Abstract
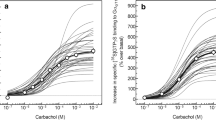
This study aimed to pharmacologically characterize the response derived from functional activation of Gq proteins coupled with native muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Rat cerebral cortical and hippocampal membranes were prepared, and the effects of a range of mAChR agonists and antagonists, allosteric modulators, and muscarinic toxins were determined by an antibody-capture scintillation proximity assay combined with [35S]GTPγS binding, using the anti-Gαq antibody sc-393. Increased specific [35S]GTPγS binding, elicited by carbachol (CCh), was selectively inhibited by the muscarinic toxin MT7, and was resistant to membrane pretreatment with N-ethylmaleimide, indicating that the response derived exclusively from Gαq, selectively coupled with the M1 mAChR. In addition to CCh, many mAChR agonists, including oxotremorine, arecholine, and methacholine, stimulated binding in a concentration-dependent manner with varied potencies and efficacies. The intrinsic activities of partial M1 mAChR agonists in the present study were generally lower than previously reported in M1-expressing cells. Xanomeline and N-desmethylclozapine had negligible or minimal agonist properties. CCh-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding to Gαq was inhibited by mAChR antagonists, including scopolamine, ipratropium, atropine, 4-DAMP, pirenzepine, and AF-DX 116, with a rank order of potency consistent with previous studies of M1-expressing cells. There was a highly significant correlation between the potencies of 13 agonists and 19 antagonists in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. The effects of several allosteric mAChR modulators were also investigated. These data provide a comprehensive pharmacological profile of the Gq-coupled M1 mAChR subtype natively expressed at physiological levels in rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adem A, Mohammed AK, Winblad B (1990) Multiple effects of tetrahydroaminoacridine on the cholinergic system: biochemical and behavioural aspects. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect 2:113–128
Birdsall NJ, Farries T, Gharagozloo P, Kobayashi S, Lazareno S, Sugimoto M (1999) Subtype-selective positive cooperative interactions between brucine analogs and acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors: functional studies. Mol Pharmacol 55:778–786
Bradley KN, Rowan EG, Harvey AL (2003) Effects of muscarinic toxins MT2 and MT7, from green mamaba venom, on m1, m3 and m5 muscarinic receptors expressed in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells. Toxicon 41:207–215
Buckley NJ, Bonner TI, Buckley CM, Brann MR (1989) Antagonist binding properties of five cloned muscarinic receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Mol Pharmacol 35:469–476
Burstein ES, Spalding TA, Brann MR (1997) Pharmacology of muscarinic receptor subtypes constitutively activated by G proteins. Mol Pharmacol 51:312–319
Bymaster FP, Whitesitt CA, Shannon HE, DeLapp N, Ward JS, Calligaro DO, Shipley LA, Buelde-Sam JL, Bodick NC, Farde L, Sheardown MJ, Olesen PH, Hansen KT, Suzdak PD, Swedberg MD, Sauerberg P, Mitch CH (1997) Xanomeline: a selective muscarinic agonist for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev Res 40:158–170
Bymaster FP, Carter PA, Peters SC, Zhang W, Ward JS, Mitch CH, Calligaro DO, Whitesitt CA, DeLapp N, Shannon HE, Rimvall K, Jeppesen L, Sheardown MJ, Fink-Jensen A, Sauerger P (1998) Xanomeline compared to other muscarinic agents on stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in vivo and other cholinomimetic effects. Brain Res 795:179–190
Caulfield MP, Birdsall NJ (1998) International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 50:279–290
Clark AL, Mitchelson F (1976) The inhibitory effect of gallamine on muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol 58:323–331
Conn PJ, Jones CK, Lindsley CW (2009) Subtype-selective allosteric modulators of muscarinic receptors for the treatment of CNS disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:148–155. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2008.12.002
