Abstract
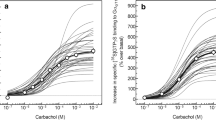
Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G-proteins) play a pivotal role in a wide range of signal transduction pathways, and receptor/G-protein coupling has been implicated in the pathophysiology of mental disorders. In this study, guanosine-5′-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate ([35S]GTPγS) binding/immunoprecipitation assay for Gαq was applied to postmortem human brains. After its optimization for human prefrontal cortical membranes, we selected 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and carbachol as efficient agonists for subsequent experiments. The concentration–response curve of 5-HT shifted towards the right by the addition of increasing concentrations of ketanserin (with a pA 2 value of 9.18), indicating the involvement of the 5-HT2A receptor. Besides, the carbachol-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding to Gαq was competitively antagonized by telenzepine (with a pA 2 value of 8.81), indicating the involvement of the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR). Concentration–response curves of 5-HT2A receptor- and M1 mAChR-mediated Gαq activation were determined in 40 subjects. The mean maximum percentage increase (%E max) was 155 and 470%, respectively, and the mean half-maximal effect concentration (EC50) was 131 nM and 15.2 µM, respectively. When the pharmacological parameters were correlated with age, postmortem delay, freezing storage period, and tissue pH, no statistically significant correlation was observed except for the negative correlation between age and %E max value of carbachol-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding to Gαq. The %E max values for 5-HT2A receptor- and M1 mAChR-mediated Gαq activation also tended to correlate with each other. These results provide fundamental information of Gαq-coupled 5-HT2A receptor and M1 mAChR in native human brains, and lay the foundation for future studies in mental disorder patients.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akam EC, Challis RAJ, Nahorski SR (2001) Gq/11 and Gi/o activation profiles in CHO cells expressing human muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: dependence on agonist as well as receptor-subtype. Br J Pharmacol 132:950–958. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703892
Ayyagari PV, Gerber M, Joseph JA, Crews FT (1998) Uncoupling of muscarinic cholinergic phosphoinositide signals in senescent cerebral cortical and hippocampal membranes. Neurochem Int 32:107–115
Biver F, Lotstra F, Monclus M, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Mendlewicz J, Goldman S (1996) Sex difference in 5HT2 receptor in the living human brain. Neurosci Lett 204:25–28
Büyükuysal RL, Ulus IH, Kiran BK (1998) Age-related alterations in pre-synaptic and receptor-mediated cholinergic functions in rat brain. Neurochem Res 23:719–726
Catapano LA, Manji HK (2007) G protein-coupled receptors in major psychiatric disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:976–993. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.09.025
Cosgrove KP, Mazure CM, Staley JK (2007) Evolving knowledge of sex differences in brain structure, function, and chemistry. Biol Psychiatry 62:847–855. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.03.001
Dean B (2001) A predicted cortical serotonergic/cholinergic/GABAergic interface as a site of pathology in schizophrenia. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28:74–78
Dean B, McLeod M, Keriakous D, McKenzie J, Scarr E (2002) Decreased muscarinic1 receptors in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 7:1083–1091. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001199
Decker MW (1987) The effects of aging on hippocampal and cortical projections of the forebrain cholinergic system. Brain Res Rev 12:423–438
DeLapp NW, McKinzie JH, Sawyer BD, Vandergriff A, Falcone J, McClure D, Felder CC (1999) Determination of [35S]guanosine-5′-O-(3-thio)triphosphate binding mediated by cholinergic muscarinic receptors in membranes from Chinese hamster ovary cells and rat striatum using an anti-G protein scintillation proximity assay. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:946–955
Dewey SL, Volkow ND, Logan J, MacGregor RR, Fowler JS, Schlyer DJ, Bendriem B (1990) Age-related decreases in muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding in the human brain measured with positron emission tomography (PET). J Neurosci Res 27:569–575. doi:10.1002/jnr.490270418
Felder CC (1995) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: signal transduction through multiple effectors. FASEB J 9:619–625
Friedman E, Wang H-Y (1996) Receptor-mediated activation of G proteins is increased in postmortem brains of bipolar affective disorder subjects. J Neurochem 67:1145–1152
