Abstract
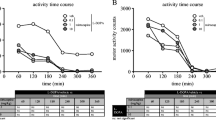
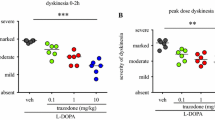
Virtually every patient affected by Parkinson’s disease (PD) eventually requires treatment with l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA), which leads to complications such as dyskinesia and psychosis. Whereas blockade of serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptors appears to be an effective way to reduce both dyskinesia and psychosis, whether it has the potential to eliminate the two phenomena remains to be determined. In a previous study, we showed that highly selective 5-HT2A receptor blockade with EMD-281,014, at plasma levels comparable to those achieved in the clinic, reduced dyskinesia and psychosis-like behaviours (PLBs), in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-lesioned marmoset. Here, we sought to determine whether further increasing the dose would result in greater therapeutic benefit or if maximal effectiveness was achieved at lower doses. Six MPTP-lesioned marmosets with stable dyskinesia and PLBs were administered EMD-281,014 (0.1, 1 and 10 mg/kg) or vehicle in combination with l-DOPA and the effect on dyskinesia, PLBs and parkinsonism was assessed. Administration of EMD-281,014 (0.1, 1 and 10 mg/kg) in combination with l-DOPA resulted in a significant reduction in the severity of dyskinesia, by up to 63%, 64% and 61% (each P < 0.001), when compared to l-DOPA/vehicle. Similarly, the addition of EMD-281,014 (0.1, 1 and 10 mg/kg) to l-DOPA also significantly decreased the severity of PLBs, by up to 54%, 55% and 53% (each P < 0.001), when compared to l-DOPA/vehicle. Our results suggest that there might be a ceiling to the reduction of dyskinesia and psychosis that can be achieved through antagonism of 5-HT2A receptors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartoszyk GD, van Amsterdam C, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA (2003) EMD 281014, a new selective serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 473:229–230
Bhattacharyya S, Raote I, Bhattacharya A, Miledi R, Panicker MM (2006) Activation, internalization, and recycling of the serotonin 2A receptor by dopamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15248–15253. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606578103
Connolly BS, Lang AE (2014) Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 311:1670–1683
Cummings J, Isaacson S, Mills R et al (2014) Pimavanserin for patients with Parkinson’s disease psychosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 383:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62106-6
Durif F, Debilly B, Galitzky M et al (2004) Clozapine improves dyskinesias in Parkinson disease: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology 62:381–388
Fox SH, Visanji N, Reyes G, Huot P, Gomez-Ramirez J, Johnston T, Brotchie JM (2010) Neuropsychiatric behaviors in the MPTP marmoset model of Parkinson’s disease. Can J Neurol Sci 37:86–95
Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Lim SY et al (2011) The Movement Disorder Society evidence-based medicine review update: treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26(Suppl 3):S2–S41
French Clozapine Parkinson Study Group (1999) Clozapine in drug-induced psychosis in Parkinson’s disease. The French Clozapine Parkinson Study Group. Lancet 353:2041–2042
Frouni I, Kwan C, Bedard D et al (2018) Effect of the selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonist EMD-281,014 on l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat. Exp Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5390-4
Goetz CG, Damier P, Hicking C et al (2007) Sarizotan as a treatment for dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mov Disord 22:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21226
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Veyres N et al (2017) The effect of mirtazapine on dopaminergic psychosis and dyskinesia in the parkinsonian marmoset. Psychopharmacology 234:905–911
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Bedard D, Gaudette F, Beaudry F, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018a) The highly selective 5-HT2A antagonist EMD-281,014 reduces dyskinesia and psychosis in the l-DOPA-treated parkinsonian marmoset. Neuropharmacology 139:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.06.038
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018b) The effect of mianserin on the severity of psychosis and dyskinesia in the parkinsonian marmoset. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 81:367–371
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018c) Trazodone alleviates both dyskinesia and psychosis in the parkinsonian marmoset model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna)125(9):1355–1360
Hely MA, Morris JG, Traficante R, Reid WG, O’Sullivan DJ, Williamson PM (1999) The sydney multicentre study of Parkinson’s disease: progression and mortality at 10 years. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:300–307
Hely MA, Morris JG, Reid WG, Trafficante R (2005) Sydney Multicenter Study of Parkinson’s disease: non-l-dopa-responsive problems dominate at 15 years. Mov Disord 20:190–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20324