Davies MA, Compton-Toth BA, Hufeisen SJ, Meltzer HY, Roth BL (2005) The highly efficacious actions of N-desmethylclozapine at muscarinic receptors are unique and not a common property of either typical or atypical antipsychotic drugs: is M1 agonism a pre-requisite for mimicking clozapine’s actions? Psychopharmacology 178:451–460. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-2017-1
Digby GJ, Noetzel MJ, Bubser M, Utley TJ, Walker AG, Byun NE, Lebois EP, Xiang Z, Sheffler DJ, Cho HP, Davis AA, Nemirovsky NE, Mennenga SE, Camp BW, Bimonte-Nelson HA, Bode J, Italiano K, Lindsley CW, Jones CK, Conn PJ (2012a) Novel allosteric agonists of M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors induce brain-specific responses that correspond with behavioral effects in animal models. J Neurosci 32:8532–8544. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0337-12.2012
Digby GJ, Utley TJ, Lamsal A, Sevel C, Sheffler DJ, Lebois EP, Bridges TM, Wood MR, Niswender CM, Lindsley CW, Conn PJ (2012b) Chemical modification of the M1 agonist VU0364572 reveals molecular switches in pharmacology and a bitopic biding mode. ACS Chem Neurosci 3:1025–1036. doi:10.1021/cn300103e
Dong GZ, Kameyama K, Rinken A, Haga T (1995) Ligand binding properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes (m1–m5) expressed in baculovirus-infected insect cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:378–384
Doods H, Entzeroth M, Mayer N (1991) Cardioselectivity of AQ-RA 741, a novel tricyclic antimuscarinic drug. Eur J Pharmacol 192:147–152
Doods HN, Entzeroth M, Ziegler H, Mayer N, Holzer P (1994) Pharmacological profile of selective muscarinic receptor antagonists on guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 253:275–281
Dörje F, Wess J, Lambrecht G, Tacke R, Mutschler E, Brann MR (1991) Antagonists binding profiles of five cloned human muscarinic receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:727–733
Eglen RM (2005) Muscarinic receptor subtype pharmacology and physiology. Prog Med Chem 43:105–136. doi:10.1016/S0079-6468(05)43004-0
Galvan M, Boer R, Schudt C (1989) Interaction of telenzepine with muscarinic receptors in mammalian sympathetic ganglia. Eur J Pharmacol 167:1–10
Gregory KJ, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A (2007) Allosteric modulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Curr Neuropharmacol 5:157–167
Hammer R, Giraldo E, Schiavi GB, Monferini E, Ladinsky H (1986) Binding profile of a novel cardioselective muscarine receptor antagonist, AF-DX 116, to membranes of peripheral tissues and brain in the rat. Life Sci 38:1653–1662
Heinrich JN, Butera JA, Carrick T, Kramer A, Kowal D, Lock T, Marquis KL, Pausch MH, Popiolek M, Sun SC, Tseng E, Uveges AJ, Mayer SC (2009) Pharmacological comparison of muscarinic ligands: historical versus more recent muscarinic M1-preferring receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 605:53–56. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.12.044
Hunter AJ, Murray TK, Jones JA, Cross AJ, Green AR (1989) The cholinergic pharmacology of tetrahydroaminoacridine in vivo and in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 98:79–86
Lameh J, Burstein ES, Taylor E, Weiner DM, Vanover KE, Bonhaus DW (2007) Pharmacology of N-desmethylclozapine. Pharmacol Ther 115:223–231. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.05.004
Lazareno S, Birdsall NJ (1993) Pharmacological characterization of acetylcholine-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding mediated by human muscarinic m1–m4 receptors: antagonist studies. Br J Pharmacol 109:1120–1127
Lazareno S, Farries T, Birdsall NJ (1993) Pharmacological characterization of guanine nucleotide exchange reactions in membranes from CHO cells stably transfected with human muscarinic receptors M1–M4. Life Sci 52:449–456
Lazareno S, Gharagozloo P, Kuonen D, Popham A, Birdsall NJ (1998) Subtype-selective positive cooperative interactions between brucine analogues and acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors: radioligand binding studies. Mol Pharmacol 53:573–589
