neural Transm 125, 1203–1216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1837-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1837-1