Howell DC (2011) Fundamental statistics for the behavioral sciences. Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Belmont
Huot P, Johnston TH, Darr T et al (2010) Increased 5-HT2A receptors in the temporal cortex of parkinsonian patients with visual hallucinations. Mov Disord 25:1399–1408
Huot P, Johnston TH, Lewis KD et al (2011) Characterization of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) enantiomers in vitro and in the MPTP-lesioned primate: R-MDMA reduces severity of dyskinesia, whereas S-MDMA extends duration of ON-time. J Neurosci 31:7190–7198. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1171-11.2011
Huot P, Johnston TH, Winkelmolen L, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2012) 5-HT2A receptor levels increase in MPTP-lesioned macaques treated chronically with l-DOPA. Neurobiol Aging 33:194 e195-115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.04.035
Huot P, Johnston TH, Lewis KD et al (2014) UWA-121, a mixed dopamine and serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, enhances l-DOPA anti-parkinsonian action without worsening dyskinesia or psychosis-like behaviours in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset. Neuropharmacology 82:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.012
Iravani MM, Tayarani-Binazir K, Chu WB, Jackson MJ, Jenner P (2006) In 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated primates, the selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1a agonist (R)-(+)-8-OHDPAT inhibits levodopa-induced dyskinesia but only with\ increased motor disability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.110429
Maertens de Noordhout A, Delwaide PJ (1986) Open pilot trial of ritanserin in parkinsonism. Clin Neuropharmacol 9:480–484
Mamo D, Sedman E, Tillner J, Sellers EM, Romach MK, Kapur S (2004) EMD 281014, a specific and potent 5HT2 antagonist in humans: a dose-finding PET study. Psychopharmacology 175:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1817-7
Meco G, Marini S, Linfante I, Modarelli F, Agnoli A (1988) Controlled single-blind crossover study of ritanserin and placebo in l-dopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Ther Res 43:262–270
Nash JF, Roth BL, Brodkin JD, Nichols DE, Gudelsky GA (1994) Effect of the R(−) and S(+) isomers of MDA and MDMA on phosphatidyl inositol turnover in cultured cells expressing 5-HT2A or 5-HT2C receptors. Neurosci Lett 177:111–115
Parkinson Study Group (1999) Low-dose clozapine for the treatment of drug-induced psychosis in Parkinson’s disease. The Parkinson Study Group. N Engl J Med 340:757–763
Riahi G, Morissette M, Parent M, Di Paolo T (2011) Brain 5-HT(2A) receptors in MPTP monkeys and levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Eur J Neurosci 33:1823–1831. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07675.x
Roberts C (2006) ACP-103, a 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonist. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7:653–660
Taylor JL, Bishop C, Ullrich T, Rice KC, Walker PD (2006) Serotonin 2A receptor antagonist treatment reduces dopamine D1 receptor-mediated rotational behavior but not l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements in the unilateral dopamine-depleted rat. Neuropharmacology 50:761–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.12.004
Vanover KE, Weiner DM, Makhay M et al (2006) Pharmacological and behavioral profile of N-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-N-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-N′-(4-(2-methylpropylo xy)phenylmethyl) carbamide (2R,3R)-dihydroxybutanedioate (2:1) (ACP-103), a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptor inverse agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:910–918. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.105.097006
Vanover KE, Betz AJ, Weber SM et al (2008) A 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonist, ACP-103, reduces tremor in a rat model and levodopa-induced dyskinesias in a monkey model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90:540–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.04.010
Veyres N, Hamadjida A, Huot P (2018) Predictive value of parkinsonian primates in pharmacologic studies: a comparison between the macaque, marmoset, and squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 365:379–397. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.117.247171
Acknowledgements
PH has research support from Parkinson Canada, Fonds de Recherche Québec—Santé, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Michael J Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research and the Weston Brain Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest. PH has received payments from UCB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwan, C., Frouni, I., Bédard, D. et al. 5-HT2A blockade for dyskinesia and psychosis in Parkinson’s disease: is there a limit to the efficacy of this approach? A study in the MPTP-lesioned marmoset and a literature mini-review. Exp Brain Res 237, 435–442 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5434-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5434-9