Lazareno S, Popham A, Birdsall NJ (2000) Allosteric interactions of staurosporine and other indolocarbazoles with N-[methyl-3H]scopolamine and acetylcholine at muscarinic receptor subtypes: identification of a second allosteric site. Mol Pharmacol 58:194–207
Lazareno S, Doležal V, Popham A, Birdsall NJ (2004) Thiochrome enhances acetylcholine affinity at muscarinic M4 receptors: receptor subtype selectivity via cooperativity rather than affinity. Mol Pharmacol 65:257–266
Lebois EP, Bridges TM, Lewis LM, Dawson ES, Kane AS, Xiang Z, Jadhav SB, Yin H, Kennedy JP, Meiler J, Niswender CM, Jones CK, Conn PJ, Weaver CD, Lindsley CW (2010) Discovery and characterization of novel subtype-selective allosteric agonists for the investigation of M1 receptor function in the central nervous system. ACS Chem Neurosci 1:104–121. doi:10.1021/cn900003h
Levey AI, Kitt CA, Simonds WF, Price DL, Brann MR (1991) Identification and localization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor proteins in brain with subtype-specific antibodies. J Neurosci 11:3218–3226
Levey AI, Edmunds M, Heilman CJ, Desmond TJ, Frey KA (1994) Localization of muscarinic m3 receptor protein and M3 receptor binding in rat brain. Neuroscience 63:207–221
Mario JE, Niswender CM, Days EL, Bridges TM, Xiang Y, Rodriguez AL, Shirey JK, Brady AE, Nalywajko T, Luo Q, Austin CA, Williams MB, Kim K, Williams R, Orton D, Brown HA, Lindsley CW, Weaver CD, Conn PJ (2009) Discovery and characterization of novel allosteric potentiators of M1 muscarinic receptors reveals multiple modes of activity. Mol Pharmacol 75:577–588. doi:10.1124/mol.108.052886
Michel AD, Delmendo RE, Lopez M, Whiting RL (1990) On the interaction of gallamine with muscarinic receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol 182:335–345
Moriya H, Takagi Y, Nakanishi T, Hayashi M, Tani T, Hirotsu I (1999) Affinity profiles of various muscarinic antagonists for cloned human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) subtypes and mAChRs in rat heart and submandibular gland. Life Sci 64:2351–2358
Mose U, Lambrecht M, Wess WJ, Mutschler E (1989) Structure-activity relationships of new analogues of arecaidine propargyl ester at muscarinic M1 and M2 receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol 96:319–324
Odagaki Y, Toyoshima R (2012) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated activation of Gq in rat brain membranes determined by guanosine-5′-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate ([35S]GTPγS) binding using an anti-G protein scintillation proximity assay. J Neural Transm 119:525–532. doi:10.1007/s00702-011-0742-2
Odagaki Y, Kinoshita M, Toyoshima R (2011) Functional coupling between metabotropic glutamate receptors and G-proteins in rat cerebral cortex assessed by guanosine-5′-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate binding assay. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109:175–185. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00705.x
Olianas MC, Maullu C, Adem A, Mulugeta E, Karlsson E, Onali P (2000) Inhibition of acetylcholine muscarinic M1 receptor function by the M1-selective ligand muscarinic toxin 7 (MT-7). Br J Pharmacol 131:447–452
Pearce BD, Potter LT (1988) Effects of tetrahydroaminoacridine on M1 and M2 muscarinic receptors. Neurosci Lett 88:281–285
Peralta EG, Ashkenazi A, Winslow JW, Smith DH, Ramachandran J, Capon DJ (1987) Distinct primary structures, ligand-binding properties and tissue-specific expression of four human muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J 6:3923–3929
Pfaff O, Hildebrandt C, Waelbroeck M, Hou X, Moser U, Mutschler E, Lambrecht G (1995) The (S)-(+)-enantiomer of dimethindene: a novel M2-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 286:229–240
Potter LT, Ferrendelli CA, Hanchett HE, Hollifield MA, Lorenzi MV (1989) Tetrahydroaminoacridine and other allosteric antagonists of hippocampal M1 muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol 35:652–660
Reever CM, Ferrari-DiLeo G, Flynn D (1997) The M5 (m5) receptor subtype: fact or fiction? Life Sci 60:1105–1112