Gibbons AS, Scarr E, McLean C, Sundram S, Dean B (2009) Decreased muscarinic receptor binding in the frontal cortex of bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder subjects. J Affect Disord 116:184–191. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2008.11.015
Giulietti M, Vivenzio V, Piva F, Principato G, Bellantuono C, Nardi B (2014) How much do we know about the coupling of G-proteins to serotonin receptors? Mol Brain 7:49. doi:10.1186/s13041-014-0049-y
Greenwood AF, Powers RE, Jope RS (1995) Phosphoinositide hydrolysis, Gαq, phospholipase C, and protein kinase C in post mortem human brain: effects of post mortem interval, subject age, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 69:125–138
Gross-Isseroff R, Salama D, Israeli M, Biegon A (1990) Autoradiographic analysis of age-dependent changes in serotonin 5-HT2 receptors of the human brain postmortem. Brain Res 519:223–227
Guerram M, Zhang LY, Jiang ZZ (2016) G-protein coupled receptors as therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular diseases. Neurochem Int 101:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2016.09.005
Hashimoto E, Ozawa H, Saito T, Gsell W, Takahata N, Riederer P, Frölich L (2004) Impairment of Gsα function in human brain cortex of Alzheimer’s disease: comparison with normal aging. J Neural Transm 111:311–322. doi:10.1007/s00702-003-0089-4
Hellström-Lindahl E, Winblad B, Nordberg A (1993) Muscarinic and nicotinic receptor changes in the cortex and thalamus of brains of chronic alcoholics. Brain Res 620:42–48
Kang K, Huang XF, Wang Q, Deng C (2009) Decreased density of serotonin 2A receptors in the superior temporal gyrus in schizophrenia—a postmortem study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:867–871. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.04.010
Knight AR, Misra A, Quirk K, Benwell K, Revell D, Kennett G, Bickerdike M (2004) Pharmacological characterization of the agonist radioligand binding site of 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 370:114–123. doi:10.1007/s00210-004-0951-4
Li X, Greenwood AF, Powers R, Jope RS (1996) Effects of postmortem interval, age, and Alzheimer’s disease on G-proteins in human brain. Neurobiol Aging 17:115–122
Mailleux P, Mitchell F, Vanderhaeghen JJ, Milligan G, Erneux C (1992) Immunohistochemical distribution of neurons containing the G-proteins Gqα/G11α in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 51:311–316
Mannoury la Cour C, Vidal S, Pasteau V, Cussac D, Millan MJ (2007) Dopamine D1 receptor coupling to Gs/olf and Gq in rat striatum and cortex: a scintillation proximity assay (SPA)/antibody-capture characterization of benzazepine agonists. Neuropharmacology 52:1003–1014. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.10.021
Marcusson JO, Morgan DG, Winblad B, Finch CE (1984) Serotonin-2 binding sites in human frontal cortex and hippocampus. Selective loss of S-2A sites with age. Brain Res 311:51–56
Mash DC, Potter LT (1986) Autoradiographic localization of M1 and M2 muscarine receptors in the rat brain. Neuroscience 19:551–564
Mengod G, Vilaró MT, Raurich A, López-Giménez JF, Cortés R, Palacios JM (1996) 5-HT receptors in mammalian brain: receptor autoradiography and in situ hybridization studies of new ligands and newly identified receptors. Histochem J 28:747–758
Michelotti GA, Price DT, Schwinn DA (2000) α1-Adrenergic receptor regulation: basic science and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther 88:281–309
Millan MJ, Rivet J-M, Gobert A (2016) The frontal cortex as a network hub controlling mood and cognition: probing its neurochemical substrates for improved therapy of psychiatric and neurological disorders. J Psychopharmacol 30:1099–1128. doi:10.1177/0269881116672342
Muguruza C, Moreno JL, Umali A, Callado LF, Meana JJ, González-Maeso J (2013) Dysregulated 5-HT2A receptor binding in postmortem frontal cortex of schizophrenic subjects. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23:852–864. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.10.006
Norbury R, Travis MJ, Erlandsson K, Waddington W, Owens J, Pimlott S, Ell PJ, Murphy DG (2005) In vivo imaging of muscarinic receptors in the aging female brain with (R, R)[123I]-I-QNB and single photon emission tomography. Exp Gerontol 40:137–145. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2004.10.002
Nordberg A, Alafuzoff I, Winblad B (1992) Nicotinic and muscarinic subtypes in the human brain: changes with aging and dementia. J Neurosci Res 31:103–111. doi:10.1002/jnr.490310115
Odagaki Y, Toyoshima R (2012) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated activation of Gq in rat brain membranes determined by guanosine-5′-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate ([35S]GTPγS) binding using an anti-G protein scintillation proximity assay. J Neural Transm 119:525–532. doi:10.1007/s00702-011-0742-2
Odagaki Y, Toyoshima R (2013) Activation of Gq proteins coupled with 5-HT2 receptors in rat cerebral cortical membranes assessed by antibody-capture scintillation proximity assay (SPA)/[35S]GTPγS binding. Pharmacology 92:2–10. doi:10.1159/000351745
Odagaki Y, Kinoshita M, Toyoshima R (2013) Pharmacological characterization of M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated Gq activation in rat cerebral cortical and hippocampal membranes. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 386:937–947. doi:10.1007/s00210-013-0887-7
Odagaki Y, Kinoshita M, Toyoshima R (2014) Functional activation of Gαq via serotonin2A (5-HT2A) and muscarinic acetylcholine M1 receptors assessed by guanosine-5′-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate ([35S]GTPγS) binding/immunoprecipitation in rat brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 726:109–115. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.040
Odagaki Y, Kinoshita M, Ota T, Meana JJ, Callado LF, García-Sevilla JA (2015) Adenosine A1 receptors are selectively coupled to Gαi-3 in postmortem human brain cortex: guanosine-5′-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate ([35S]GTPγS) binding/immunoprecipitation study. Eur J Pharmacol 764:592–598. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.07.049
Overk CR, Felder CC, Tu Y, Schober DA, Bales KR, Wuu J, Mufson EJ (2010) Cortical M1 receptor concentration increases without a concomitant change in function in Alzheimer’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 40:63–70. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2010.03.005
Rashid AJ, So CH, Kong MM, Furtak T, El-Ghundi M, Cheng R, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2007) D1-D2 dopamine receptor heterooligomers with unique pharmacology are coupled to rapid activation of Gq/11 in the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:654–659. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604049104
Rinne JO (1987) Muscarinic and dopaminergic receptors in the aging human brain. Brain Res 404:162–168
Salah-Uddin H, Thomas DR, Davies CH, Hagan JJ, Wood MD, Watson JM, Challiss RAJ (2008) Pharmacological assessment of M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-Gq/11 protein coupling in membranes prepared from postmortem human brain tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325:869–874. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.137968
Salah-Uddin H, Scarr E, Pavey G, Harris K, Hagan JJ, Dean B, Challiss RAJ, Watson JM (2009) Altered M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (CHRM1)-Gαq/11 coupling in a schizophrenia endophenotype. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2156–2166. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.41
Schudt C, Boer R, Eltze M, Riedel R, Grundler G, Birdsall NJM (1989) The affinity, selectivity and biological activity of telenzepine enantiomers. Eur J Pharmacol 165:87–96
Tsang SW, Lai MK, Kirvell S, Francis PT, Esiri MM, Hope T, Chen CP, Wong PT (2006) Impaired coupling of muscarinic M1 receptors to G-proteins in the neocortex is associated with severity of dementia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:1216–1223. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.07.010
Versijpt J, Van Laere KJ, Dumont F, Decoo D, Vandecapelle M, Santens P, Goethals I, Audenaert K, Slegers G, Dierckx RA, Korf J (2003) Imaging of the 5-HT2A system: age-, gender-, and Alzheimer’s disease-related findings. Neurobiol Aging 24:553–561
White P, Hiley CR, Goodhardt MJ, Carrasco LH, Keet JP, Williams IE, Bowen DM (1977) Neocortical cholinergic neurons in elderly people. Lancet 8013:668–671
Wong DF, Wagner HN Jr, Dannals RF, Links JM, Frost JJ, Ravert HT, Wilson AA, Rosenbaum AE, Gjedde A, Douglass KH, Petronis JD, Folstein MF, Toung JKT, Burns HD, Kuhar MJ (1984) Effects of age on dopamine and serotonin receptors measured by positron tomography in the living human brain. Science 226:1393–1396
Yoshida T, Kuwabara Y, Sasaki M, Fukumura T, Ichimiya A, Takita M, Ogomori K, Ichiya Y, Masuda K (2000) Sex-related differences in the muscarinic acetylcholinergic receptor in the healthy human brain—a positron emission tomography study. Ann Nucl Med 14:97–101
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Saitama Medical University Internal Grant 26B-1-12 and 16-B-1-11 to YO, the Spanish MINECO-FEDER (SAF 2009-08460, SAF 2013-48586-R, and SAF 2011-29918 to JJM, LFC and JAG-S, respectively), and the Basque Government (IT-616-13). We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odagaki, Y., Kinoshita, M., Ota, T. et al. Functional activation of Gαq coupled to 5-HT2A receptor and M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in postmortem human cortical membranes. J Neural Transm 124, 1123–1133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1749-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1749-0