Richards MH, van Giersbergen PL (1995) Human muscarinic receptors expressed in A9L and CHO cells: activation by full and partial agonists. Br J Pharmacol 114:1241–1249
Scarr E (2012) Muscarinic receptors: their roles in disorders of the central nervous system and potential as therapeutic targets. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:369–379. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2011.00249.x
Servent D, Fruchart-Gaillard (2009) Muscarinic toxins: tools for the study of the pharmacological and functional properties of muscarinic receptors. J Neurochem 109:1193–1202. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06092.x
Shannon HE, Bymaster FP, Calligaro DO, Greenwood B, Mitch CH, Sawyer BD, Ward JS, Wong DT, Olesen PH, Sheardown MJ, Swedberg MDB, Suzdak PD, Sauerberg P (1994) Xanomeline: a novel muscarinic receptor agonist with functional selectivity for M1 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269:271–281
Shinoda M, Katada T, Ui M (1990) Selective coupling of purified a-subunits of pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding proteins to endogenous receptors in rat brain membranes treated with N-ethylmaleimide. Cell Signal 2:403–414
Stockton JM, Birdsall NJ, Burgen ASV, Hulme EC (1983) Modification of the binding properties of muscarinic receptors by gallamine. Mol Pharmacol 23:551–557
Sur C, Mallorga PJ, Wittmann M, Jacobson MA, Pascarella D, Williams JB, Brandish PE, Pettibone DJ, Scolnick EM, Conn PJ (2003) N-desmethylclozapine, an allosteric agonist at muscarinic 1 receptor, potentiates N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13674–13679. doi:10.1073/pnas.1835612100
Thomas RL, Mistry R, Langmead CJ, Wood MD, Challis RA (2008) G protein coupling and signaling pathway activation by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor orthosteric and allosteric agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:365–374. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.141788
Thomas DR, Dada A, Jones GA, Deisz RA, Gigout S, Langmead CJ, Werry TD, Hendry N, Hagan JJ, Davies CH, Watson JM (2010) N-desmethylclozapine (NDMC) is an antagonist at the human native muscarinic M1 receptor. Neuropharmacology 58:1206–1214. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.02.017
Tumiatti V, Wehrle J, Hildebrandt C, Moser U, Dannhardt G, Mutschler E, Lambrecht G (2000) Muscarinic properties of compounds related to arecaidine propargyl ester. Arzneimittelforschung 50:11–15
Wang SZ, El-Fakahany EE (1993) Application of transfected cell lines in studies of functional receptor subtype selectivity of muscarinic agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:237–243
Weiner DM, Meltzer HY, Veinberg I, Donohue EM, Spalding TA, Smith TT, Mohell N, Harvey SC, Lameh J, Nash N, Vanover KE, Olsson R, Jayathilake K, Lee M, Levey AI, Hacksell U, Burstein ES, Davis RE, Brann MR (2004) The role of M1 muscarinic receptor agonism of N-desmethylclozapine in the unique clinical effects of clozapine. Psychopharmacology 177:207–216. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-1940-5
Winslow JW, Bradley JD, Smith JA, Neer EJ (1987) Reactive sulfhydryl groups of α39, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein from brain. J Biol Chem 262:4501–4507
Wood MD, Murkitt KL, Ho M, Watson JM, Brown F, Hunter AJ, Middlemiss DN (1999) Functional comparison of muscarinic partial agonists at muscarinic receptor subtypes hM1, hM2, hM3, hM4 and hM5 using microphysiometry. Br J Pharmacol 126:1620–1624
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Grant for Research Work from the Saitama Medical University, Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odagaki, Y., Kinoshita, M. & Toyoshima, R. Pharmacological characterization of M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated Gq activation in rat cerebral cortical and hippocampal membranes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 386, 937–947 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0887-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0887-7